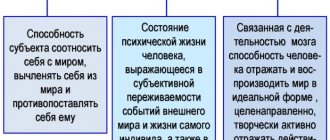
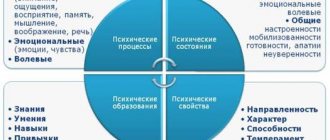
General ideas about the psyche
The psyche is a multifaceted construct that determines a person’s personality. There are several links in it:
- Mental processes. These are dynamic indicators that are criteria for understanding the world, help to take and analyze information from everything that surrounds a person, form his emotions in a specific episode of life, his behavior, goals and motives, and also regulate communication, depending on the situation, changing gestures and posture, volume and tone of voice, facial expressions. In the process of personality development, they constantly vary.
- Mental properties. Properties include:
- temperament, which is established at birth;
- character, which, when studying personality, also turned out to be largely dependent on the hereditary factor and only 10% on the external one;
- abilities that are both inherent in nature and formed during the development of the individual.
Properties are a static concept, but are subject to relative variation when exposed to a prolonged irritating factor.
- Mental states. Determines exactly which processes and properties of a person will manifest themselves in a given situation and which of them will prevail over others.
Mental properties
Mental properties are the most stable and constantly manifested personality traits, providing a certain level of behavior and activity typical for it. These are mental phenomena that are realized in a certain society.
Mental properties include:
- Temperament;
- Character;
- Capabilities;
- Directionality.
When talking about the mental properties of a personality, we are talking about its essential, more or less stable, permanent features. These are the characteristics that distinguish each person. Their totality determines a person’s individuality, because it is impossible to meet 2 people with exactly the same mental properties.
You should not confuse some isolated cases of manifestation of any traits with mental properties. After all, each of us has happened to forget something, but “forgetfulness” is not a characteristic feature for everyone. Everyone has been in an irritable state at some point, but “irritability” is characteristic only of some. Thus, a mental property can only be a stable and permanent feature of a person, which is developed and formed during life.
Psychological states as the main criteria for personality research
A person's personality in a particular situation is reflected by the psychological state that shapes its response to a stimulus. That is, some emotions prevail over others, gestures change, behavior changes, sometimes even motivation and other processes. The state is a relatively static indicator, however, with long-term identical stimuli, the time-varying state turns into a practically non-variable property.
In the process of personality research, the following components of the mental state were identified:
- Physiology (physical indicators, for example, pulse);
- Motor functions (facial expressions, speech, etc.);
- Emotions (depending on the situation, both positive and negative);
- Cognitive processes (the ability to adequately think, think through your further actions, analyze the situation);
- Behavior (any actions caused by a specific situation);
- Communication skills (the ability to contact and adequately communicate with a person).
All psychological states are divided into two groups: situational and stable (personal). Each group has its own classification.
Situational states are characterized by instability and the individual’s response to a certain atypical situation. They can be:
- general-functional;
- mental stress;
- conflicting.
Stable, that is, those that persist for a long time, are divided into:
- optimal or crisis;
- various borderline states (dementia, psychopathy);
- disturbances of consciousness.
It is necessary to dwell separately on crisis conditions, which can manifest themselves in the form of:
- negativism (the predominance of negative emotions even under optimal conditions);
- opposition (aggression in certain similar situations or towards certain individuals, but similar by some criterion);
- autism (complete social withdrawal).
Yu. V. Shcherbatykh is the founder of another classification of mental states. The classification is presented in the form of a table and thanks to it you can calculate the formula for a certain state, for example, fear or admiration. The table examines 7 criteria, each of which is divided into transitional and extreme variants of the mental state.
Study methods
In the field of psychiatry and cognitive science, the following methods are used to study the processes of memory, perception, thinking, attention and other functions:
- Recognizing figures by touch and manipulating them tactilely (Seguin board).
- Visual recognition of real, noisy, contour and defocused images (Poppelreiter test).
- Perception of objects requiring visual-spatial processing (contour geographical map, schematic clock).
- Recognizing familiar portraits of famous people.
- Listening perception and assessment of rhythmic structures.
- Detection of memory impairments (Pictogram technique).
It should be said that it is possible to identify a violation of the mental process only with the help of several methods, that is, problems need to be diagnosed in a complex manner.
