Many of us are accustomed to thinking in only one way, and this leaves its mark on a person’s entire life: work, study, success, career, financial condition, satisfaction, romantic relationships, family, communication with others. And if the result is in some way unsatisfactory, the thinking model can and even needs to be changed. All that is required for this is to master at least a few thinking techniques that differ from the ordinary one. In this collection, we will introduce you to different thinking techniques, help you learn to think differently, and therefore act more effectively.
1
Development of thinking: ways to train the brain
Thinking can rightfully be called the crown of human knowledge. It is a mental activity with its own goals, motives, operational functions and results. It can be characterized in different ways, but, regardless of interpretation, it can be established that the better a person’s thinking is developed, the more effectively he can interact with the world around him and other people, study and cognize, understand phenomena and truths. In addition, everyone is capable of developing their own thinking, and we will talk about how this is done in this article. Read more…
2
Is it possible to develop the thinking of an adult?
Perhaps another equally important reason for the reluctance to develop thinking is the belief that it is impossible for an adult to do this. And the only way to become even a little smarter is to accumulate knowledge.
But this point of view is wrong. It is not only possible, but also necessary to develop the thinking of an adult, but knowledge alone will not get you far. Information, regardless of its volume, is only a building material for thinking. Bricks alone are not enough for a mason to build a beautiful castle; he also needs skills, abilities, knowledge of techniques and craftsmanship as an alloy of all this combined.
One can, of course, recall the statement of the developers of intelligence tests that intelligence does not change with age. But thinking is not exactly intelligence. Thinking is an activity, and any activity requires the development and formation of skills. The process of developing thinking skills not only enriches a person with new ways and techniques of thinking, but also develops and complicates the brain itself.
Our brain is a very flexible and sensitive instrument that is designed to be constantly active. The effectiveness and quality of our thinking depend on it. Indeed, in the process of brain work, new connections are formed between neurons, neural networks become more complex, and therefore, thinking abilities develop.
So, the answer to the question “is it necessary to develop thinking” is obvious. It remains to figure out how to do this.
Mental operations
In the process of evolution of views on the nature and essence of the thought process, the issue of the formation of mental operations attracted special attention of scientists. Thinking, unlike other physiological processes, occurs on the basis of a certain logic. This allows you to identify individual structural elements (abstraction, analysis and synthesis, classification and categorization, specification, generalization, comparison) and characterize them. The patterns of functioning of the named operations of thinking are essentially the main internal, specific foundations of thinking. Their study helps to obtain a detailed explanation of all external manifestations of mental activity. Read more…
4
How to write a term paper on speech therapy
07.09.2010 257496
These guidelines are compiled to help students gain an understanding of the content and structure of coursework in speech therapy.
Logopedia of pedagogical science that studies anomalies of speech development with normal hearing, explores the manifestations, nature and mechanisms of speech disorders, develops the scientific basis for overcoming and preventing them means of special training and education.
The subject of speech therapy as a science is speech disorders and the process of training and education of persons with speech disorders.
The object of study is a person suffering from a speech disorder.
The main task of speech therapy as a science is the study, prevention and elimination of various types of speech disorders.
Coursework in speech therapy is a student's scientific and experimental research. This type of educational activity, provided for by the educational and professional program and curriculum, contributes to the acquisition of skills in working with literature, analyzing and summarizing literary sources in order to determine the range of insufficiently studied problems, determining the content and methods of experimental research, processing skills and qualitative analysis of the results obtained. The need to complete coursework in speech therapy is due to the updating of knowledge concerning the content, organization, principles, methods and techniques of speech therapy work.
As a rule, during their studies, students must write two term papers - theoretical and practical.
The first course work should be devoted to the analysis and synthesis of general and specialized literature on the chosen topic. Based on this analysis, it is necessary to justify and develop a method of ascertaining (diagnostic) experiment.
