Heredity
By heredity we mean those properties of an organism that are transmitted to children from parents through a certain genetic code. In this case, mainly physiological data is transmitted: the structure of the body, features of functioning, some diseases and inclinations for certain areas of activity (music, drawing).
If we talk about the concept of heredity, then the behavior and development of the individual are determined, first of all, due to the innate characteristics inherent in the formation of the organism. This can be confirmed by the expression “talent will always find its way,” even under negative life circumstances and growth conditions.
It is believed that congenital inclinations or, in other words, heredity are fundamental. However, is this so? There are situations when a person changes over the years and discovers new facets of ability or works on the formation and development of such.
And as for the root cause in physiological characteristics, we can recall the stories of a human baby entering the animal world from the first days of life. For example, the wolf article. It was only in the cartoon that Mowgli was strong and brave; in reality, such children did not have speech or communication skills, and their habits completely copied the animals that were nearby.
Maybe society plays a key role after all, because man is a social being? Let's analyze in more detail the second condition, which has a significant impact on personality development.
Who is a formed personality
Psychology has proven that a person is not born, but rather becomes. However, the question of who can be considered a person remains open. There is still no single list of requirements, description of properties or classification of criteria. But some features characteristic of a formed personality can be identified.
- Activity. It implies voluntary activity, the ability to manage one’s life in any situation.
- Subjectivity. It assumes control over one’s life and responsibility for choice, that is, the role of the author of life.
- Bias. The ability to evaluate the surrounding reality, accept something or not, that is, not be indifferent to the world and your life.
- Mindfulness. The ability to express oneself in public forms.
Habitat
Of course, the environment and communication with people largely determine the personality; the child absorbs the culture, norms and rules of behavior accepted in a certain society. And people of different nationalities and cultures can be radically different. Thus, we come to the conclusion that everything is closely interconnected.
Naturally, family, friends, kindergarten and school have a great influence on a person. The child is taught to certain norms and rules of behavior, and the foundations are laid for the formation of moral principles. Under the influence of the people around them, children learn role-playing games, behavior patterns, absorb and learn a huge amount of knowledge thanks to the school curriculum.
Proponents of the “environment” theory believe that a person, like a blank slate, comes into this world, and parents and environment write and create personality. However, we often hear comments that even in the same family, under equal conditions, children are completely different? This means that the natural principle also has a great influence on the development of personality.
So, there are two basic conditions - the external environment and heredity. The question arises: can a person independently influence his development or does everything depend on external factors?
Formation of human personality
The process of personality formation is the emergence in an individual of historically formed human qualities. What quality will manifest itself in a person depends on several factors.
Personality formation factors:
- Education in childhood and self-education in adulthood
The role of the family in the formation of personality cannot be overestimated. The educational function is the main function of the social institution of the family.
In full-fledged and prosperous families, harmoniously developed individuals grow up. Unresolved childhood problems become factors that prevent a person from developing. The child learns to be a member of society by listening and copying his parents.
Children copy the styles and patterns of behavior, roles, strategies, habitual types of thinking and expressions of feelings of significant adults. Values and ideals, positive and negative (for example, anxiety and suspiciousness) qualities are unconsciously adopted from parents.
Later, parental instructions turn into an “inner voice”, and such moral qualities as conscience, honor, morality and others are formed (or not formed). Becoming an adult, a person uses the knowledge given by his parents about socially approved and acceptable behavior and develops new ones.
- Genetics
People are different because no one person has the same set of genes. A person receives some of the characteristics and components of individuality at birth with a set of genes.
The child experiences and is able to express basic emotions from the first days of life; temperament is determined from birth. Regarding the genetic factor, the role of the family in the formation of personality is no less important than in education. Some mental illnesses are genetically transmitted.
Social influence of reference (significant) groups, relatives, friends, colleagues and other people from the close environment.
- Life experience
Every event that happens to a person affects his inner world, especially if it is a significant incident. Individual experiences can change the course and direction of life. A person develops willpower, character, develops abilities, finds or loses motivation under the influence of events that have happened in his life.
- Mentality and culture
The mentality is influenced by the environment and climate in which representatives of a particular nationality live. Mentality can be defined as the “character” of a people. For example, in southern countries, people are usually active, emotional, and temperamental.
