Abstract thinking is of great importance to all people. The high level of its development allows not only to improve the quality of life, but also to achieve much greater success. You should develop this type of thinking already in childhood, but you should not stop training as you grow up. Only regular exercise will improve and maintain your intellectual abilities. Knowing how to develop abstract thinking in adults and children will help with this. All methods can be put into practice independently, without resorting to outside help.
Forms
Abstraction is the abstraction of some properties of objects from others in order to identify their features. The definition of abstract thinking is almost the same. This phenomenon refers to a type of intellectual activity during which a person thinks about a situation, separating it from some details. Abstractness has a significant impact on the physiology of thinking and allows you to cross certain boundaries, discovering new knowledge.
This type of thinking develops in parallel with ontogenesis from an early age. It first appears at the moments when the child begins to fantasize, composing his own stories or acting out unusual situations, and abstracts himself from toys, preferring to think about their certain properties.
Abstract thinking is divided into forms, each of which corresponds to the characteristics of the thought process accompanied by abstraction. There are 3 of them in total:
- Concept. Involves defining one common property for different objects. A very important point is the significance of this unifying feature. For example, the legs of tables or green leaves of different trees.
- Judgment. In judgment, an affirmation or denial of a certain event occurs. Everything is usually described in a phrase or short sentence. Judgments can be simple or complex. In the first case, they relate to one active object or person (for example, “the boy bought milk”). In the second, the judgment affects several sides at once (“clouds appeared, it became dark outside”). It can also be true, based on subjective conclusions, or false, based on personal interest.
- Conclusion. Inference is understood as a thought, the formation of which occurs on the basis of several judgments. It consists of premises, conclusion and conclusion. All three processes occur sequentially in the human head. It all starts with initial judgments (premises), then moves to the stage of reflection (conclusions), and ends with the formation of a new judgment (conclusion).
Abstract thinking can be used in any of these three forms. An adult uses them all in everyday life. Nevertheless, it is necessary to develop them even for those who are good at abstraction.
Modern artificial intelligence is endowed with abstract thinking that is superior in quality to human thinking.
How to develop logical thinking in another way
Try writing a diary, or take up poetry, or try to talk about something in writing
It doesn’t matter if it turns out to be a story, or a note, or a sketch, or a poem (blank verse is also welcome!). Why does this work? Because logical thinking is inextricably linked with speech, and is realized mainly in the form of signs and concepts
Why does this work? Because logical thinking is inextricably linked with speech, and is realized mainly in the form of signs and concepts.
What to do if creativity is “not your strong point”?
Firstly, it’s still worth trying, and if you don’t even want to try, you can take a different path. To do this, name any three objects at random, for example: an elephant, a chair, a fan. Now come up with a sentence in which all three selected objects can logically fit. For example:
There was a plate of sliced fruit on the chair, and Timka was sitting on the carpet, watching a cartoon about an elephant, chewing a slice of apple and waving his grandmother’s fan.
Or show your imagination by combining the words hammer, fish, geyser in a sentence. For example, like this: “Grandfather threw a hammer into the geyser, and from the depths to the very top of the fountain a real fish flew up, not just an ordinary one, but a golden one, and threatened grandfather with its fin.”
Peculiarities
Abstract thinking is used by children from the first years of life. It begins to appear along with the development of articulate speech. A younger child fantasizes, thinks about unusual things, explores the world, compares his toys, using abstraction skills. They are underdeveloped, but you can still use them.
School age is combined with an increase in the importance of abstract thinking. The student will need to think outside the box when faced with solving various problems. This is especially true in mathematics, where abstraction plays a big role. Later, when the teenager is in high school, the importance of such thinking will become even greater.
Abstract thinking is also used in philosophy, writing, engineering, managerial psychology, time management and many other areas. Its good development allows you to achieve success in any field.
Signs
Thinking with abstraction has its own characteristic features. They allow us to distinguish it from other thought processes and better understand why abstraction is so useful for a person.
Signs:
- Reflection of the surrounding world without using the senses. A person does not need to use his senses or contact an object to obtain information about it. It is abstraction that allows you to use old existing knowledge to solve a particular problem.
