Mental states are necessary for a person to successfully carry out various types of activities. In psychology, they are classified on various grounds, the most popular among which is the energy expenditure of the individual. A person’s mental state has a direct impact on the overall functioning of the nervous system, organically fitting into the general construct of personality.
Having a general understanding of the functioning of the psyche and its impact on the performance of a person is necessary in order to be able to manage one’s emotions and maintain the functioning of the nervous system. This knowledge will be relevant both for schoolchildren and students, as well as for adults engaged in intellectual or physical labor in an enterprise.
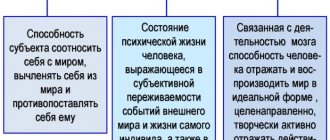
Definition of mental state
To understand how to formulate a definition of a mental state, you need to turn to the study of the biological and psychophysiological principles of the nervous system.
In psychology, the features of mental life are considered a category of the general methodology of science, which determines the features of the activity of a particular individual. The variety of phenomena in the emotional sphere as an object of scientific research was first discovered in the works of N.D. Levitova.
In theoretical articles, the author defined the state of a person’s mental sphere as a peculiar feature of the psyche, reflecting the work of the nervous system, supporting his judgments with empirical results. At the same time, the researcher draws the reader’s attention to the fact that conclusions about the current emotional status of an individual at the time of his study must be made based on events that happened to him recently. At the same time, the scientist does not deny that tragic events of the past can make themselves felt many years later, when a person, it would seem, no longer remembers them. It follows that signs of a mental state increase or decrease the efficiency of the body.
The psychological state is the basis for mastering the norms and rules of behavior of an individual in society. They occupy an intermediate position between personality traits and processes such as voluntary attention, short-term and long-term memory, logical thinking, imagination, and speech. In labor psychology, this phenomenon is taken into account when preparing a personnel reserve for representatives of different professions.
Examples of mental states are moods, feelings and emotions, as well as sleep and wakefulness. The stages of development of mental states are determined by the predominance of processes of inhibition or excitation in the nervous system.
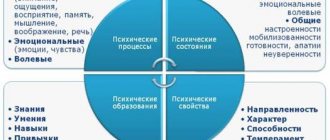
Mental properties
Mental properties are the most stable and constantly manifested personality traits, providing a certain level of behavior and activity typical for it. These are mental phenomena that are realized in a certain society.
Mental properties include:
- Temperament;
- Character;
- Capabilities;
- Directionality.
When talking about the mental properties of a personality, we are talking about its essential, more or less stable, permanent features. These are the characteristics that distinguish each person. Their totality determines a person’s individuality, because it is impossible to meet 2 people with exactly the same mental properties.
You should not confuse some isolated cases of manifestation of any traits with mental properties. After all, each of us has happened to forget something, but “forgetfulness” is not a characteristic feature for everyone. Everyone has been in an irritable state at some point, but “irritability” is characteristic only of some. Thus, a mental property can only be a stable and permanent feature of a person, which is developed and formed during life.
Categorization criteria
It is customary to divide psychological experiences into independent categories according to such basic characteristics as:
- the source of their occurrence (they are born internally under the influence of a person’s thoughts or are formed as a result of the influence of external factors);
- degree of awareness (formed in the unconscious layer, in the preconscious or in the conscious layer of the psyche);
- duration (short-term, medium-term or long-term);
- degree of severity (barely noticeable, medium severity, pronounced);
- emotional background (positive or negative);
- area of manifestation (behavior, work activity, mood, will, motivation).
Diagnosis and assessment
For diagnosis, researchers use:
- Observation. It can be carried out without warning a person or in specially created conditions. A voice recorder, video camera, or photo camera can be used for observation.
- Experiments. They can be carried out in specially created conditions or in a natural environment. In the first option, equipment can be used to monitor the physical state and its changes under the influence of stimuli.
- Self-report, self-observation. The patient independently makes notes about mood changes over a certain period. Observation can be entrusted to close relatives.
