If we analyze the work of a modern person with information, we can come to the conclusion that people remember most of the necessary information through repeated repetition, reading, and cramming. This kind of memorization takes a lot of time. There is a special type of memory - figurative memory. It is based on the sensations a person receives from the senses (images).
Images in memory
Figurative memory in psychology
Figurative memory is natural memorization. After listening to information once, a person will remember 10% of what was said. If an individual reads a text once, he will remember 30% of the information. If a person listens and reads this text at the same time, he will remember half of the information contained in it. If he had the opportunity to use the other senses, then after a single acquaintance with the text the individual would be able to reproduce it practically without loss.
Figurative memory is a persistent mnemonic form that is based on a person’s interests and knowledge. Images are inseparable from the consciousness of the individual. An example of figurative memory is the smell of tangerines, which people associate with the approaching New Year.
Attention! All babies have a well-developed figurative memory from birth. But adults force them to memorize material, abstracting from sensations, so they lose it.
Tests for older children and adults
It has already been noted that other types of assimilation and reproduction of knowledge progress with age. In high school, it is effective to engage in creativity and draw more often. An adult needs to find out which type of figurative memory predominates in him and develop the most promising direction.
Ask someone to write 20 words for you or take them from this article. First, someone else needs to read these words. Memorize the maximum quantity along with the serial number in 40 seconds:
- Slope. 2. Preamble. 3. Lavender. 4. Atmosphere. 5. Economics.
- Giraffe. 7. Forecast. 8. Schizophrenia. 9. Training. 10. Athlete.
- River. 12. Comet. 13. History. 14. Wardrobe. 15. Dumpling.
- Icon. 17. Megapolis. 18. Computer. 19. Bank. 20. Equality.
Write down the words you remember along with the numbers on a piece of paper. The number of correct answers must be divided by 20 and multiplied by 100. For example, 15/20*100 = 75% is the efficiency of auditory acquisition. Now take another similar list yourself, read and memorize the words in the same time. Calculate the effectiveness of visual assimilation of the material using the same formula.
Any direction of figurative memory is trained:
- visual – remember people’s facial features, the design of dishes in restaurants, book covers;
- auditory – listen to music, recordings of poetry
- olfactory - enjoy the aromas of flowers, visit perfume shops and try to distinguish one smell from another;
- tactile – touch objects and catch yourself feeling emotions while feeling;
- gustatory – try to taste each dish, catch the taste of each ingredient (it’s better to start with simple ones).
Why does a person need
Eidetic memory - what does it mean in psychology, examples
Figurative memory is an alternative to the principle “Repetition is the mother of learning” because it:
- Forms a holistic image, recreating missing sensations;
- Activates all channels of perception;
- Increases self-confidence, helping to remember information without stress, maintains mental health;
- Transforms mental activity into creativity;
- Frees up time for something more useful than repeatedly repeating what you need to remember;
- Reduces learning to understanding;
- Allows a person to do several things at the same time;
- Increases the pace of work;
- Can reconstruct any picture after a quick glance at it;
- Increases the amount of information that a person is able to retain in consciousness;
- Makes the process of forgetting arbitrary.
Important! Images return to an adult a child’s perception of the world and natural memory.
Children's perception of the world
Verbal-logical memory
The verbal-logical type of memory stores information in the form of verbal concepts and numbers. It is responsible for meaning, logic, interaction between elements of verbal information . In the learning process, both figurative and verbal-logical memory are widely used. Figurative memory is inextricably linked with imagination and is in demand in many areas of human life.
We use the verbal-logical type of memory all the time. When we study new material, it is mainly she who works. The development of all other types of memory in a person also depends on the development of verbal-logical memory: it relies on them and plays a leading role in the assimilation of new knowledge.
It is very important to develop the verbal and logical memory of younger schoolchildren, because, as practice shows, if a child does not master the techniques of mental activity and learn to study (forgive the tautology) in the lower grades, then he will fail in the middle and high grades, falling behind in his studies.
The development of verbal and logical memory helps to improve erudition and increase education. The peculiarity of verbal-logical memory is that thoughts do not exist without the participation of language, without words, and neither does their reproduction. We always work with thoughts expressed in words, hence the name - verbal-logical memory.
Peculiarities
Long-term memory - what does it mean in psychology, how to improve it
Distinctive features of figurative memory are:
- Temporary storage of images. The necessary images are saved for a long time, and the unnecessary ones are erased after a day.