- Generalization of phenomena. By generalizing various objects and identifying their characteristic features, a person is able to quickly access his knowledge. If he is able to identify certain patterns and similarities, then in the future it will be much easier to remember and find the necessary information in memory.
- Linguistic expression. All thoughts are easily expressed in the form of internal dialogue, which can be translated into real life. In this case, abstract concepts can be thought through in the head without the use of linguistic expression at all, and the result will be a final judgment that will be easy to express in speech.
The development of abstract thinking allows you to improve all of the characteristics listed above, which are also useful skills, without which it is difficult to achieve success.
Impact on humans
It is difficult for the average person to imagine exactly what someone with highly developed abstract thinking looks like. Such people, as a rule, always achieve their goals, they are successful and happy. At the same time, something is always happening in their heads: they reason, think about events, imagine the future figuratively, and solve difficult problems. Most often, they speak a complex language, which causes difficulties in communication. Their high efficiency allows them to occupy high positions, and their developed intelligence makes them very important for any company.
Such people may face a number of problems. They are often too selfish, which makes it difficult for them to find true friends. At the same time, people with developed abstract thinking cannot show enough physical activity and are passive in practical work. Sometimes they are careless in appearance, which alienates others.
Most often, men in technical professions have developed abstract thinking.
Types of abstractions
Images formed without the participation of the content side of the concept:
- Insulating. Its goal is to highlight a characteristic feature of an object and increase attention to it. For example, there is an apple on the table. A person notices that it is green or sour.
- Generalization. Here the brain receives a complete picture of the appearance of the entire image. Let's use a mathematical equation as an example. The goal is a solution without taking into account individual numbers, pluses, minuses and other signs.
- Idealization. Discarding unimportant elements. A method of obtaining knowledge, without which exact and natural sciences cannot do.
In reality, there are no separate, unrelated elements. They cannot be touched or measured in isolation.
Exercises for adults
It is quite difficult for an adult to develop abstract thinking, because... his intellect has long been formed. However, with the help of some exercises you can still achieve results. It is recommended to perform them daily for several weeks.
The most effective exercises:
- Representation of emotions. You need to mentally imagine exactly how different emotions manifest themselves in a certain person. It is recommended to use the full range of people's possible feelings.
- Reverse reading. You need to turn the book over and read it in reverse order. In parallel with this, it is necessary to establish logical connections between various events. It is best to choose simple works written in easy language.
- Analysis of communication. You should remember all the people with whom you had to communicate during the day. It is necessary to analyze not only the conversation itself, but also the facial expression, gestures and voice of the interlocutor. It is recommended to do this with your eyes closed.
- Inventing contradictions. You just need to come up with different phrases that seem contradictory. They can be absolutely anything (hot ice, bitters, etc.).
- Compiling abbreviations. It is enough to come up with any phrase, shorten it to the first letters, and then decipher it throughout the day. For example, independent development of thinking (SDM).
- Listing the functions of objects. You need to select any existing item and list all its functions. You can even come up with unusual purposes that are not usually used.
- Brainstorm. You need to choose any letter of the alphabet and write it on a piece of paper. The task is to remember the maximum number of words starting with this letter in a limited amount of time, writing them all down on paper.
- Combination of words. You need to write nouns on one piece of paper, and adjectives on the second. This does not need to be done right away. It's best to start with just one noun. You will need to select suitable, as well as completely incompatible adjectives for it. All of them should be written down in different columns.
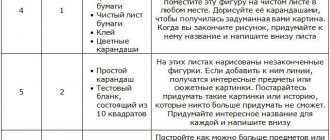
- Title of a painting from life. It is required to visually record any event that happened in reality and give it an unusual name. It should be what an artist might call a painting.
- Painting. You need to paint any pictures using colored paints. During the process, the characteristics of all present items should be presented. If it is not possible to use paints, you can start with regular pencil drawing.
The listed methods will help develop abstract thinking also in a teenager or an elderly person. You just need to apply them on a regular basis, without missing regular classes.
Development of abstract thinking in children with the help of a Swedish wall
The sports corner will help develop the ability to think abstractly from birth. For example, the Early Start complex with the Cheese case is a real puzzle! Place the little one in a corner and let him find his own way out of it. As the second task, let him find a second way out, not as obvious as the first, and so on.