Culture, moral values and morality prevalent in society are instilled in people from birth and guide the process of personality formation. In some cultures, people behave more freely, naturally and casually, while in others, restraint is cultivated, and the need to strictly adhere to the rules of behavior.
Personality formation factors influence it whenever a person finds himself in a new sociocultural environment. The formation of a personality, in essence, is a series of a person’s entry into a new social community and the result of staying in it. How individuality is formed and manifests itself in a particular environment depends on the success of the three phases of development.
Phases of personality development:
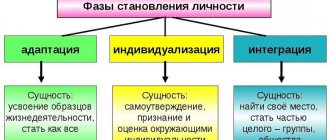
- Adaptation
The formation of personality occurs through its acceptance of norms and forms of activity in a social community. The individual strives and to some extent becomes the same as all other people.
- Personalization
At the second stage, a person, realizing that he is “like everyone else,” searches, finds and shows his individual characteristics, actively strives for personalization.
- Integration
This phase determines not only the formation of personality, but also the development of the society in which a person operates. An individual must successfully harmonize his individuality with society and demonstrate those unique distinctive qualities that are useful for people. By benefiting society, a person develops.
If these stages of personality development are not completed, disintegration occurs and the person is not accepted by society. He is either forced out, or he himself isolates himself from people. The formation of personality during disintegration stops and can be reversed. If a person returns to earlier stages of his development, his degradation occurs.
Personal influence
A person continues to develop throughout life. Naturally, everyone has certain inclinations, innate characteristics that we do not choose - there is a family and habitat that we can partially correct over time. How to be? A strong personality who knows what he wants will always strive for self-development, directing it towards the necessary character traits, abilities, and areas of life. Only through willpower and constant work can one influence these processes.
Moreover, philosophers consider work both literally and figuratively. Labor has made a person a person; in the process of activity and direction of his efforts, the person also develops and acquires certain skills. There is also professional growth, as one of the facets of a holistic personality.
Now psychologists are talking more and more about the personal factor of development and calling for responsibility for one’s life. It is wrong to say that I am the way nature created me and I can’t do anything; this is a passive position in life.
Determinants of development
Determinants are factors and conditions that play a leading role in the development of something. In our case, these are the leading factors in the development of personality.
Heredity
In the article “The Concept of Personality in Psychology: Essence and Structure” we found that the phenomenon of a person as a person implies consideration of both elements: biological and social. The innate characteristics of a person, that is, temperament and body constitution, inclinations, etc., undoubtedly contribute to the formation of personality.
- Initially, theories about personality followed only this approach. It was generally accepted that heredity transmits genes, genes form the hormonal background, which forms the physique and psyche, and they give the shape of personality.
- A little later it became clear that individual characteristics make their contribution, but social factors have a greater influence on personal formation.
Environment
Personality is formed under the influence of the psychology of the group, with whose members it is on an equal footing. The environment influences the formation of personality through:
- culture;
- installations;
- norms and values of family, circle of friends, and other social groups;
- structure of the country.
The social environment shapes character, which is one of the elements of the personality structure.
Interesting fact: it has been scientifically proven that even the birth order of a child plays an important role in the formation of personality. Thus, children born first and subsequently having a brother or sister are more likely to:
- care about social acceptance or rejection;
- hardworking and responsible;
- prone to cooperation and submission to authorities;
- do not seek to break the rules;
- are distinguished by ambition;
- prone to feelings of guilt and anxiety.
Situation
This factor began to be identified as a separate category not so long ago. It is assumed that it restrains both the social and the natural in man. This is a kind of personality regulator.
- It is no secret that some situations dictate the style of behavior and the boundaries of what is acceptable or unacceptable. The more often a person finds himself in a situation of forced behavior, the easier it is for him to constantly show himself in this form.
- However, precisely because of the situational nature, it is impossible to judge a person’s personality in isolation.
Currently, attempts are being made to identify specific situations, their descriptions and the essence of the influence on the individual. But in practice this is very difficult to do. For now, to assess a personality, it remains necessary to have information about his behavior in various situations.
Activity as a condition for personality formation
The main condition for the formation of personality is activity:
- labor,
- educational,
- gaming,
- communication.
