By receiving and processing data from our senses, we not only understand the world, but to the best of our abilities we transform it, not only in reality, but also at the level of consciousness. Changing figurative information plays a key role in creativity, and without it no productive activity is possible. This mental transformation of reality is imagination - one of the highest cognitive processes inherent only to man.
What is imagination
By definition, imagination in psychology is a process in which images appear in the subconscious that are closely related to life experience, fantasy and way of thinking. It helps to imagine the consequences of certain actions, as well as outline a plan of action in an unclear situation.
According to scientists, imagination is one of the types of brain activity in which new additional neural connections are formed. We can also say that this is a process of transforming reality, creating images associated with it, processing the resulting practical, intellectual and sensory experience. These images are bright, original and at the same time truthful.
Imagination can be called a way of understanding the world around us. It leaves an imprint on our consciousness. Thanks to this, you can not only replay what happened recently, but also imagine what will happen in the future. You have the opportunity to imagine non-existent or absent objects and mentally use them in your consciousness.
It is interesting that even the most pragmatic, skeptical people have imagination. They may live by logic, ironclad principles and rules, but will still dream or think creatively.
Imagination and the desire to achieve
The first three years of life, a child is under the influence of direct impressions from objects accessible to perception. Then imagination is formed - the ability to mentally see missing objects and situations of manipulating them, transform them, desire or be afraid.
From this point on, two trends emerge. One is to persistently master the objects presented in the imagination - get a coveted toy, a trip to the zoo, a favorite pastime. Another is to give up achievement and make do with imagination. Their balance depends on the family environment and the already established personality traits of the child.
Functions of the imagination
The importance of imagination is difficult to overestimate. Like any other mental process, it has a number of functions:
- Cognitive. This is a function of both thinking and imagination. Helps broaden your horizons, obtain new information and knowledge, and draw up a plan of action in an unfamiliar situation. Teaches a person to be guided by guesses, reasoning and considerations.
- Prediction function. A person can imagine what will follow his actions. This type of imagination is involved in the formation of dreams and daydreams.
- Understanding. It manifests itself in the ability to assume what another person feels and experiences in a given situation, what emotions and sensations he or she has now. This type of imagination is somewhat similar to empathy. It allows you to look into the inner world of your interlocutor and understand what worries him at the moment.
- Protection. When a person plays out a situation in his mind, a possible outcome of events or the consequences of his actions, he can prevent troubles and protect himself from problems.
- Self-development. This function of imagination helps to fantasize, come up with something new, and create.
- Memories. Images from the past emerge in the subconscious.
Not every person has all the functions of the imagination. Their set depends on character, behavior, personal qualities.
History of discovery and study
In Russian psychology, interest in the phenomenon arose along with the study of other functions of the psyche. The main contribution to the study process was made by L. Vygotsky. He dedicated a book and dozens of articles to the imagination - a fundamental presentation of findings and theories regarding the development of the ability to imagine in ontogenesis.
Vygotsky paid great attention to the development of cognitive processes in preschool age. The scientist believed that this period was critical
He considered the ability to imagine in preschool age as the ability to create a whole from elements.
Vygotsky noted the complexity of mental activity and gradual development. According to his theory, creative activity depends on acquired experience. The child expresses accumulated knowledge through creativity. The accumulation process is influenced by various factors: interests, needs, desires. The ability to express oneself in childhood and adulthood depends on the speed of their satisfaction. Negative experiences acquired in childhood affect the adult individual.
Types of imagination
The most basic types of human imagination are passive and active. Each of them is divided into subgroups. Among them are voluntary, involuntary, creative, reproductive imagination, etc. Let's take a closer look.
Passive
Such imagination may have a purpose. It can be regulated and directed using consciousness and willpower. It can also be involuntary, that is, working at the subconscious level.
Operations of imagination have varying degrees of awareness and unconsciousness. You've probably also encountered a state where thoughts fly through your head one after another. Along with them, some images and pictures appear. They replace each other until something interests you. At this moment, awareness turns on. You begin to control the process. In addition, you become aware of the line between reality and the fictional world.
In the case of the involuntary variety of imagination, everything happens spontaneously, uncontrollably. You don't have images and associations.
In psychology, dreams and hallucinations are classified as passive involuntary types of imagination:
- Dreams are the result of a healthy psyche. This is a combination of inhibition and excitation processes occurring in the cerebral cortex. During braking, the subconscious comes into play, which stores a huge amount of various information. For example, remember the children's toy kaleidoscope. So, images and associations from the subconscious are mixed and intertwined, as a result of which colorful and sometimes unusual dreams appear.
- Hallucinations occur when the functioning of the cerebral cortex is disrupted. They often occur in cases of serious illness, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages or drugs, or mental disorders. It also happens that they are a consequence of emotional overexcitation, a state when a person is unable to control himself.
The main property of both types is the inability to control them.