Sports complexes with numerous attachments, for example, such as the ROMANA Karusel S7, are a real treasure trove for logical exercises. The following exercises will help you learn to think abstractly:
- What's extra
In addition to sports equipment, hang something not related to sports on the complex. Let the child name it and say why it is extra.
- Associations
Ask your child to select an association for each element of the complex.
- Finding a solution
Ask your little one to climb from one part of the complex to another without touching the steps. This can be done using, for example, rings or rope.
Of course, all these exercises can not only be performed, but combined with physical elements. It will not only be interesting, but also extremely useful.
Post Views: 8,078
Exercises for children
It is easiest to develop in childhood. At this time, the brain is open to external influences and can undergo any changes. Exercises for children differ from those offered to adults, but are no less effective.
Best exercises:
- Reverse reading of inscriptions. Parents should invite their child to play a game in which they read the signs they see in reverse order. It will be very difficult to do this with all the advertising posters. Therefore, additional conditions should be negotiated (for example, read only red signs).
- Drawing unusual animals. The child must draw an animal consisting of parts of other animals. When the drawing is ready, you need to come up with an unusual name for the new species.
- Shadow play. With the help of his hands, on which the light from a lamp falls in the dark, the child must create unusual shadows depicting certain things. You can even invite him to act out his favorite fairy tale using shadows.
- Mental arithmetic. The child will be required to calculate simple examples using special abacus called an abacus. Such training will also develop perseverance and general intelligence.
- Puzzles. You need to choose puzzles, rebuses, anagrams, etc. games, taking into account the baby's preferences. His task will be to solve all the problems provided. At an older age, you can add crosswords to them.
- Studying clouds. The child should look at the clouds together with his parents and name what exactly he sees. The ability to visually evaluate each cloud for its similarity to different objects or animals increases the chances of successful development.
- Construction. Parents need to give their baby a task, which involves building certain objects from toy blocks. This will help develop imaginative thinking and creativity.
- Associations. The baby needs to come up with associations for everything he sees or feels. You can also ask him to imagine animals by hearing the sounds they make.
- Classification. The child needs to sort all available things or toys according to certain criteria. For example, by shape, weight or purpose. Parents should monitor the process and give hints if necessary.
- Questions. Parents should ask their child “why?” and “what if?” questions. etc. to make him think and analyze the situation. You can ask at any time.
Such simple exercises will allow you to achieve good results in a few weeks of training. It is recommended to combine them with other activities that will be aimed at developing general intelligence.
Using special tests, you can accurately determine the level of abstract thinking in a person of any age.
Why develop logic for a child?
The process of personality formation is conventionally divided into several stages. One of them is fundamental – childhood. It is during this period that the beginnings of personal qualities are laid. This includes mental activity.
Is it worth describing the importance of developing children’s logical thinking at the stage of preschool education? Yes, it's worth it. It is more difficult for an untrained preschooler to adapt to the role of a first-grade student. It is more difficult for him to master new material. Solving basic exercises becomes a process that takes a lot of time and effort. An open hatred of learning arises, which will continue until the end of high school. Logical thinking of preschool children is a job that every parent must do.
When does logical thinking begin?
Logic shows its initial form when a baby learns to speak. At this moment, his brain actively uses resources in verbal construction. In the sixth year, the individual reaches the maximum level of verbal and logical development. The child’s logical thinking becomes familiar with analysis, synthesis, and classification. He exhibits the minimal basics of induction and deduction. 6 years of age is the period when the baby bombards his parents with annoying questions “What? How? Why?". Logical thinking for children 6 years old is a stage of a sharp transition of thinking abilities to a new period - preschool age.
Problems and tasks for spatial thinking
Gradually move from simple tasks to more complex ones.
Simple games to develop spatial thinking for children from 3 years old
The main goal of gaming activity, starting from the age of 3, is the formation of new skills and the development of those already acquired
It is important to provide the child with as much knowledge as possible about existing geometric shapes and their possible location in space
- Game "Place the cat". The bottom line: ask your child to imagine any insect or animal and ask him to think about where it might fit (box, mug, closet, etc.).