Each activity is specific and plays a certain role in human development, meets his age needs, and develops certain components of personality. You can read more about activity in the article “Human activity – what is it in psychology. Types of activities and their characteristics.”
Views on Personality Development
For many years and centuries, discussions have continued on the topic of the conditions for the development of a person’s personality and influencing factors. V. Stern was inclined to the duality of human nature and the balance of biological and social factors as interconnected and inseparable in their influence.
S. Freud put forward another theory, suggesting a confrontation between two main factors in a person - the constant desire for pleasure and the reality of life. Freud in psychoanalysis considers personality at the level of basic instincts that influence life and the formation of personality - a person strives to realize and obtain the necessary pleasures and only morality, the norms of society, restrain him in this direction.
The theory was called "confrontation of two factors." At different times, this idea was supported by A. Adler and K. Jung. There were also psychologists who criticized Freud's assumptions, believing that they led to a strong opposition between the individual and society.
Everything flows and develops. New research has made it possible to discover a new biogenetic law of E. Haeckel and F. Muller, according to which ontogeny (individual development) is a short repetition of phylogeny (development of the species). These stages of development can be observed in the development of the embryo. This theory is quite interesting and partly true - man repeats his ancestors in his development.
Moreover, such reduced copying is not observed for all characteristics of the organism; some properties arise as a result of adaptation to the external environment. In the 30-70s of the 20th century, there was an opinion that a person in his development repeats the development of his species: an infant is at the stage of mammals, at the end of the first year - at the stage of a monkey, in the second year - reaches human development, in adulthood - the level of modern culture .
Quite an interesting theory, although personality development is a rather complex process, and it cannot be characterized by just one parameter. Rather, it is a complex of conditions and factors that inextricably influence a person. At the same time, a strong, stable personality independently shapes himself in the process of life to a greater extent than a weak-willed person who absorbs everything from his environment.
Factors in personality formation
The word “personality” is used only in relation to a person, and, moreover, only from a certain stage of his development. We do not say “the personality of a newborn child.” Actually, everything is already a personality... But not yet a personality! A person becomes a person, he is not born as such. We do not talk seriously about the personality of even a two-year-old child, although he has acquired a lot from his social environment.
Personality not only exists, but is also born for the first time as a “knot” tied in a network of interconnectedness. Indeed, there is not a personality in the human body, but its one-sided projection onto the screen of biology, carried out through the dynamics of neural processes. The development process occurs as the perfection of a human being, a biological being. First of all, biological development, like development in general, is determined by the factor of heredity.
A newborn carries a complex of genes not only from the parents, but also from their distant ancestors, i.e. has its own rich hereditary fund, unique to it, or its own credit-predetermined biological program, thanks to which its individual characteristics arise and develop. This program is implemented naturally and harmoniously if, on the one hand, biological processes are based on sufficiently high-quality hereditary factors, and, on the other hand, the external environment provides the growing organism with everything necessary for the implementation of the hereditary principle.
Patterns of personality development
The development of personality, its formation is an interconnected and holistic process, which is characterized by stages of personality development. Let's think about the question: what are the patterns of personality development? Why does personality develop and how does it happen?
So, the main patterns of personality development:
- Age factor - the younger a person is, the faster his physical development occurs. Over time, the process slows down. There are similar observations about spiritual development; the younger a person is, the faster his spiritual growth occurs.
- Therefore, we often hear that young and old, children understand old people very well, they can quickly understand the story, show interest, absorb knowledge and feel the state of mind of the narrator.
- Uneven development is observed in the presence of certain periods of growth, which we observe in the development of our children. The body does not develop constantly, it seems to us that the child suddenly begins to grow at a certain stage, these are the physiological characteristics of the body. The same can be said about spiritual development - there is unevenness
At different times, a person’s properties can change and be at different levels of development. In life there are more favorable conditions for personal development and less favorable ones. However, these conditions will be temporary. What influences a person?
Of course, communication with the outside world and people, spiritual development occurs in the knowledge of the world and oneself. There are also leaps in the development and awareness of processes due to stressful situations that make fundamental changes in a person’s personality. “Every cloud has a silver lining,” people say. Even in times when the world seems to be collapsing, think about what you will build from scratch.
3. Fluctuations in development - the organs of the human body develop each at their own pace. This is reflected in mental and nervous processes. Basically, differences between people and the level of development are manifested in behavioral aspects, thinking, intellectual level, social and moral development.