- Conversation, test survey, interview. Questions can be prepared in advance or be spontaneous, depending on the patient’s mood and physical well-being.
Types of mental states
Depending on the leading processes in the psyche, emotional, gnostic (cognitive) and volitional psychological states of a person are distinguished. Examples of emotional varieties are love passion and sexual desire, immediate joy and good spirits, sadness and doom, depression and depression, melancholy and despair, grief, indignation and resentment, panic, anger and affect.
The essence of gnostic experiences is conveyed by such short-term emotions as cognitive interest, curiosity, concentration and absorption in work, puzzlement and bewilderment, surprise, doubt and skepticism, daydreaming and a tendency to fantasize. All the emotions listed here are inextricably linked with the process of activity and do not exist in isolation from it.
The strong-willed varieties include: activity and initiative, determination and purposefulness, confidence, calmness and self-control, restraint and diametrically opposed characteristics paired with them. Unlike the previous group, these personality characteristics do not arise on their own; they are formed in the process of upbringing in childhood and adolescence.
The system-vector direction of psychology is based on a similar classification. In this approach, emotional phenomena of the psyche are represented by such groups as tension and relaxation in activity and motivation, feelings of pleasure and displeasure in the process of cognition or experience, activity and passivity as permanent personality types.
It must be said that supporters of this approach to classification emphasize that not everything can be corrected. Some experiences are determined by the type of nervous system and its mobility, which cannot be changed. Therefore, the passivity and slowness of some people, as well as the excessive activity of certain individuals, sometimes need to be taken for granted and a person must be taught to live with these individual typological characteristics.
According to the criterion of connection with the structural components of personality, it is customary in psychology to distinguish such types of mental phenomena as personal experiences that are related to activity, emotions of individuality.
What are the different types of mental states that influence a person? Stenic varieties - they stimulate the activity of the individual; asthenic types - they inhibit the activity of the individual.
What would be a simplified classification of mental states?
Moral and psychological
This type is born as a result of the individual’s personal (subjective) experiences when contemplating the surrounding reality. The degree of correspondence between the phenomenon seen and the emotional experience that appears characterizes the level of adequacy of the individual’s response. The structure and types of moral experiences are determined by the characteristics of a person’s nervous system and the type of his temperament, as well as characterological characteristics.
Emotional-psychological
The definition of this group is based on the psychological characteristics of the individual and the emotions of a person that arise in a particular life situation. The types of this group are affects, passion, a person’s mood, his experience of stress or discomfort from frustration. Mood reflects the state of a person engaged in one or another type of research, practical, labor, or creative activity. The predominance of positive or negative connotations of emotional and mental states is also determined by the type of personality temperament. The mental state of an energetic choleric person is characterized by rapidly changing brightly colored experiences (outbursts), while the main characteristic of the emotional background of a slow-moving phlegmatic person will be calmness and the absence of bright outbursts and causeless changes in mood. Negative mental states predominate among melancholic people prone to depression, while positive mental states prevail among carefree, cheerful sanguine people.
Stress and the mental state of frustration are those types of emotional states that require immediate elimination. Sometimes a person cannot cope with them on his own; he needs the help of a qualified psychologist or psychotherapist. In some cases, to correct an individual’s well-being, he requires drug therapy and observation by a psychiatrist.
Psychological states of a person
The psychological block of personality includes all components of the human psyche: characteristics of the nervous system, worldview, value orientations, motivational-need block. The concept of an individual's attitudes and beliefs in the formation of mental states is of paramount importance.
Psychological state of the child
The structure and types of mental states of a child are explained by the age-related characteristics of his development. The possibility of an objective assessment of the psychological status of children does not appear until they reach 15–16 years of age. Until this time, children are characterized by momentary changes in mood and a superficial perception of what is happening.
The characteristics of the child’s mental processes and emotional states depend on the home environment and psychological climate in the family.
Socio-psychological
What refers to the socio-psychological states of the individual? First of all, these are all social contacts of a person. The emotional orientation of a person is determined by the level of development of a person’s communication skills, his self-esteem, and image.