- The longer the image is stored, the paler it becomes. After a long period of time, it will be difficult for a person to remember the smallest details of the image.
- Unconscious nature. A person does not need to make an effort to remember something.
Fading images
What this is cannot be demonstrated clearly. Figurative memory is an abstract concept and all processes occur in your brain, but it is quite possible to describe what it is. So, imagine that you are traveling on public transport during the day. Returning home, you remember that you saw a woman in a blue coat, she was sitting next to you. At this point, you may remember other details such as the color of her hair, her facial features, the accessories she wore, and so on. But if you don’t think about it for at least a day, then the next day you will have difficulty remembering those details that seemed obvious to you yesterday. What can we say about what will happen in a week or month. Figurative memory is different in that the images stored in the brain become pale and fuzzy over time. They are unstable and may be fragmentary. For example, in a month you will forget what the girl was wearing in principle, but the earrings that she wore then will be imprinted in your brain. And of course, it is worth noting that each image can deceptively change over time and after a month it may seem to you that the girl was wearing a green coat, although in fact she was wearing a blue one. This is explained by the fact that it is easier for the human consciousness to create something new to replace the lost element of the image than to waste energy on remembering this element.
What is “vivid” figurative memory?
Vivid figurative memory is called eidetic. It is of an emotional nature. Preschoolers have this type of memorization. They can easily describe a friend’s favorite toy when it is no longer in sight, because the vivid image is imprinted in the brain and is of interest to them.
When reciting a long poem by heart, schoolchildren's eyes move as if a book with it was open in front of them. Their mind's eye actually sees the pages of the book where this poem is written. While telling it, they “see” all the drawings that were on this spread of the book.
Children gradually lose their eidetic ability when they enter school. Having mastered other methods of memorization, they less often turn to eidetics. It is replaced by abstract thinking.
Additional Information. Eidetic memorization is based on primary visual perception. It fully corresponds to the physiological development of preschool children and their inherent visual-figurative thinking. From the moment children enter school, verbal and logical thinking begins to actively develop, they learn definitions, rules, and draw conclusions, so eidetics and visual images give way to practical actions, logic and associative memorization.
Photographic memory
As you have already learned, figurative memory includes any memory associated with the senses, since all such information does not come in the form of specific data, but in the form of abstract images. But at the same time, I would like to separately highlight photographic memory, which most likely every person has heard about.
Photographic memory is a subtype of visual figurative memory, but is distinguished by its incredible detail, which is unusual for most people, and the complete absence of pallor and clarity. What does it mean? Imagine how figurative memory works, it was described above. You look at an object and your brain takes a “snapshot” of that object, recording it in your brain. But this photo is initially blurry, and you are unlikely to be able to see all the details in it to reproduce them. If you have a photographic memory, then your brain can take perfect pictures that you can store for a long time without any loss in quality. Naturally, every person would like to have a photographic memory, however, given the fact that many parents do not strive to develop figurative memory in children, and also do not develop their own memory, this concept is now perceived more as a phenomenon than as something to what you can strive for and what you can achieve. But in reality this is not so, and you can independently change the order of things.
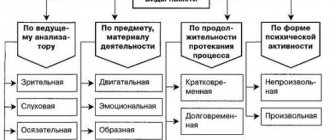
Types of figurative memory
Types of figurative memory
In psychology, the following types of figurative memory are distinguished:
- Visual. This type of memorization is based on retaining the faces of loved ones, advertising posters, and landmarks in the mind.
- Auditory. From all the variety of sounds, this type of memory helps a person choose the important ones to remember: his mother’s voice, the sound of an approaching car, the melody of his favorite song.
- Tasty. This type of memory allows a person to retain long-term ideas about the taste of lemon, pepper, and strawberry.
- Olfactory. Thanks to this type of memory, when a person smells a fire, he dreams of being on a camping trip.
- Tactile. Touch and tactile sensations help a person remember events. People enjoy petting cats because they remember the pleasant softness of their fur.
Visual memory
Visual memory is associated with the storage and reproduction of visual images. Visual figurative memory involves the use of a visual analyzer to process information. For many people, visual figurative memory represents the main type of memorization.
The development of visual memory is especially important for artists, but we all use it widely. By developing imagination, we also help the development of visual memory, because what we imagine is easier for us to remember and reproduce.