The largest number of techniques explore thinking. The most famous is “Classification of Objects”, where it is possible to study various aspects of the thinking process. Also known: understanding the figurative meaning of metaphors and proverbs, solving arithmetic problems of varying degrees of complexity, comparing and defining concepts.
Now let's talk separately about the course of mental processes and states, their characteristics, properties and functions.
Criteria for a mature personality
Before conducting personality research, you should decide on the criteria that a formed, holistic personality must meet. There is no general approach to this concept, but it is customary to consider the most reliable criteria of V.V. Petukhov, who claims that a person:
- must be capable of creativity;
- can be multiple with simultaneous integrity;
- is constantly evolving.
L. I. Bozhovich approached the question more simply, highlighting only two criteria for an individual: the ability to set priorities, sacrificing one’s “want” for the sake of “need,” as well as the ability to manage one’s actions, setting goals and overcoming obstacles.
Psychological studies of personality
All research methods are divided into 4 categories, united by some common approach to the study of personality.
- Observation. The main ways to assess a personality are through examination, questioning both the person himself and those around him, reading the medical history, if any, reading diaries or autobiographies. The last two sources, as practice shows, are very valuable information.
- Experiment. Includes various studies using equipment. It is also possible to simulate some emergency situations or situations that are important for a particular person to assess his mental state.
- Questionnaires and other similar techniques. They allow you to evaluate many criteria: motivation, focus, self-esteem, willpower, etc.
- Design. Using the techniques of this area, the personality as a whole is determined, without highlighting its individual criteria.
However, in practice all 4 methods are actively used, which can also be mixed, complementing each other, so their separation is conditional.
Pedagogy tests
1. The subject of pedagogy as a science is...
A) purposefully organized pedagogical process
2. The subject of psychological science is
D) psyche
3. In the literal sense, the term “pedagogy” is translated ...
B) child rearing
4. In the literal sense, the term “psychology” is translated ...
B) knowledge about the soul
5. The most significant and stable mental characteristics of a person are called
B) mental properties
6. A certain level of performance and quality of functioning of the human psyche, characteristic of him at any given moment in time, is called ...
D) mental states
7. Mental phenomena that are formed in the process of a person acquiring life and professional experience, the content of which includes a special combination of knowledge, skills and abilities are called ...
D) mental formations
8. Mental phenomena that provide a person’s primary reflection and awareness of the influences of the surrounding reality (have a clear beginning, a definite course and a clearly defined end) are called ...
A) mental processes
9. Mental processes include...
C) sensation, perception, memory, thinking, imagination, emotions, will
10. Mental properties include...
A) temperament, character, abilities, orientation
11. Mental states include...
B) fatigue, concentration, vigor, mobilization
12. Mental formations include...
D) knowledge, skills, abilities
13. A purposeful process of interconnected activity between a teacher and a student, aimed at solid mastery of a system of knowledge, skills and abilities, is called ...
B) training
14. Purposeful activity aimed at developing certain qualities, views and beliefs in a person is called...
A) education
15. The process and result of mastering a certain system of knowledge, skills, abilities, accompanied by a statement of the achievement by a citizen (student) of the educational levels established by the state...
D) education
16. The main task of psychological science is...
A) study of the laws of mental activity
17. The main task of pedagogical science is:
B) study of the laws of education and training
18. Psychology is becoming an independent and experimental field of scientific knowledge...
A) in the 19th century.
19. According to the theory of humanistic psychology, the main driving force in the development and formation of the human psyche is...
A) the desire for self-actualization
20. According to the theory of the cognitive approach in psychology, the main driving force for the development and formation of the human psyche is:
D) development of cognitive processes
21. Pedagogy is becoming an independent field of scientific knowledge...
A) in the 17th century.
22. The founder of domestic pedagogical science is...
D) K.D. Ushinsky
23. Training and education should be carried out through “doing” - the essence of pedagogy...
A) pragmatism
24. The main goal of training and education of the humanistic paradigm of education ...
C) contribute to the development of human abilities
25. The main goal of training and education in the conditions of this educational paradigm is to give a person deep, lasting, versatile academic knowledge...
B) knowing
26. From the position of the subject of the activity being performed, the following areas of psychology are distinguished...