A person’s negative assessment of his mental state during interactions with others can lead to the development of psychosomatic diseases.
Mental health
28.Oct.2019
Mental health
- an important part of human health. This is primarily due to the fact that the human body, in which all elements are interconnected and influence each other, is largely under the control of the nervous system, therefore the mental state affects the work of each of the functional systems, and the state of the latter, in in turn, affects the psyche.
Mental health should be characterized by:
1. The absence of mental or psychosomatic diseases. 2. Normal age-related development of the psyche.
3. Favorable (normal) functional state.
Mental health is an integral part and essential component of health. The WHO Constitution states: “Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.” An important implication of this definition is that mental health is not only the absence of mental disorders and disabilities.
Mental health is a state of well-being in which a person realizes his or her abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, work productively, and contribute to their community. In this positive sense, mental health is fundamental to individual well-being and the effective functioning of communities.
How to maintain your mental health?
1. Nutrition.
Food affects both physical and mental health, it’s not for nothing that they say “You are what you eat.” Excessive consumption of certain foods (salt, sugar, onions, garlic, chili peppers, carbonated drinks) can increase the production of hormones in the body that contribute to anger and irritability during times of emotional stress. Drinking plenty of water, on the contrary, helps manage emotions.
2. Physical activity
. Physical health is closely related to mental health. Exercise not only strengthens muscles and the heart, but also contributes to the formation of hormones - endorphins, which improve mood and act as natural energy sources. It is important to properly combine physical activity and sufficient rest (from 7 to 8 hours of sleep every night), to rest on time, and not when you “fall from fatigue.” Walk outdoors with enough sunlight (10 to 15 minutes a day).
3. Accept your feelings
. Anger, sadness, fear, and feelings of frustration are all very unpleasant, and many people try to avoid anxiety by pushing these feelings away. Sometimes, in an effort to avoid worry, we try to hide our emotions, which can lead to destructive behavior - false detachment or composure. By trying to suppress emotions, we thereby lose the ability to perceive the normal joys and sorrows that are part of our relationships with other people.
Unpleasant emotions are a normal reaction to many (non-normal) situations. There is no reason to be ashamed of being homesick, or afraid when learning to ski, or angry when someone cheated you. These emotions are natural and it is better to acknowledge them than to deny them. When emotions cannot be expressed directly (for example, it is stupid to reprimand your boss), you can find another way to relieve tension. Taking a long walk, playing with a tennis ball, or discussing the situation with a friend may help the anger dissipate.
4. Managing your emotions.
Managing anger and negative emotions is an important factor in good mental health and an indicator of your emotional intelligence. There are certain techniques (counting from 20 to 0, breathing exercises) and relaxation techniques that can be used to combat anger and irritability, such as yoga and meditation. Choose for yourself an adequate way to express negative emotions (speak, breathe, draw...). You can talk by naming your feelings: “I feel... when...”. Instead of: “You are deceiving me,” it is better: “I feel deceived,” Instead of: “You are a rude person,” it is better to say: “I am very upset by the way you talk to me,” “I feel upset when you talk to me.” That's how they talk."
5. Know your weak points
. Knowing what situations trigger you to become upset or overreact can help keep you from stressing out. You can avoid them or try to understand what it is about them that bothers you. If you try to pinpoint the cause of your discomfort, you may be able to see the situation in a new light.
6. Change your thinking from negative to positive
. First, we need to stop pumping ourselves up with negative information every day, stop criticizing the existing order, unwanted neighbors, co-workers, etc. We learn to notice and enjoy the simplest things: the first spring flower, a long-awaited vacation that you will spend with the whole family, a new store that was built next to your home...
7. Careful planning
and taking breaks from work will help you avoid feeling overwhelmed at the last minute. Many people become especially anxious when they are under pressure. A strategy that purposefully leaves you with more time than you think you need to get to a business meeting can help eliminate this source of stress.