- Game "Put it right." Place objects in front of the child and ask them to arrange them based on your instructions - to the left, to the right, further or closer. You can take it for this game.
"Metamorphoses". The idea is simple: you need to draw a circle behind a square, a rectangle behind a triangle, and so on. The task can be complicated by moving on to three-dimensional figures (cubes, cylinders, spheres).
- "Special agent on a mission." The child needs to look carefully at the room he is in in order to remember the objects in his environment. Then you need to ask him questions while the child, with his eyes closed, tries to reproduce in his mind what he saw.
- "Drawing on the back." The game is simple: you draw figures on the child’s back, and he tries to guess them.
- "Fly". The game involves 3 people: 2 players and 1 presenter. The essence: a 9x9 field is presented, a fly is placed in the upper corner on the right. The presenter, marking on the diagram, tells the path of the fly, after the word “stop” the participants voice the expected place of the fly. The one who names the correct position wins.
- "Route of movement." Using a map, you show your child the starting and ending points, and he, in turn, names each turn and tells his route from point A to point B.
- "Magic bag" You need to put different three-dimensional figures into a small bag so that the child can then guess by touch what is inside.
- Simple tasks with paper. Since the games listed above require certain consumables and time, you can use the simplest option - take paper and pen and come up with your own simple games: Figures from dots according to the pattern
- Repeating line patterns
- Finishing the mirror half of the picture
- Mathematical dictations and so on
Exercises for middle preschool children
- Story games:
- “House of Toys”: toys are placed in the closet, then the children are asked to play with them (they say the toys are tired and want to have fun), after the game they need to put the toy in the place where it stood before.
- “Who lives where?”: a tree is created on which the animals are located, you need to ask the children to carefully look at the image and answer the questions about who lives and where.
- In a similar manner, you can come up with many stories.
- Hide and seek games. Hide and seek develops spatial thinking in the form of a game. In order to win, you need to hide well, and for this you need to find an advantageous place, be able to navigate the place in order to avoid the leader.
- Outdoor games. Active games are based on the ability to navigate in space. Catch-up - good orientation on the spot and speed allow you to win the game. This type of activity will also help get rid of information overload in children.
Tasks for children of senior school age to develop spatial thinking
A whole set of educational board games for children and adults
- Graphic dictation is one of the educational games aimed at children aged 6-11 years. Dictations help develop not only fine motor skills and coordination, but also spatial thinking.
- . Train concentration skills, strategic and spatial thinking.
- Game "traffic controller". Using a map, you show your child the starting and ending points, and he, naming each turn of the route, describes his route to the destination.
- Labyrinth. The child follows the instructions with his eyes closed, drawing a path on a piece of paper according to the words of the leader.
- The mirror is the opposite. The rules are simple: you show certain actions, the child repeats, as if becoming your reflection.
- Word games. There are many different word games (cities, two truths and one lie, associations and many others). They all use imagination and the ability to perceive information by ear. Care is also important to follow the rules of the game.
Processes
The thinking process is a purposeful process of operating with concepts and judgments to obtain a result. The process is preceded by a certain situation (which by default will be the condition of the task), followed by the collection of information and its analysis.
At the end of the chain, a person comes to a conclusion, which involves solving a given problem and finding a way out of the current situation or predicting various options for the development of events.
There are only 4 stages of the process aimed at finding a solution:
- Preparation;
- finding a solution;
- inspiration to achieve it;
- checking the results.
The whole process consists of a chain of points flowing from each other.
The process begins with motivation, characterized by the desire to find a solution. This is followed by the collection of information (initial data), their evaluation and conclusion.
Thinking techniques:
- analysis is a mental “sorting out”. Analysis represents the decomposition of a problem into its components and the isolation of its fundamentals;
- synthesis is the process of combining parts into a single whole according to certain characteristics. The relationship of each component to the whole is mentally established. Synthesis is the opposite of analysis and is represented by the generalization of existing details into a single whole;
- comparison is the process of identifying the similarities between objects and phenomena and their differences;
- classification represents a breakdown point by point, forming certain classes and subclasses;
- generalization is the identification of what is common among various objects or phenomena and the identification of what has been identified into one group. A generalization can be simple (based on one sign or property) or complex based on different components;
- specification allows you to determine the essence of a phenomenon or object;
- abstraction is the opposite of concretization, when an abstract image is created during the process. The development of abstract perception is influenced by exercises that require a creative approach.