Psychological essence of personality
The word “personality,” like many other psychological terms, is used in everyday communication along with other terms. Therefore, in order to answer the question: “What is personality?”, it is first necessary to distinguish between the concepts of “personality”, “personality”, “individuality”, “individual”.
On the one hand, man is a biological being, an animal endowed with consciousness, which has language and the ability to work; on the other hand, man is a social being, he must communicate and interact with other people.
A person is one and the same person, but is considered only as a social being. Speaking about personality, we deviate from its biologically natural side. Not everyone is an individual. It's probably not without reason that you hear "real person!" from one and “no, this is not a person” from the other.
Individuality is the personality of a particular person as a unique combination of unique mental characteristics. Man is a single representative of the human race, a specific bearer of all the social and psychological characteristics of humanity: mind, will, needs, etc. In this case, the term “individual” is used to mean “a specific person”. This way of asking the question does not take into account the influence of various biological factors (age, gender, temperament) and differences in the social conditions in which a person lives. In this case, the individual is considered the starting point for the formation of personality from the initial state of human feilogenesis; personality is the result of the development of the individual, the most complete embodiment of all human qualities.
Some scientists believe that the human psyche is biologically determined, that all aspects of personality are innate. For example, character and abilities are inherited, such as eye and hair color.
Other scientists believe that everyone is in relationship with others. These social relationships form the human personality, that is, a person learns the rules of behavior, customs and moral standards accepted in this society.
Is it possible to ignore and neglect the biological nature of man? No, its biological, natural nature cannot be ignored. Of course, for the spiritual development of a person, appropriate natural, biological characteristics are absolutely necessary. The human brain and nervous system are necessary for the formation of human mental characteristics on this basis.
Conditions for the development of human personality: motor skills and child development
For the spiritual development of a person, certain stages are distinguished - age limits characteristic for the acquisition of certain qualities. It is customary to call such periods “sensitive”. Based on research data, psychologists can determine whether a child is developmentally appropriate for his age or diagnose developmental delay.
Thus, for the development of speech, the optimal period is considered to be 1-2 years, and intellectual development most actively occurs before the age of 13. The basis of such periods is that the maturation of the nervous system and brain occurs not constantly, but in periods. Everything in the body is formed gradually and acquired experience plays a very important role.
Now there are special schemes of work to help children who have developmental delays, based on the complex use of treatment by a neurologist, sessions with a psychologist and speech therapist. As a rule, speech development is associated with the maturation of the cerebral cortex, and there are special methods to speed up such processes (medicines, sensory training, Montessori games).
With physical retardation, it often happens that children begin to walk later; there are also programs - massage, swimming, exercise therapy. It is very important to monitor these moments and help children develop comprehensively in time.
Qualities
Stability of qualities - as a result of personality development, a person acquires stable and permanent mental qualities, but plasticity is also preserved. The complexity of these processes comes down to the fact that a person acquires character traits and at the same time there is always the possibility of changing them and improving them under the right circumstances of life. Thanks to the plasticity of the nervous system, education is possible.
And besides, compensation occurs due to stronger personality traits. So, for example, there are children who grasp knowledge on the fly without working too hard, while others achieve results through hard work, which compensates for their weaker memory.
Every person has strengths and weaknesses, and the strong ones very often override the weak ones and allow them to successfully cope with life situations.
Integration
Personal development occurs as a merging of different spheres - intelligence, spiritual development, emotional component, spirituality. Each sphere integrates its own properties. So, emotional - feelings, intellectual - mind. Over time, a person’s psyche hardens and strengthens; in adulthood, a person reacts more calmly to life’s difficulties, with a sufficient level of development. In addition, a worldview and understanding of life processes are formed.
At every stage of life, a person has a dominant activity, which has a great impact on the development of personality.
During school years we study, acquire knowledge and communication skills. As adults, we learn in the process of interaction in the family, communication with loved ones, as well as the work team and profession leave their imprints, the professional development of the individual is formed. All this contributes to the formation of mental qualities and personality traits.
Afterword
Personal development is a difficult and contradictory process that continues throughout life. A stop in development is fraught with degradation and disintegration of personality.