8. Develop your talents and interests
. Bored and unhappy people rarely have many interests in life. Modern educational programs provide almost unlimited opportunities for people of all ages to explore their talents in many areas, including sports, science, music, art, theater and crafts. Often, the more you know and can do, the more interesting life becomes for you. The sense of competence that comes with developing skills can do a lot to support self-esteem.
9. Learn to smile
. It’s not so difficult to “hang” a “duty smile of politeness” on your face, to smile at a passerby who asks you a question. One of the ways to strengthen mental health is to visit the department of psychotherapy and neurosis, where an integrated approach aimed at restoring mental balance, body care, restorative procedures and consultations with leading specialists will allow you to maintain high body tone and gain strength even in a short time.
Properties
All mental states have special properties:
- Integrity is the interconnection and interdependence of all components of the psyche. This property influences the efficiency of human activity.
- Sustainability. All types of human mental states are more permanent than momentary emotions.
- Mobility is the property of mental states to change their functions following a change in the situation.
- Polarity – this property expresses the pairing of emotional experiences. For every positive experience, you can select a diametrically opposite (negative) emotional experience.
Levels
The essence and classification of mental states in psychology are manifested at different levels:
- the physiological level reveals the neurophysiological, biological and morphological features of a person’s response to what is happening;
- psychophysiological level, which determines the sensory and vegetative reactions of the body;
- socio-psychological level, taking into account a person’s status in interpersonal relationships, his attitude to work;
- psychological level that sets the general emotional mood of the individual.
Forming factors
What factors influence a person’s psychological state? It is generally accepted that the factors of a person’s mental states include: general personality tone, motivation, mood, expectation of success, subjective attitude to activity. Based on these components, the factors received names such as:
- Motivational and incentive is the most powerful factor that stimulates the activity of an individual. The leading components here are a person’s satisfaction with his relationship with his loved one and financial security.
- Emotional-evaluative is a factor indicating a person’s attitude towards a particular type of activity and the result of his work.
- Activation-energy is a factor that characterizes a person’s physiological activity and manifests itself in the natural change of sleep and wakefulness. Human health is also considered an active energy factor. Strong experiences are usually associated with excitement, and weak ones with inhibition in the nervous system.
Classification
Over the entire period of studying possible human psychological states, scientists have created many classifications. Depending on the source of formation:
- sharp emotional reactions—personally determined;
- manifestations of emotions due to the situation.
Depending on the emotional coloring:
- neutral;
- negative;
- positive.
Depending on the degree of external expression:
- strong, deep;
- weakly expressed, superficial.
Depending on the degree of awareness:
- conscious - arise in situations where a person makes efforts to achieve a goal;
- unconscious - appear when a person is sleeping.
Depending on the level of manifestation:
- psychophysiological;
- psychological;
- physiological.
Depending on the duration:
- Long lasting. These include nervous breakdowns, depression, and apathy.
- Medium duration. Driven by fears.
- Short-term. For example, rage, anger, laughter.
Typical types:
- Professional interest. This state is necessary for productive work. Characteristic manifestations are concentration of attention on the chosen business, the production process, the desire to develop existing skills, and gain experience.
- Hard work. Occurs if a person has worked for a long time in extreme conditions. There is active work of the nervous system and increased psychological stress.
- Optimal working condition. Helps achieve results over a long period of time. High concentration of attention is determined by the presence of a conscious goal of activity, activation of thinking, and sharpening of memory.
- Stress. Increased stress that arises due to the inability to adapt to the current situation. Lasts from one day to several months. Prolonged stress often leads to the development of psychological disorders.
- Relaxation. A person regains the strength that was expended. Voluntary relaxation can be achieved with constant psychological training, knowledge of yoga, and reading prayers. Involuntary relaxation occurs after prolonged labor.
- Fatigue. Decreased performance, which can be long-term or short-term. Occurs due to prolonged physical or mental stress. Concentration and memory are temporarily impaired. Caused by depletion of the body's resources.