In the second course work, it is necessary to provide an analysis of the results obtained during the ascertaining experiment, as well as determine the directions and content of speech therapy work, and select adequate methods and techniques of correction.
So, let’s present the general requirements for the content and design of coursework in speech therapy.
The initial and most important stage of working on a course project is the choice of a topic, which is either proposed by the supervisor or chosen by the student independently from a list of topics that are consistent with the areas of scientific research of the department.
Each topic can be modified, considered in different aspects, but taking into account a theoretical and practical approach. Having chosen a topic, the student needs to think through in detail its specific content, areas of work, practical material, etc., which should be reflected both in the formulation of the topic and in the further construction of the study. It should be recalled that the chosen topic may not only have a purely theoretical orientation, for example: “Dysarthria. Characteristics of the defect”, “Classification of dysgraphia”, but also take into account the practical significance of the problem under consideration, for example: “Speech therapy work on speech correction for dysarthria”. It should also be taken into account that when formulating a topic, excessive detail should be avoided, for example: “Formation of prosodic components of speech in preschoolers of the sixth year of life attending a preschool institution for children with severe speech impairments.”
The course work includes such mandatory parts as: introduction, three chapters, conclusion, bibliography and appendix.
The text of the term paper begins with the title page . An example of its design can be seen here.
Then the content of the work is given, in which the names of chapters, paragraphs, and sections are formulated in strict accordance with the content of the thesis. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the text, each subsequent chapter and paragraph begins on a new page. At the end of each chapter, the materials are summarized and conclusions are formulated.
The introduction reveals the relevance of the problem under consideration in general and the topic being studied in particular; the problem, subject, object, and purpose of the study are defined. In accordance with the goal and hypothesis, objectives and a set of research methods aimed at achieving the objectives must be defined.
The relevance of the topic lies in reflecting the current level of pedagogical science and practice, meeting the requirements of novelty and usefulness.
When defining the research problem, it is important to indicate what practical tasks it will help to implement in training and educating people with speech pathology.
The object of research is understood as certain aspects of pedagogical reality, perceived through a system of theoretical and practical knowledge. The ultimate goal of any research is to improve this object.
The subject of research is some part, property, element of an object, i.e. the subject of research always indicates a specific aspect of the object that is to be studied and about which the researcher wants to gain new knowledge. An object is a part of an object.
You can give an example of the formulation of the object, subject and problem of research:
– The object of the study is the speech activity of preschool children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The subject of the study is the features of intonation speech of children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The research problem is to determine effective directions for speech therapy work on the formation of intonation expressiveness of speech in the system of correctional intervention.
The purpose of the study contributes to the specification of the object being studied. The goal of any research is to solve a specific problem. The goal is specified in tasks taking into account the subject of research.
The research objectives are formulated in a certain sequence, which determines the logic of the research. The research objectives are set on the basis of a theoretical analysis of the problem and an assessment of the state of its solution in practice.
The first chapter is an analysis of literary sources, which examines the state of this problem in historical and modern aspects, and presents the most important theoretical principles that formed the basis of the study.
When writing the first chapter, you should pay attention to the fact that the text of the course work must be written in a scientific style. When presenting scientific material, it is necessary to comply with the following requirements:
– Specificity – a review of only those sources that are necessary to disclose only a given topic or solve only a given problem;
– Clarity – which is characterized by semantic coherence and integrity of individual parts of the text;
– Logicality – which provides for a certain structure of presentation of the material;
– Reasoning – evidence of thoughts (why this and not otherwise);
– Precision of wording, excluding ambiguous interpretation of the authors’ statements.
A literary review of the state of the problem being studied should not be reduced to a consistent presentation of literary sources. It should present a generalized description of the literature: highlight the main directions (currents, concepts, points of view), analyze in detail and evaluate the most fundamental works of representatives of these directions.
When writing a work, the student must correctly use literary materials, make references to the authors and sources from which the results of scientific research are borrowed. Failure to provide required references will reduce your coursework grade.