Personality formation is a purposeful and organized process. At first it is organized by the parents and the child’s environment, and later by the person himself and the environment.
Thus, the formation and development of personality occurs in the process of human interaction with the outside world and people. However, in order to become a person, you need to learn to set boundaries between the understanding of “yourself” and “not yourself.” What does it mean:
- participation in the life of society, but not total dissolution in it;
- the ability to resist and maintain individuality.
Recently, it has been important to talk not only about the creative element of personality, but also about the creative principle, which means “being the creator of life.”
The question of the boundaries of the influence of the biological and social in a person during the development of personality has not yet been settled. Gene research continues. Scientists do not rule out that in the future some phenomena recognized as acquired will actually be transferred to the category of hereditary ones.
A person’s personality is formed and developed as a result of the influence of numerous factors, objective and subjective, natural and social, internal and external, independent and dependent on the will and consciousness of people acting spontaneously or according to certain goals. At the same time, the person himself is not thought of as a passive being who photographically reflects external influences. He acts as the subject of his own formation and development.
Bearing in mind that the human personality is formed in its unity by genetic and social programs, we note the existence of subjective
and
objective
conditions for the formation of personality, its improvement in the course of life, as well as as a result of development and upbringing.
Biological factors
: heredity (transmission from parents of psychophysiological properties and inclinations: hair color, eyes, skin, temperament, speed of mental processes, as well as the ability to speak, think, walk upright - universal human characteristics and national characteristics) largely determine the subjective conditions influencing the formation personality. The structure of the mental life of the individual and the mechanisms of its functioning, the processes of formation of both individual and integral systems of properties constitute the subjective world of the individual.
A person is a living organism, whose life is subject to both the general laws of biology and the special laws of anatomy and physiology. But it is not personality traits that are inherited, but certain inclinations. Inclinations are a natural disposition to a particular activity. There are two types of inclinations: universal (the structure of the brain, central nervous system, receptors); individual differences in natural data (features of the type of nervous system, analyzers, etc.).
Natural features determine different ways and methods of formation of mental properties. They can influence the level and height of a person’s achievements in any area. Moreover, their impact on the individual is not direct, but indirect. No congenital feature is neutral, since it is socialized and imbued with personal attitudes (for example, dwarfism, lameness, etc.). The role of natural factors varies at different age stages: the younger the age, the more natural characteristics affect the formation of personality.
Natural characteristics are important prerequisites, factors, but not driving forces in the formation of personality. The brain as a biological formation is a prerequisite for the emergence of consciousness, but consciousness is a product of human social existence. The more complex an education is in its mental structure, the less it depends on natural characteristics. personality freedom philosophy responsibility
But the influence of biological factors is always mediated by training, upbringing and social conditions. The formation of personality occurs in unity with the objective conditions that influence it. Human mental activity, being determined by external conditions, develops according to its own specific internal laws. [5, 15c.] “Ideas, feelings and beliefs,” said G.V. Plekhanov, “are combined according to their own special laws. But these laws are put into action by external circumstances that have nothing in common with these laws.”
Social factors
(they are also “external circumstances”): socio-economic living conditions, family and purposeful upbringing form a system of objective conditions that influence the formation of personality. It is the environment - the entire social reality surrounding a person, in the conditions in which his development and formation of personality takes place - that is the objective condition for the formation of his personality, determining purely human inclinations - thinking and speech. Objective conditions make it possible to develop human inclinations through communication with people. Because if you isolate a child after birth from society, he will have character, temperament, abilities and a number of other personality properties, but he will not be a person, since he will develop outside of human relationships, human society.
Socialization
represents the process of personality formation, the gradual assimilation of the requirements of society, the acquisition of socially significant characteristics of consciousness and behavior that regulate its relationship with society. Socialization of the individual begins from the first years of life and ends by the period of civil maturity of a person, although, of course, the powers, rights and responsibilities acquired by him do not mean that the socialization process is completely completed: in some aspects it continues throughout life.
- 1) the impact of society on the individual in the process of upbringing, education, communication with parents, peers, in the process of using mass media sources of information;
- 2) own personal activity, manifested both in the deobjectification of phenomena and objects, and in their objectification.