- Monotony. Occurs under the same loads. Accompanied by indifference, boredom, and a rapid decrease in concentration.
Conditions that have a physiological basis include wakefulness and sleep.
Attention should also be paid to reactive states. They represent acute affective reactions or shock disorders that are observed with mental trauma.
Functions of mental states
Mental states are a structural component of the psyche. The list of functions they perform looks like this:
- formation of personal self-esteem;
- discussion of a person to perform certain actions;
- predicting the success of certain undertakings;
- forcing a person to complete the work he has begun;
- formation of a person’s attitude to activity;
- evaluating the results of your work;
These 6 functions are explained by the essence and classification of mental states.
Diagnostics
Some people have the unique ability to accurately assess their mental state. Physical well-being is the main “barometer” for them. Other people need the help of a psychologist in this matter.
In psychology, determining a person’s mental state is an analysis of his psychophysiological and psychological levels. The study of the psychophysiological level allows us to study the nature of the emerging feeling and determine (if necessary) ways to correct it.
The most popular diagnostic tools are psychological tests. With their help, the mood, well-being and level of activity of an individual are diagnosed. The most indicative results are obtained by such methods as the Luscher color test, SAN, PAT, “Nervous-Mental Tension Questionnaire,” “Relief of Emotions,” and personal anxiety tests.
In medicine, methods for diagnosing mental conditions include ECG and GSR results, heart rate, and brain encephalogram.
Negative and positive states
Negative states include: • suffering; • anger; • disgust; • contempt; • shame.
These are asthenic emotions that negatively affect the body, worsen well-being and reduce the supply of vital energy. There is a feeling of chills, shortness of breath, blood circulation slows down, and muscle tone decreases.
Positive emotional states are positive emotions perceived by the subject as good health and mood: joy, interest, satisfaction. They are accompanied by a beneficial expansion of small blood vessels, blood flow to organs, and an increase in motor activity.
Problems of psychological states
What are the problems in studying psychological states? First of all, this is the difficulty of separating the subjective and objective factors that give rise to this or that emotional experience.
The predominance of negative psychological experiences leads to a feeling of dissatisfaction with one’s life. Awareness of problems in psychological terms and the ability to analyze one’s own state are not the methods by which a person can cope with psychosomatics. To restore performance, normalize sleep and get rid of causeless headaches, a person needs to consult a psychologist. Only a qualified specialist will be able to correctly determine the cause of the problem and choose effective methods to eliminate it.
My recommendations
Clients often come to me with complaints of chronic fatigue, loss of appetite, and lack of desire to do anything. They do not understand what is happening to them, they report that they have been to many doctors, have undergone a bunch of tests, but the cause of the decrease in performance and apathy has not been established. "What happened with me?" - they ask me. My answer that these symptoms relate to anomalies in the mental state of the individual usually surprises them. However, my initial assumptions are confirmed by the results of psychological tests. At the next stage of working with the client, I tell him about what types of mental states are distinguished in modern psychology, since often, having familiarized themselves with the diagnostic results, they say: “Indicate what refers to the mental states of the individual.”
In most cases, 5-10 sessions with a psychologist are enough to correct the psychological state that occurs when you are in a low mood. I give recommendations on developing reflection skills and teach relaxation techniques. The main method in my work is art therapy. In my opinion, this method is the key to the inner world of the individual. Through art therapeutic exercises, a person finds harmony with himself and learns to manage his emotional field.
Criteria for a mature personality
Before conducting personality research, you should decide on the criteria that a formed, holistic personality must meet. There is no general approach to this concept, but it is customary to consider the most reliable criteria of V.V. Petukhov, who claims that a person:
- must be capable of creativity;
- can be multiple with simultaneous integrity;
- is constantly evolving.
L. I. Bozhovich approached the question more simply, highlighting only two criteria for an individual: the ability to set priorities, sacrificing one’s “want” for the sake of “need,” as well as the ability to manage one’s actions, setting goals and overcoming obstacles.