As a rule, in coursework on speech therapy, references to literary sources are formatted as follows: the number of the cited source in the general list of references is placed in square brackets. For example: General speech underdevelopment is a speech pathology in which there is a persistent lag in the formation of all components of the language system: phonetics, vocabulary and grammar [17].
When using quotations, in square brackets, in addition to indicating the source number, the page number from which this excerpt is taken is indicated, for example: Speech rhythm is based on a physiological and intellectual basis, since, firstly, it is directly related to the rhythm of breathing. Secondly, being an element that performs a communicative function, “correlates with meaning, i.e. controlled intellectually” [23, P.40].
However, course work should not be of a purely abstract nature, so you should not abuse the unreasonable abundance of citations. Quoting should be logically justified, convincing and used only when really necessary.
In the second chapter , devoted to experimental research, the organization should be described and the program of the ascertaining experiment should be presented. The survey methodology, as a rule, consists of a description of several series of tasks, with detailed instructions, visual and lexical material, the procedure for completing tasks by experiment participants, and scoring criteria. This chapter also provides a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the results obtained.
When analyzing the results of an experiment, it is necessary to use a scoring system. Examples of various criteria for quantitative and qualitative assessment are presented in the following works:
– Glukhov V.P. Formation of coherent speech in preschool children with general speech underdevelopment. - M.: Arkti, 2002. - 144 p.
– Fotekova T.A. Test methodology for diagnosing oral speech of primary schoolchildren. - M.: Arkti, 2000. - 56 p.
– Levchenko I.Yu. Pathopsychology: Theory and practice. - M.: Academy, 2000. - 232 p.
In order to visually present the results obtained during the experimental study, it is recommended to use tables, graphs, diagrams, etc. Histograms can be used in a variety of ways - columnar, cylindrical, planar, volumetric, etc. An example of the design of tables, figures, and histograms can be found here.
The third chapter provides a rationale for the proposed methods and techniques and reveals the content of the main stages of correctional work.
The conclusion contains a summary of the material presented and the main conclusions formulated by the author.
The bibliography must contain at least 25 sources. The list includes bibliographic information about the sources used in preparing the work. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the application you can present bulky tables or illustrations, examination protocols, observation records, products of activity (drawings, written works of children), notes from speech therapy classes, etc.
The volume of one course work must be at least 30 pages of typewritten text.
In general, coursework in speech therapy is the basis for a future thesis, in which the study of the begun problem can be continued, but from the standpoint of a different approach or a comparative analysis of the disorders being studied in different age categories of people with different types of speech disorders.
The content and format of theses in speech therapy can be found here.
Literature:
1. How to write a term paper on speech therapy: Methodological recommendations. Educational and methodological manual / Comp. Artemova E.E., Tishina L.A. / Ed. Orlova O.S. – M.: MGOPU, 2008. – 35 p.
2. Research work of students in the system of higher professional pedagogical education (specialty 031800 - Speech therapy). Methodological recommendations for completing the thesis / Compiled by. L.V. Lopatina, V.I. Lipakova, G.G. Golubeva. - St. Petersburg: Publishing house of the Russian State Pedagogical University named after. A. I. Herzen, 2002. - 140 p.
Two Ways of Thinking by Carol Dweck
In 2007, American psychologist Carol Dweck published a book called Mindset, where she argued that intelligence, talent and education do not necessarily lead a person to success. The main criterion is the way of thinking and how a person copes with life’s problems, difficulties and challenges. In this article, we'll explore what Carol Dweck's mindset is and how a fixed mindset can harm you when developing it will help you achieve your goals, increase self-motivation, and increase productivity. Read more…
5
Judgment
Judgment as a form of thinking involves confirmation or denial of some fact, event, property, feature, connection. It manifests itself in phrases, but we must remember that not every phrase is a judgment. Thus, an interjection or a one-syllable sentence does not belong to this form of thinking (examples: “Oh!”, “How is that possible?”).