Indeed, a social individual does not receive his social content hereditarily and is forced to acquire it in ontogenesis and throughout his life. Conventionally, the process of socialization has three periods:
- - primary socialization, or socialization of the child;
- - intermediate socialization, or socialization of a teenager;
- - stable, holistic socialization, that is, the socialization of an adult, basically mature person.
Being an important factor influencing the mechanisms of personality formation, socialization presupposes the development in a person of his socially determined properties (beliefs, worldview, ideals, interests, desires).
Upbringing
also acts as an important factor in personality development. It ensures the socialization of the individual, programs the parameters of its development, taking into account the versatility of the influence of various factors. Education is a planned, long-term process of specially organized life for children in the conditions of education and upbringing. It has the following functions:
- — diagnostics of natural inclinations, theoretical development and practical creation of conditions for their manifestation and development;
- — organization of educational activities for children;
- — the use of positive factors in the development of personality traits;
- — content of education, means and conditions of the social environment;
- — impact on social conditions, elimination and transformation (if possible) of negative environmental influences;
- - the formation of special abilities that ensure the application of forces in various fields of activity: scientific, professional, creative-aesthetic, constructive-technical, etc.
So, a person always lives and acts as part of a certain nation, class, social group, collective and shares with others the material and cultural conditions of life and, which is quite natural, the psychology of the social group of which he is a member. This circumstance determines what is special in the mental appearance of the individual (national character traits, needs, interests, attitude towards various aspects of social life).
Psychological moment
Personality formation is determined by the microenvironment - part of the environment and the conditions in which a person lives directly (for example, family). The microenvironment objectively influences the mental appearance of a person. As a consequence of this influence, individually unique traits are discovered that reflect the specific life path of an individual.
Consideration of the question of the influence of objective conditions on the formation of personality will be incomplete without noting the decisive importance of social heredity in human development.
Each person represents, to one degree or another, the entire human race; its human, bodily organization embodies the result of the development of not only the human race, but also its closest ancestors. The universal human natural organization of personality was formed according to the laws of biology, and therefore acts as a socially determined human nature.
A person inherits from previous generations the tools of labor and experience in organizing production, material and spiritual values, traditions, etc. By mastering all this, he joins the universal and national culture, becomes capable of work, creative development of the inheritance left to him.
Thus, personality formation is a complex, long-term process determined by socialization, in which external influences and internal forces, constantly interacting, change their role depending on the stage of development. The basis of personality is the totality of its relations to the world, which are social in nature, but relations that are realized; and they are realized by its activities, or more precisely, by the totality of its diverse activities.
—>
1. Anthropological features, races. The legacy of the fathers leaves its result. The black race of people is far from perfect. They have less cranial capacity than representatives of the white race.
2. Conditions for conception are very important. Even if a child has good heredity, but the parents had bad habits, there will be a delay in development.
3. Economic conditions. He paid special attention to nutrition. Improper or insufficient nutrition will lead to physical weakening of the body. The person will quickly become exhausted and this will disrupt the normal development of the individual.
4. The most important condition for personal development is the presence of social activity. There cannot be complete development of personality if there is no social activity. Countries where social activity is not in demand give rise to passive individuals.
5. Factor of education and training. How and what to educate, what is hygiene of physical and mental activity. First of all, it is important to get used to systematic work. Secondly, this is the development of independent thinking. Third, strength of character.
This is how the formation of an active, relatively independent person who can defend his positions occurs.
40. V.N. Myasishchev. Personality as a system of relationships.
Vladimir Nikolaevich Myasishchev is a very bright personality in psychology. Developing the ideas of A.F. Lazursky about the attitude of the individual, Myasishchev builds his own concept of the individual, choosing the concept of attitude as the central element.
The attitude of the individual is an active, conscious, integral, selective connection of the individual based on experience with various aspects of reality. According to Myasishchev, relationships are objective and subjective . Relationships are objective due to the fact that between people there are different statuses, different distances, different levels of education. The objective factor of relationships can change, but the subjective factor of relationships is in the power of each person.
Relationships are selective , because people have different relationships to different spheres of reality. This system of relationships is never the same. Myasishchev says that, as many phenomena in life, there are so many relationships. We describe the most important ones that are typical for each person. These are relationships to oneself, to people, to activities, to the world.
Relationships are conscious, although the degree to which relationships are conscious may vary. Here is a hint of unconscious phenomena in the system of relationships.