Passive voluntary types of imagination can be controlled. Most of them are related to forecasts for the future. A person predicts the probable, unlikely and completely incredible outcome of events. In this case, you don’t have to limit your imagination.
Passive voluntary imagination has 2 forms:
- Daydreaming is not just a way to fantasize. This is an opportunity to recreate images of the future. And, what’s most interesting, they are quite feasible. The main property of such imagination in psychology is to encourage a person to take active action, to coordinate his actions in the direction of his dreams.
- Dreams have nothing to do with reality. This is an illusion, a figment of the imagination, something that cannot be realized.
Sometimes it is difficult to see the line between dreams and daydreams. For clarity, let's give an example. Imagine a girl reading an exciting novel. According to the plot, three young men fall in love with the main character. If a girl also wants to be in such a situation, this is a dream. And if she wants to write and publish an equally exciting story, this is a dream come true.
Active
Active voluntary imagination is the most significant thing in a person’s life. It is used in almost all areas of life. Helps to recreate images from the subconscious in reality.
According to the classification of types of imagination, active is divided into 2 subtypes: reproductive and creative.
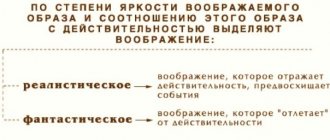
Imagination and creativity are closely related. Creative imagination is considered the highest form of all cognitive processes. It helps in creating both fantastic and very real images. Take, for example, painting realistic landscapes or literary works. This type of imagination plays a special role in science, the work of designers, etc. One might even say that it is involved in almost all areas of life.
The creative imagination has another interesting feature. It helps you see a situation from different angles, generate unusual ideas and make innovative decisions.
In psychology, this type of imagination is associated with inspiration, the subconscious, and intuition. A lot of creative imagination techniques have also been developed, the use of which helps to increase productivity and make your activities more interesting and exciting.
Reproductive imagination is also called re-creative. It is used when you need to recreate images based on a ready-made description, diagram or drawing. What can you imagine? There are a number of examples:
- house according to the drawn up project;
- drawing connected according to a pattern;
- the hero whose description is given in the book;
- cake or other dish that will be prepared according to the recipe.
Recreative imagination has an interesting characteristic. All images are based on what a person already knows. Take, for example, the house project described above. Only a person who has special knowledge and skills can understand it.
Development methods
In the modern world, creative people are in great demand. That's why there are trainings and seminars on developing imagination.
Such exercises are designed not only for children, but also for adults.
Brief recommendations for the formation of imagination allow parents to help children improve their skills. To begin with, adults must create a sensory environment, i.e. introduce the child to different objects and phenomena. The baby should actively play and talk with peers. It is oral speech that contributes to the emergence of abstract thinking.
Important! We need to support any creative endeavors: drawing, playing music, sculpting, etc. Adults can develop their imagination too
To do this, they should constantly train. For example, come up with new properties for an existing item or try to come up with something from scratch
Adults can develop their imagination too. To do this, they should constantly train. For example, come up with new properties for an existing item or try to come up with something from scratch.
Knowing the exact characteristics of imagination and the characteristics of its manifestation, any person can develop this type of mental activity. Additionally, you can count in your head, read books, watch movies and learn to analyze your environment.
The more sensory experience a person has, the higher the likelihood of fantasies. Meditation and other trance techniques can help. It is useful to recreate the past day every day before going to bed. With regular practice you will be able to achieve good results.
Creating images
A person creates images in the imagination in several ways:
- Agglutination. The qualities and parts of individual objects are combined into a single whole. Examples: centaur, fairy-tale hut on chicken legs, seaplane, snowmobile.
- Emphasis. Part of the object is divided into separate parts. A good example is caricatures in which the artist highlights a certain feature.
- Hyperbolization. Involves reducing, enlarging, or shifting individual parts of the selected object. Here you can also remember fairy tales, for example, about dragons with several heads.
Another way to create images in the imagination is typification. It is considered the most difficult. Imagine any picture. Contemplating it, you draw in your subconscious the image that the artist conveyed. Or take, for example, a book. The author describes in it the features of the main character. Thanks to this, you can imagine how he looks, thinks, behaves. It is as if you are transported into the world around him.
What does imagination give to a person?
So, we found out what imagination is and what functions it plays. But why do you need it personally? There are several points:
- helps in communicating with other people;
- makes it possible to visualize the goal;
- promotes the development of creative talents;
- participates in decision making and creation of new ideas;
- helps you mentally recreate an image of an object or phenomenon that you have never seen.
Plus, imagination is used in making predictions and action plans for the future. It is needed in all areas of activity, especially in those that cannot be fully automated. We are talking about design, research work.
Does a child need imagination? The answer is clear: yes. Without it, full development is impossible. The first few years of a child's life explore the world around him. And if for some reason his imagination does not work at full strength, the formation of important abilities is inhibited.
The imagination developed in childhood will help an adult to become creative in the future, develop creative skills, and learn to find an unusual way out of a difficult situation. And this will be useful in life.