When does imagery appear?
The ability to perceive images appears in a child during early childhood. At the age of 1.5-2 years, the baby is able to remember brief figurative information. It is from this moment that long-term memory begins to exist. The baby’s sufficiently developed brain allows him to build simple logical chains and formulate concepts based on images.
Important! Figurative memory is usually called the foundation of all other types of storing information in consciousness. With poorly developed figurative memory, the volume of other types of memory will be small.
Workout
You can independently influence how developed your figurative memory is, even if your parents did not pay much attention to it as a child. To do this, you need to conduct daily training that will allow you to better remember images. How to do it? You need to memorize various images and then reproduce them. Exercises can be very varied. For example, it could be a series of pictures that you need to look at and remember the images, rather than trying to come up with verbal associations. Then you need to reproduce the order of these images. You can also memorize a picture and then try to reproduce as many details as possible. There are a wide variety of games that involve memorizing images, so this can also help you, and photographic memory may soon seem no longer an unattainable phenomenon.
How to develop figurative memory
Methods for developing figurative memory are called mnemonics. To improve figurative memorization, you can:
- Train in memorizing a sequence of geometric shapes, applying the method of associations to them. A square can be associated with a window, and a trapezoid with a skirt.
- You can practice memorizing a number of words that are not related to each other in meaning if you compose a story that contains all these words. In addition, you can try to imagine a drawing or picture where all the words that you need to remember will be present in the form of images. Psychologists say that if the picture is illogical and absurd, this will ensure that the image is firmly imprinted, since people tend to pay attention to the unusual. For example, to remember the words “upside down”, “house”, “loaf”, “tree”, “get”, “woman”, “boat”, “axe”, you can imagine an absurd picture: loaves grow on a tree so that they to get it, the woman stood on the stairs, the ax was drowning in the river, and the boat did not float on the grass.
Nonsense
- When memorizing foreign words, you can associate their sounds with Russian words, giving each an image. For example, the German word “Krawatte” (tie) is similar in sound and spelling to the Russian word “bed”. To remember it, you can imagine a tie with a crib pattern.
- If you need to remember a date, each number can be endowed with a vivid image in your imagination.
- When memorizing any information, you need to try to use all your senses. This will ensure quick memorization and long-term storage of information in memory.
Thus, figurative memory is based on the simultaneous work of both hemispheres. You can force the brain to work at full capacity if you stimulate the simultaneous operation of all analytical systems when perceiving information. In this case, a vivid image is formed in a person’s mind, which is imprinted for a long time without the application of mental effort.
Good memory
Exercises and games
Childhood is the best time to develop imaginative thinking. However, it has been proven that there are no clear boundaries between types of memory. The ability to remember images in an untrained adult is much weaker. But there are exercises for different ages.
Group classes for children 3-7 years old
Most exercises are best done in a group. This is what kindergarten and primary school teachers do. A group can be created by a family or just children they know from the yard.
Popular games and exercises:
- "Throw and catch." Children are divided into pairs. Everyone gets a ball. Task: Throw your ball and catch your partner's ball when a word or number is called (for example, “table” or “one”).
- “Come up with a word.” The presenter (teacher, parent) names the letter to which the word must be named. One person participates in the game, but he can ask the team for help if difficulties arise.
- "Minefield". The presenter draws cages on the asphalt that the children will jump on in the future. It is implied that this is a field where mines are buried. Input and output are indicated. On a piece of paper it is thought out which areas will be mined. Children take turns jumping around the cages, and if someone runs into ammunition, he leaves the distance and stands at the end of the line. Children only learn about danger when they make a mistake. All sections are calculated by trial and error. At the end of the game, all children must pass unhindered from the entrance to the exit.
Individual sessions
The simplest exercise for a little one is to list clothes before getting dressed. The task is for him, without seeing things, to name their names and colors. When transferring, the order of dressing must be observed.
Alone with your child, you can offer one of the following games:
- “Find a mate for the object.” The child is shown an object (for example, headphones). After memorization, the object is removed and 15 pairs of selected objects are shown instead. All of them should differ in size, shape, color, shades.
- "Tall tales." A number of images with different situations are shown. Some pictures tell about real events, others contain obvious signs of fiction. The child identifies and lists invented events.
- “Make a proposal.” 10–12 words are dictated and must be transformed into a meaningful story.