An integral characteristic, because if a person is included in a new reality, then new relationships are formed. If a person enters into a relationship, then the entire personality as a whole is transformed. One attitude can transform an entire personality structure. That is why this is an integral characteristic based on experience with various aspects of reality.
Relationships come in varying degrees of generality - from the subject’s connections with individual parties or phenomena of the external environment to connections with all reality as a whole.
According to V.N. Myasishchev, attitude is a system-forming element of personality . The personality itself is presented as a system of relationships. Personal relationships are formed under the influence of social relations by which the individual is connected with the surrounding world in general and society in particular.
From the moment of birth, a person is forced to enter into social relations. First, with the mother in a direct emotional relationship. Then with his loved ones, peers, educators, teachers, and so on. Relationships, refracted through “internal conditions,” contribute to the formation of subjective human relationships. These relationships express the personality as a whole and constitute the inner potential of a person. They are the ones who manifest, that is, they reveal for the person himself his hidden, invisible capabilities and contribute to the emergence of new opportunities. The author especially emphasizes the regulatory role of relationships in human behavior.
In the structure of the relationship. V. N. Myasishchev identifies the sides:
"emotional"
“evaluative” (cognitive, educational) and
· “conative” (behavioural).
Each side of the relationship is determined by the nature of the individual’s life interaction with the environment and people, including various aspects from metabolism to ideological communication.
The emotional component contributes to the formation of the individual’s emotional attitude towards environmental objects, people and himself. The emotional side of a relationship is expressed through affection, love, sympathy and opposite feelings - hostility, enmity, antipathy.
The cognitive component of relationships contributes to the perception and evaluation (awareness, understanding, explanation) of environmental objects, people and oneself. The cognitive or evaluative side is manifested in the moral values accepted by the individual, developed beliefs, tastes, inclinations, and ideals.
The behavioral (conative) component contributes to the choice of strategies and tactics of a person’s behavior in relation to environmental objects, people and himself that are significant (valuable) for him. The behavioral side of the relationship is expressed through needs, since the need itself, pointing to its object, thereby gives an indirect indication of the way to achieve this object.
Relationships are divided into types: positive and negative, both from the point of view of emotional and rational assessments.
The process of personality development is determined by the course of development of relationships. V.N. Myasishchev points out that the initial period of increasing selectivity of human behavior is characterized by pre-relationship , in which there is no element of consciousness. Something that a person is not aware of prompts him to action (unconscious motivation of behavior).
Subsequently, a 2-3 year old child develops a pronounced selective attitude towards parents, educators, and peers.
At school age, the number of relationships increases, extra-family responsibilities, academic work, and the need to voluntarily control one’s behavior arise.
At high school age, principles, beliefs, and ideals are formed.
V.N. Myasishchev separates the concepts of “attitude” and “attitude” (each of them claimed to be a comprehensive psychological category).
V. N. Myasishchev considers both relationships and attitudes as integral mental formations that arise in the process of individual experience. The attitude is unconscious and therefore impersonal, and the attitude is conscious , “although, as V.N. Myasishchev emphasizes, its motives or sources may not be realized.” Another difference between attitude and attitude is that attitude is characterized by selectivity, and attitude by readiness.
Thus, attitudes and attitudes are mental formations that are distinct from each other. Since the concept of attitude is irreducible to other psychological categories (attitude, needs, motives, interests, etc.) and cannot be decomposed into others, it represents an independent class of psychological concepts.
Relationships are closely related to various substructures of personality. The substructures of personality are temperament, character, abilities and self-awareness. All of these substructures can be revealed from a relational perspective. For example, temperament as a natural texture of relationships will clearly manifest itself from the position of relationships, or be masked through the prism of relationships. If a person is slow due to his natural properties, and his activity requires him to react quickly, then, provided he has a positive attitude towards the chosen activity, he will develop an individual work style that masks the slowness.
Character is a system of relationships and the way a person implements them. This is a fixed ratio in typical situations.
A person’s abilities are in a natural relationship with inclinations, which represent the driving force for the development of abilities. An inclination is an attitude towards a certain type of activity and a need for this type of activity.