Sentences tend to be narrative in nature: “The Earth revolves around the Sun.”
A proposition can be true or false, which is determined by logic. The first involves the presence of one subject with characteristics or the comparison of two subjects.
When a simple judgment is separated, the words cease to carry a semantic load. Example: “A mouse is smaller than a cat.” If this sentence is divided into two, the meaning is lost.
Complex judgments are various combinations that consist of a complex and a simple, two complex or two simple judgments. Examples: “If it hails, the plants may be damaged.” Here, “plants may be harmed” appears as a simple proposition.
Judgment as a form of thinking of a complex nature is impossible without grammatical connectives (“but”, “or”, “and”, “if so, then...”, “when..., then...”, etc.).
It is necessary to distinguish between judgment and other logical forms of thinking: a concept is expressed in a word, and a conclusion is expressed in a conclusion.
This form of thinking can also be:
- affirmative (“Botany is the science of plants”, “The tiger is a predator”);
- negative (“This sentence is constructed incorrectly”, “In Russian cities there are no bears walking on the streets”).
There is another classification. A general judgment presupposes a statement (negation) that refers to phenomena, subjects, united by a common concept (“All healthy cats have four paws”). Particular implies a part of objects, subjects, phenomena that are united by a concept (“Some poets are graphomaniacs”). An individual property is expressed in a single judgment (“F.M. Dostoevsky is the author of “Crime and Punishment””).
In essence, a judgment reveals the content of a concept (or several) - therefore, in order to make a statement, it is necessary to know the content of all the concepts used.
Harmful Thinking Styles
Harmful thinking styles are sometimes called cognitive distortions. These are systematic deviations in behavior, perception and thinking, caused by prejudices and stereotypes, failures in processing and analyzing information, as well as physical limitations and structural features of the human brain. These thinking styles are based on automatic patterns that we follow throughout our lives. If they are not recognized, the problem will remain and will affect all areas. With them it is impossible to realize your full potential. There are many harmful thinking styles, so in this article we will list only a few, and then show you how to get rid of the most catastrophic of them. Read more…
6
What types of logical thinking exist
In psychology, there are several types of the named skill (or, rather, groups of skills and approaches). Based on the main way of perceiving and reproducing information.
Abstract logical thinking
This is the basis of the named concept. When they talk about logic, they mean precisely this part of the activity. Its foundation lies in the ability to non-verbally, with great speed and efficiency, build complex connections, find relationships, notice subtle facts, and classify them. Also, a person with a high culture of this kind is able to quickly sift out the “husks”, find implicit connections, and come to non-trivial conclusions. Independently putting forward complex hypotheses and formulating one’s own theories are also important skills within the framework of this method of mental activity.
An important quality that should not be forgotten is consistency. That is, individual aspects, conclusions, must be consistent with each other and with the general outline of the reasoning. Otherwise, this is “pseudology” and is of little use. Possible flaws in your own reasoning also need to be noticed and corrected in a timely manner. Mistakes are possible even with developed skills.
The difference between the degrees of development lies in the ability to find and eliminate them. The abstract variety requires a long development and forms the basis for all other types. With sufficient mastery, problems no longer arise.
Verbal and logical thinking
A subtype based on verbal abilities. That is, the ability to put your thought into speech and convey it to the audience. Including in writing. Skill plays a huge role in the work of speakers, writers and publicists, writers. It is impossible to do without the ability to consistently formulate thoughts for scientists and workers in the educational environment.
There is also an important pairing skill. Be able to evaluate the speech of another, notice all inaccuracies and contradictions. The same goes for text. The ability to analyze other people's thoughts is indispensable when writing reviews or working as a public speaker (for example, a lawyer). Paradoxically, a well-developed abstract form of logical thinking does not mean that a person will automatically be quite effective in verbal form.