D) personality psychology, social psychology, developmental psychology, special psychology
27. From the perspective of the content of the activity being performed, the following areas of psychology are distinguished...
A) educational psychology, medical psychology, legal psychology, sports psychology.
28. The study of psychological patterns of training and education is carried out by...
B) educational psychology
29. The study of the psychological characteristics of human activity in various professional fields is carried out ...
D) work psychology
30. The study of various deviations in the development of the psyche is carried out ...
B) special psychology
31. Mental phenomena in the process of relationships between people in large and small groups are studied ...
B) social psychology
32. Branches of pedagogy as a science include
B) general pedagogy, history of pedagogy, didactics
33. The following branch of pedagogy deals with the specific application of general laws of learning to the teaching of individual subjects...
A) didactics
34. The study of the patterns of functioning and development of educational and educational systems in different countries by comparing and finding similarities and differences is carried out ...
B) comparative pedagogy
35. Corrective pedagogy arose on the basis of the connection between pedagogy and...
B) medicine
36. Empirical (practical) methods of psychological and pedagogical research include...
C) observation, conversation, questioning, experiment
37. A holistic psychological structure that is formed in the process of a person’s life on the basis of his assimilation of social norms of consciousness and behavior is ...
B) personality
38. The highest need in the hierarchy of needs according to A. Maslow’s pyramid ...
D) the need for self-realization
39. Determine the type of temperament - characterized by great excitability and imbalance; hot-tempered, aggressive, straightforward in relationships with people; energetic in his activities, but cyclical in his work (not interested - quits)…
A) choleric
40. Humanism, responsiveness, justice, dignity, shame are manifestations of ___feelings...
A) ethical
41. Sensation, perception, memory, imagination, thinking make up the group...
+ cognitive processes
42. Attention caused by the action of a strong, contrasting or new, unexpected stimulus that arises by itself is called
B) involuntary
43. A mental process consisting of consolidation, preservation and subsequent reproduction of past experience in a person’s mind...
B) memory
44. Thinking carried out in a non-standard, original way...
A) productive
45. As types of imagination we can distinguish...
B) dreams, dreams, fantasy
46. Education as a pedagogical process is...
D) specially organized interaction between teachers and students, aimed at solving problems of personal development
47. One of the global trends in the development of education is...
D) continuity of education throughout human life
48. The main functions of the pedagogical process are...
A) educational, educational, developmental
49. Objects of material and spiritual culture that act as substantive support for the learning process are defined as
B) teaching aids
50. Coordination and consistency of actions of all participants in the educational process, services, social institutions is the essence of the principle
A) unity of educational influences
51. Egalitarian, patriarchal, matriarchal types of families are distinguished by...
C) characteristics of leadership in the family
52. Encouraging initiative and independence of younger family members is typical for ____ style of family education...
B) democratic
53. The interpersonal function of communication is...
D) in organizing and maintaining relationships between individuals at the level of certain emotional contacts
54. Forming an image of another person, understanding his personality traits is...
B) the perceptual side of communication
55. An unorganized, random, temporary association of previously unknown people based on similar interests or common space is called...
A) conglomerate
56. The presence of a contradiction, disagreement of interests, needs and goals, disrupting the normal interaction of people, preventing the achievement of their goals, leading to confrontation is called:
B) conflict
57.
teaching staff , together with parents from grades 7–9, prepared and held a scientific and practical conference “Family as a factor in the socialization, education and development of a teenager.”
In preparation for the conference, the school psychologist conducted a diagnosis of child-parent relationships in adolescent families. Within the framework of the conference, the experience of family education was summarized, a meeting was organized with a psychologist, pediatrician, and social teacher, a review of literature and Internet sources on the problems of family education was prepared, and the results of the competition of student research projects “Family - Seven Selves” were summed up. As one of the decisions made at the conference, it was proposed to organize a system of thematic seminars and trainings for parents of teenagers “Parent School”. Family refers to the _______ socialization of the individual.