Myasishchev V.N. became the first to openly raise the question of personality structure. “A structural characteristic illuminates a person from the point of view of his integrity or fragmentation, consistency or inconsistency, stability or variability, depth or surface, the predominance or relative insufficiency of certain mental functions . This fundamental position, apparently, determined the specifics of his views.
On the structure of personality, where there are no separate components, but there is a psychological reality - an attitude that closes all other psychological characteristics of the personality. It is the attitude, according to V. N. Myasishchev, that is the integrator of these properties, which ensures the integrity, stability, depth and consistency of a person’s behavior. The development of personality involves not only a change in relationships, but, first of all, a change in its structure, that is, a change in the relationships between its individual elements.
The principles of relationship psychology formed the basis of the pathogenetic concept of neuroses developed by Myasishchev. Neurosis is interpreted as a personality illness caused by circumstances of significance in the system of its personal relationships.
41. B.G. Ananyev. Basic parameters of personality research.
Ananyev Boris Gerasimovich (1907-1972) is an outstanding Russian psychologist. He began his scientific activity as a graduate student at the Brain Institute during Bekhterev’s lifetime. He is the founder of the Leningrad psychological school. He proposed one of the most popular approaches to studying humans in Russian psychology. It should be emphasized that he developed a fundamentally new methodological approach to the study of the human psyche.
Ananyev identifies four main concepts in the system of human knowledge: the individual, the subject of activity, personality and individuality.
1) AN INDIVIDUAL is something natural in a person, the biological essence of a person, a representative of the species Homo Sapiens. In this case, the biological essence of man is emphasized.
Man as an individual has certain properties. Ananyev distinguishes primary and secondary properties. He considered the properties inherent in all people to be primary.
Sources used:
- https://psychologist.tips/800-formirovanie-i-razvitie-lichnosti-protsess-faktory-usloviya-etapy.html
- https://studwood.ru/2038158/psihologiya/usloviya_formirovaniya_lichnosti
- https://studopedia.ru/10_7290_usloviya-razvitiya-lichnosti.html
Controversy and progress
Contradictory personality is a quality that Freud and other psychologists talked about. Man is structured in a rather interesting way and is constantly in interaction with the world around him. At the same time, every day he makes decisions and makes life choices, and it happens that he goes against the grain of his immediate environment in his judgments and enters into confrontation.
We can also recall situations when we have an internal conflict and struggle between different parts of the personality - an adult, a child, a teacher. Or maybe this is a conflict between good and evil, it’s hard to say, the main thing is that in these moments the truth is born, it is important to find yourself and form the necessary qualities.
The desire for progress - it is natural that everyone wants to achieve success in life; in the process of overcoming life's obstacles, on the way to the goal, character is strengthened and the strong-willed qualities of the individual are formed. All life situations are lessons that we go through, and as a reward we receive a new “I”, with new and even better qualities.
Self-development
Personal self-development - we constantly improve ourselves by working on our inner world, subordinating mental processes and emotions to our will, improving character traits. Such work can be done either independently or through special training. Each person determines for himself how it is easier for him to develop. The main thing is the desire to achieve new results, constantly work on shaping your personality, and search for the necessary information and knowledge.
Development can also act as a protective function. A person is constantly developing, both physically and spiritually, this is necessary for survival in our world. A successful life requires certain qualities, such as immunity to fight diseases, willpower to achieve results, and patience is an important weapon for conquering peaks. Naturally, for a full life we need: good health, high intellectual and spiritual qualities, which we develop in the process of life, voluntarily or involuntarily, under the influence of life circumstances.
Thus, we have examined the patterns of personality development, and now we better understand the cause-and-effect relationships. Of course, our development is influenced by many factors, the conditions for the development of a person’s personality, and yet we are happy that we can correct our life and development through our own efforts.
Topic: Personal growth
Development criteria
From the above, we can highlight the criteria for personality development, or personal growth:
- strengthening subjectivity;
- integrity and integration into the world;
- productivity growth;
- development of mental (spiritual) qualities and abilities.
A characteristic feature of a mature personality is overcoming egocentrism and acquiring a broad identity (the ability to identify oneself with the world, society, situations, nature; a sense of community and understanding).
- In children and adolescents, personality development is assessed according to the characteristics of socialization and reflection.
- In adults - by the ability to self-actualize, the ability to accept responsibility and stand out from society, maintaining a connection with it.