To become competent in this area, you must have a wide vocabulary and literate speech skills. The ability to accurately convey thoughts is born with experience and develops with it. Therefore, everything can be improved with the proper number of hours of practice. Another name for this group of skills is verbal-logical thinking. Specific examples where an understanding of this approach is required are speeches in court. The lawyer is a reference example. On the one hand, he must be able to prepare his own speech and defend his position if the other party or the court has questions. On the other hand, to detect inaccuracies in the opponent’s speech, to catch him using ambiguous wording and so on. Such a person must have an extensive arsenal of skills: from on-site system analysis to competent argumentation, the ability to debate, and quickly navigate the situation.
Visual-logical thinking
Required for situational analysis. It plays a major role in the work of criminologists, forensic experts, and doctors of various specialties. Workers of such profiles deal mainly with visual, visual material: be it the scene of investigative actions, radiography (image), a picture on the screen of an ultrasound machine, or something else in the same spirit. The specialist’s task is to track important visual data and interpret it correctly, integrate it into the overall picture and create a consistent concept. In the case of doctors, it may look like this. A radiology specialist takes a picture, deciphers it and gives general information about the condition of the lungs (optional). He does not make diagnoses. Its contribution is to assess the characteristics of the organ and search for anomalies. This requires developed logical thinking. The therapist or pulmonologist, based on X-ray data and other objective studies, already draws conclusions on the diagnosis. Which requires systematization and in-depth analysis skills.
It is not always necessary for all three varieties to be developed to an equal, high degree. It all depends on the person himself, his desires, professional activities, and experience. It's all about skills and willingness to practice. In any case, you cannot do without logical thinking. It lies at the basis of knowledge. Moreover, one cannot achieve success in academic and scientific activities if one does not master such a rich toolkit.
Applying design thinking to life
Bill Barnett, in his book Designing Your Life: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful Life, teaches people to apply the principles of design thinking (a strategy for improving a product or experience) in their personal and professional lives. Design thinking is a problem-solving system that uses mental, creative and analytical skills. Typically, designers look at business problems, but design thinking can also be used by the average person. Marelissa Fabrega in her article analyzes design thinking and gives advice to those who want to improve their lives with its help. Read more…
7
Harson's productive thinking model
Creativity is essential to solving any problem. If you are not creative and more logical, you will not be able to evaluate the problem from different points of view and come up with an unusual and simple solution. And if you combine critical and creative thinking, your effectiveness increases significantly. Harson's productive thinking model will help you do this. This model encourages using both sides of the brain and alternating between creative thinking and critical and logical thinking. This means that you can look at a problem from different angles and find the best solutions. Read more…
8
More details about the concepts
It is impossible to understand this issue in detail without finding out the definitions of all terms. Thinking is the process of processing information data and bringing it to a specific conclusion. This ability gave rise to the emergence of speech, which we use to communicate with each other. People come to reflection in order to resolve all troubles and problems, explore the world around them, find out relationships and patterns. By thinking, a person creates innovations, makes scientific discoveries and finds himself in art. Without a mental component, we would be similar to ordinary animals that act within the framework of their instincts.
Forms of thinking are the result of thought and mental processes that manifest themselves in a specific situation, which allows one to understand the essence of phenomena and objects, determine the relationships of objects and notice general signs. There are only three varieties, which I will discuss in detail below.
Design Thinking: What is it and How to Apply It
How to combine design and business? This question has been asked by many entrepreneurs for decades, and they have finally found the answer - using design thinking - a human-centered technique that allows you to find non-standard solutions to problems. Design thinking is not an aesthetic, but a mental work that defines the principle of problem solving, builds processes and installs tools. What are its principles and how to implement it in your activities? We will talk about this in our article. Read more…
9
Visual-effective thinking
This type of thought process is a product of the left hemisphere and consists of creating a copy of an existing object or object in the mind and identifying its properties and possible benefits, first in one’s imagination for subsequent application in reality. For simplicity, you can imagine a small child who, looking at an object and touching it, imagines where it will fit, whether it is edible or not, whether it can be thrown or hit with it. Adults also use this technique, going over in their heads the possible useful properties of an object, they imagine it in action and make a preliminary conclusion about its suitability for such use. This is clearly expressed when an adult is looking for something to replace a missing part or what to make it from.