A) microfactors
58. One of the global trends in the development of modern education.
The concept of lifelong learning was put forward by UNESCO in the report “Learning to Be” in 1972. It contains the idea of combining, in one form or another, vocational education and advanced training with general education at different levels. The main goals of lifelong education may include the adaptation of a citizen to the changing conditions of his professional activity and the satisfaction of his individual needs. One of the founders of the theory of lifelong education is the Czech teacher J. A. Komensky, who in the 17th century developed an education system based on the principle of conformity with nature. Currently, the goals and objectives of lifelong education are implemented in various forms of educational organization. A special role in the implementation of the idea of lifelong education is given to higher education institutions, which, as part of the Bologna process, are recommended to integrate the ideology of lifelong education into general strategies and development plans. Technology plays an important role in the implementation of the concept of lifelong education at the present stage... A) distance learning
1. The subject of pedagogy as a science is...
A) purposefully organized pedagogical process
2. The subject of psychological science is
D) psyche
3. In the literal sense, the term “pedagogy” is translated ...
B) child rearing
4. In the literal sense, the term “psychology” is translated ...
B) knowledge about the soul
5. The most significant and stable mental characteristics of a person are called
B) mental properties
6. A certain level of performance and quality of functioning of the human psyche, characteristic of him at any given moment in time, is called ...
D) mental states
7. Mental phenomena that are formed in the process of a person acquiring life and professional experience, the content of which includes a special combination of knowledge, skills and abilities are called ...
D) mental formations
8. Mental phenomena that provide a person’s primary reflection and awareness of the influences of the surrounding reality (have a clear beginning, a definite course and a clearly defined end) are called ...
A) mental processes
9. Mental processes include...
C) sensation, perception, memory, thinking, imagination, emotions, will
10. Mental properties include...
A) temperament, character, abilities, orientation
11. Mental states include...
B) fatigue, concentration, vigor, mobilization
12. Mental formations include...
D) knowledge, skills, abilities
13. A purposeful process of interconnected activity between a teacher and a student, aimed at solid mastery of a system of knowledge, skills and abilities, is called ...
B) training
14. Purposeful activity aimed at developing certain qualities, views and beliefs in a person is called...
A) education
15. The process and result of mastering a certain system of knowledge, skills, abilities, accompanied by a statement of the achievement by a citizen (student) of the educational levels established by the state...
D) education
16. The main task of psychological science is...
A) study of the laws of mental activity
17. The main task of pedagogical science is:
B) study of the laws of education and training
18. Psychology is becoming an independent and experimental field of scientific knowledge...
A) in the 19th century.
19. According to the theory of humanistic psychology, the main driving force in the development and formation of the human psyche is...
A) the desire for self-actualization
20. According to the theory of the cognitive approach in psychology, the main driving force for the development and formation of the human psyche is:
D) development of cognitive processes
21. Pedagogy is becoming an independent field of scientific knowledge...
A) in the 17th century.
22. The founder of domestic pedagogical science is...
D) K.D. Ushinsky
23. Training and education should be carried out through “doing” - the essence of pedagogy...
A) pragmatism
24. The main goal of training and education of the humanistic paradigm of education ...
C) contribute to the development of human abilities
25. The main goal of training and education in the conditions of this educational paradigm is to give a person deep, lasting, versatile academic knowledge...
B) knowing
26. From the position of the subject of the activity being performed, the following areas of psychology are distinguished...
D) personality psychology, social psychology, developmental psychology, special psychology
27. From the perspective of the content of the activity being performed, the following areas of psychology are distinguished...
A) educational psychology, medical psychology, legal psychology, sports psychology.
28. The study of psychological patterns of training and education is carried out by...
B) educational psychology
29. The study of the psychological characteristics of human activity in various professional fields is carried out ...
D) work psychology
30. The study of various deviations in the development of the psyche is carried out ...
B) special psychology
31. Mental phenomena in the process of relationships between people in large and small groups are studied ...
B) social psychology
32. Branches of pedagogy as a science include
B) general pedagogy, history of pedagogy, didactics
33. The following branch of pedagogy deals with the specific application of general laws of learning to the teaching of individual subjects...
A) didactics
34. The study of the patterns of functioning and development of educational and educational systems in different countries by comparing and finding similarities and differences is carried out ...
B) comparative pedagogy
35. Corrective pedagogy arose on the basis of the connection between pedagogy and...
B) medicine
36. Empirical (practical) methods of psychological and pedagogical research include...
C) observation, conversation, questioning, experiment
37. A holistic psychological structure that is formed in the process of a person’s life on the basis of his assimilation of social norms of consciousness and behavior is ...