How to develop your imagination
Psychologists have identified a number of techniques for developing imagination.
In adults
The main thing is to be ready to experiment, not to be shy and not afraid of mistakes. There are many ways:
- Visualization. You need to mentally reproduce the appearance of an object, location or action. Start with simple tasks. For example, look at what lies in front of you. Then close your eyes and imagine this object in detail.
- Reading. This method is related to the previous one. Visualization is also needed here. It's just much more difficult to make it. You will have to remember several characters, images, landscapes at once. And after that, look at their participation in the plot. All this will help you see the full picture. And by the way, reading is much more interesting than watching movies. In the case of reading, no one limits your imagination and imagination.
- Associations. Every adult has associative thinking. Most likely, when you hear the word “green,” you think of grass and trees. And with the word “orange” - about an orange.
- Creation of unusual animals. This is a great way to develop your creative imagination. Let it be, for example, a cat dog. Of course, they don’t talk about it in a biology textbook. But you'll have fun. This exercise is suitable for both adults and children.
- Art. Exhibitions or master classes will make up for the lack of imagination. By observing other people, you yourself can easily create an unusual idea or at least get inspired.
- "Box". Here you will have to take an example from the cartoon character SpongeBob. Remember your favorite activity? He sat in the box and turned on his imagination. No, don't think that you need to do the same. Although children can try. Walk into an empty room and mentally design the interior. Next time, rearrange it, etc. This way you will improve your imagination and perception.
Another way is role-playing games. You control the hero, while observing certain requirements and conditions. Games can be tabletop or real. The latter include quests.
In children
It's a little easier with children. They already love to fantasize, often coming up with unusual stories and even imagining imaginary friends next to them.
How to develop children's imagination?
- Read fairy tales, fantasy stories. Try to read, for example, to the middle. And then invite the child to continue the story.
- Observe the people around you. Let the child think about how someone lives along the way. If you can’t go outside, use photographs or ordinary pictures. This way you can help develop the imagination of both preschoolers and older children.
- Go to exhibitions together, visit museums, cinemas.
- Get creative together. Model from clay and plasticine, make appliqués, draw, assemble car models, etc.
As with adults, role-playing games with parents or peers help children develop their imagination.
Passive
Passive (involuntary) imagination means the emergence of images that does not require conscious effort from a person .
With weakened conscious control, they arise by themselves, without a person’s volitional effort.
The source of their occurrence is not a logical connection and a person’s awareness of reality.
The passive images that arise often serve as a reflection of his internal state, fears, aspirations, desires, and speak about the personal needs of the individual.
Involuntary imagination is often not subject to logical comprehension, often representing a combination of completely contradictory images.
It is also often difficult to verbalize it after the experience, since such images are often symbolic, abstract and incomprehensible to other people.
Passive imagination is governed by two basic principles:
- Each affect strives to preserve , exaggerating the subjective logical value of ideas. Thus, a cheerful person will more often have positive images, and a sad person, on the contrary, will have sad ones.
- A person strives to preserve pleasant experiences , and, therefore, pleasant images that have arisen.
Often passively arising images are not tied to time. Thus, the person observing them also loses the sense of time .
Subspecies
Passive imagination is divided into two subtypes:
- unintentional. Includes hallucinations, dreams and daydreams. They arise on their own, without the volitional participation of a person;
- intentional - hypnotic states caused by another person.
Description
- Dreams. On the scale of voluntariness, they occupy the position furthest from awareness.
Often in dreams we see bizarre images and strange plots. Nevertheless, they are important for the regulation of a person’s psycho-emotional state, since they are not only echoes of what a person has previously heard and seen, but also represent material that has been very deeply processed by the psyche. - Dreams. Dreams, like daydreams, are often a departure from reality, with the difference that dreams are aimed at the future, and daydreams replace the present. For example, a schoolboy who is offended by his comrades may imagine how he takes revenge on the offenders. In this case, the emerging images will represent an alternative reality, bringing the student some satisfaction, but at the same time leading him away from the real state of affairs.
- Hypnotic states. The deeper the hypnotic trance, the less attention a person pays to external stimuli, the less real reality means to him. The subjective sense of time may also change, and negative hallucinations may arise - when a person does not see real objects. Only the connection with the hypnotist inducing the trance is maintained. Hypnotic trance is quite often used in psychotherapy.
- Hallucinations. Hallucinations usually occur in people with congenital physiological brain damage, as a result of traumatic brain injury, viral infections, and the use of psychotropic substances. Often perceived as genuine reality.
Example from life
I enjoy reading. Imagination helps you immerse yourself in the story. Even seemingly tedious descriptions of the area become much more interesting. I try to see the landscape through the eyes of the author, hear sounds, feel the wind or the scent of flowers.
The same goes for heroes. I try to imagine not only their appearance, but to monitor how their behavior and thinking changes in different situations. Thanks to this, after reading the book, it seems that I have visited this book world.