This process is trained in all games where various combinations of moves are calculated, for example in chess or checkers, but there are also specially designed exercises:
- Determining the characteristics of an object - choose one of the objects lying in your room and try to imagine its weight. After that, check how it feels by picking it up and determine whether it’s how you imagined it. Also mentally determine its area and try to figure out the relationship with the area of your room. How many of these items will fit in one layer, but what about the volume? If you filled the whole room with such objects, how many would there be?
- Puzzles – both physical and virtual puzzles help develop visual and effective thinking. They force you to first perform actions several steps forward in your imagination, and then check the results in practice.
- A construction set is not only a desirable toy for children, but also a great way to come up with many different shapes and try to assemble them. This is a great workout for your brain, and the more details in the constructor, the better.
- Modeling figures , like a construction set, helps bring to life an object you previously conceived and try to make it exactly the way you imagined it. If you have the desire and time for such an activity, be sure to try it.
Edward de Bono's Six Thinking Hats Method
Among other theories of creativity, the method of lateral thinking specialist Edward de Bono is distinguished by its youth. The Six Thinking Hats was first published in 1985, introducing the public to a technique for organizing thinking and a way to solve creative problems and disputes. Today, this technique has become popular enough to gain both its fans and opponents. Perhaps philosophers would consider it necessary in this situation to joke about the hermeneutic circle, saying that the methodology that defends different views on things is itself evaluated differently. But without irony, we will try to understand the essence of the 6 hats technique, its pros and cons, as well as its application possibilities. Read more…
10
Online program "Cognitive Science"
Within two months, with the help of special brain training, you will learn to apply more than 20 thinking techniques in your life. This will allow you to think logically and consistently, quickly make effective decisions and find innovative approaches to difficult problems. The lessons not only train general memory and logic skills, but also provide specific models and algorithms of thinking. While participating in the program, you will learn to apply your knowledge and skills in practice, receive examples, case studies, special games and exercises, and short lessons of 15-20 minutes will help you develop your thinking without distraction from your main activity and show results in the first week . Find out more...
We hope that now you will have more faith in your own strengths and confidence that getting rid of templates and ossified thinking is very simple. Good luck!
Briefly about the development of forms of thinking: psychology of thought
While still studying at school, a person already masters mental activity and begins to operate with concepts. There are several steps to forming a conceptual process:
- familiarity with certain things and phenomena;
- identification of characteristics of objects;
- selection of the most essential properties;
- designating them with a specific word.
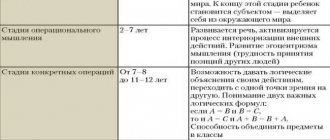
For example, children at 2-3 years old point with a finger at some thing (a toy car), then when they grow up and turn 4-5 years old, they begin to highlight a common feature that is of greatest importance (a toy is designed to play her). At 5-6 years old, children describe things, listing their properties without any sequence (a car has wheels, a steering wheel, a trunk, headlights). Having become one more year older, the child begins to select the most basic characteristics (a toy car is a child’s toy, a dog is an animal, a plate is dishes).
Ask a question
Sometimes understanding is not acquired at all, then illogicality (fantasticity) occurs - this is an unusual and original reasoning that does not lend itself to the laws of logic. The reasons for this are:
- Lack of knowledge and lack of experience.
- Replacing unfamiliar task conditions with familiar ones.
- Inconsistent expression of thoughts.
Ways to correctly draw conclusions:
- search for expediency in reality;
- determining the purpose and essence of surrounding things;
- finding connections between external characteristics and functions of objects.