B) personality
38. The highest need in the hierarchy of needs according to A. Maslow’s pyramid ...
D) the need for self-realization
39. Determine the type of temperament - characterized by great excitability and imbalance; hot-tempered, aggressive, straightforward in relationships with people; energetic in his activities, but cyclical in his work (not interested - quits)…
A) choleric
40. Humanism, responsiveness, justice, dignity, shame are manifestations of ___feelings...
A) ethical
41. Sensation, perception, memory, imagination, thinking make up the group...
+ cognitive processes
42. Attention caused by the action of a strong, contrasting or new, unexpected stimulus that arises by itself is called
B) involuntary
43. A mental process consisting of consolidation, preservation and subsequent reproduction of past experience in a person’s mind...
B) memory
44. Thinking carried out in a non-standard, original way...
A) productive
45. As types of imagination we can distinguish...
B) dreams, dreams, fantasy
46. Education as a pedagogical process is...
D) specially organized interaction between teachers and students, aimed at solving problems of personal development
47. One of the global trends in the development of education is...
D) continuity of education throughout human life
48. The main functions of the pedagogical process are...
A) educational, educational, developmental
49. Objects of material and spiritual culture that act as substantive support for the learning process are defined as
B) teaching aids
50. Coordination and consistency of actions of all participants in the educational process, services, social institutions is the essence of the principle
A) unity of educational influences
51. Egalitarian, patriarchal, matriarchal types of families are distinguished by...
C) characteristics of leadership in the family
52. Encouraging initiative and independence of younger family members is typical for ____ style of family education...
B) democratic
53. The interpersonal function of communication is...
D) in organizing and maintaining relationships between individuals at the level of certain emotional contacts
54. Forming an image of another person, understanding his personality traits is...
B) the perceptual side of communication
55. An unorganized, random, temporary association of previously unknown people based on similar interests or common space is called...
A) conglomerate
56. The presence of a contradiction, disagreement of interests, needs and goals, disrupting the normal interaction of people, preventing the achievement of their goals, leading to confrontation is called:
B) conflict
57.
teaching staff , together with parents from grades 7–9, prepared and held a scientific and practical conference “Family as a factor in the socialization, education and development of a teenager.”
In preparation for the conference, the school psychologist conducted a diagnosis of child-parent relationships in adolescent families. Within the framework of the conference, the experience of family education was summarized, a meeting was organized with a psychologist, pediatrician, and social teacher, a review of literature and Internet sources on the problems of family education was prepared, and the results of the competition of student research projects “Family - Seven Selves” were summed up. As one of the decisions made at the conference, it was proposed to organize a system of thematic seminars and trainings for parents of teenagers “Parent School”. Family refers to the _______ socialization of the individual.
A) microfactors
58. One of the global trends in the development of modern education.
The concept of lifelong learning was put forward by UNESCO in the report “Learning to Be” in 1972. It contains the idea of combining, in one form or another, vocational education and advanced training with general education at different levels. The main goals of lifelong education may include the adaptation of a citizen to the changing conditions of his professional activity and the satisfaction of his individual needs. One of the founders of the theory of lifelong education is the Czech teacher J. A. Komensky, who in the 17th century developed an education system based on the principle of conformity with nature. Currently, the goals and objectives of lifelong education are implemented in various forms of educational organization. A special role in the implementation of the idea of lifelong education is given to higher education institutions, which, as part of the Bologna process, are recommended to integrate the ideology of lifelong education into general strategies and development plans. Technology plays an important role in the implementation of the concept of lifelong education at the present stage... A) distance learning
This is interesting
The experimental method is subject to widespread criticism for reasons of humanity, but its results always turn out to be the most reliable and interesting for science. For example, Stanley Schachter conducted a very interesting experiment, during which it was found that in an emergency, life-threatening situation, a person prefers to be not alone, despite the understanding of joint death. Further research showed that a person prefers to be close to someone who experiences the same fears or emotions as him. That is, in a threatening situation, a person needs not just a friend, but a “suffering” friend.
Based on the conducted personality studies, it is possible to reliably determine all the criteria and indicators of a person’s psyche in order to create a holistic personal portrait.