Methods for developing thinking are known to psychologists, neurologists and teachers. Techniques include problem solving, games, learning to look from different angles, training imaginative and intuitive thinking through creativity
In development, it is important to take into account individual characteristics of thinking
A person with a pronounced tendency towards fantasy should pay more attention to the development of a creative and extraordinary approach in the process of processing information. On the contrary, if you have accuracy and consistency, you should pay more attention in this direction.
Analogies
Tasks on finding semantic connections are difficult to complete for children with poorly developed logical thinking and a small vocabulary. At the same time, performing such exercises will help enrich the child’s vocabulary and develop logic.
How to do it? We need to identify the relationship between the first two words. Then find a similar connection in the second pair.
For example: Friday/Sunday, Tuesday/(Wednesday, Thursday, Saturday, Sunday)
Let's look at: "Friday - Sunday" what is the connection? These are the days of the week, going every other day. In the second pair, “Thursday” is suitable for the word “Tuesday”. He also comes the day after Tuesday.
Run / stand Scream / (Yell, yell, student, call, be silent)
Theater/ spectator Library/ (Listener, books, shelves, reader)
Iron / blacksmith Wood / (Table, cabinet, carpenter, board, plane)
Spruce / table Oak / (Wood, boards, cabinet, saw, sander)
Steamship/ pier Train/ (Conductor, rails, compartment, station, carriage)
Machine / motor Yacht / (Sea, sail, captain, deck, helmsman)
Eyes/ glasses Leg/ (Walking, shoes, crutch, bandage, socks)
Steam locomotive/ Horse carriages/ (Hoofs, cart, races, road)
Needle/point Razor/ (Barber, blade, beard, mustache, face)
Music/ orchestra Singing/ (Song, choir, music school, singer)
Cows/ herd Wolves/ (Attack, hunting, pack, grey, leader)
Rye/ field Apple tree/ (Apples, harvest, garden, gardener, juice)
Mountain / cave Tree / (Garden, hollow, forest, branches, trunk)
House/ floors Stairs/ (House, railings, steps, walk, rise)
Number/ numbers Word/ (Sheets, book, notebook, letters, reading)
Disease/ treatment Breakdown/ (Car, motor, repair, mechanic, car wash)
Cool/frost Blue/ (Blue, sky, purple, red)
Enemy/enemy Market/ (Buyer, bazaar, counters, sellers)
Raspberry/ berry Mathematics/ (Textbook, scientist, science, student, school)
Plant/ seed Duck/ (Bird, pond, ducklings, quacks, egg)
Year/ spring Life/ (Man, youth, long, cheerful)
Chapter/ book Apartment/ (New, balcony, three-room apartment, house)
Hunger/ lean Labor/ (Hard, tired, in the field, in the factory)
Film / Opera screen / (Curtain, theater, stage, artists, orchestra)
Monday/Tuesday Sunday/(Week, Monday, calendar, Saturday, day after tomorrow)
Tuesday/ Thursday Sunday/ (Wednesday, Tuesday, Friday, evening)
Morning/night Winter/ (Spring, autumn, year, summer, week)
Ball / circle Cube / (Figure, square, brick, constructor)
Goat / animal Bread / (stove, food, mold, dough, roll)
Voice/ echo Face/ (Reflection, mirror, clean, beautiful)
Working with patterns
The pattern can be hidden in drawings, between numbers, letters, or any elements of a series.
To learn how to correctly find a pattern, we follow the following algorithm:
- We look carefully at a number of numbers, figures, animals, objects.
- Let's try to guess what the pattern is based on - what rule the elements are arranged according to.
- We are trying to determine the type of pattern.
- We test our assumptions one by one to see which rule holds.
- Having made sure that the “intended” rule is observed, we will be able to accurately name the next elements of the series.
Examples of patterns with numbers:
2, 5, 8, 11, 13, …
3, 4, 7, 8, 11, 12, …
99, 10, 88, 20, 77, …
4, 16, 5, 25, 6, …
Coloring books with logical patterns are perfect for children aged 5-9 years.