What alternatives to Maslow's pyramid exist today?
Before we begin a detailed study of the hierarchy of needs according to Maslow’s pyramid, it is worth saying that there are other approaches to assessing human behavior and the incentives that force him to be active. Here are just a few of them:
- Alderfer's theory. It is based on Maslow’s pyramid, but tries to make the system more generalized and simpler, reducing all human needs to the following: the need to exist, the need for connections with others, the need for constant growth;
- McClelland's theory. This researcher believed that in the hierarchy of human needs, only the highest motives are the most important: the desire for power, success, involvement in great deeds and achievements;
- Herzberg's theory. A more applied theory, which is aimed at analyzing people working in a business. Shows that the higher the motivation of employees, the more non-standard tasks they solve, the more responsibility they have for their work, and the more they receive decent remuneration. Otherwise, motivation deteriorates sharply.
There are other theories, but we will look at the 5 steps of Maslow’s pyramid of needs and try to figure out whether all this works today or not.
Functions
There are three stages that determine a person's needs. First, a need is formed when a person has a certain attitude, feelings and emotions towards external stimuli. Then motivation is built, and the third stage is awareness of the need. At the same time, a person experiences negative or positive emotions, specific thoughts, goals and plans appear.
There are two main functions:
- Signal. When a need arises, a person feels a shortage, thoughts change, and the state becomes more restless until the need is satisfied.
- A driving need. The individual begins to act in his own interests. Activity and work activity manifest themselves, and a person’s behavior changes radically.
In fact, the classification of human needs closely intersects with functions. However, only a few species have been described. Many psychologists count more than 130 human needs. This is a lot, but people still strive to live better and satisfy their needs with both material and spiritual benefits. The same can be said about the needs of society.
Authorship
Abraham Maslow developed his theory on his own, spending a lot of time reading other authors on related topics. As a child, he was one of the best students in his school, later he entered law school in New York, but after his first year he left this institution. Later he moved to Cornell University, where he began studying psychology under the guidance of Edward Titchener.
Maslow's classification of needs was the fruit of many years of work that he conducted independently. But it is worth noting that the psychologist’s work was influenced by many famous personalities whom he knew personally: John, Watson, Alfred Adler, Margaret Mead, Erich Fromm and others.
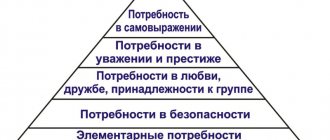
Need levels table
In general, human needs according to Maslow can be expressed in the following table:
| Physiological needs | The need for food, shelter, rest, sleep, water, etc. |
| Need for security | Stable environment around, personal safety, good relationships with others |
| Need to belong | A person wants to be part of society, family, friendly team, etc. |
| Need for recognition | Normal self-esteem, the need for respect from others |
| Self-expression | The highest level of development of needs, involving creativity, scientific activity, personal achievements in something |
Typically, this data is depicted in the form of a pyramid, so it is more visual and understandable.
Structure of Maslow's pyramid of human needs
As shown above, Maslow’s pyramid of human needs consists of 5 parts. Its lowest parts are responsible for basic, biological phenomena that simply ensure our existence. As the lower levels are satisfied, higher needs and spiritual impulses come into play.
Physiological needs
The very first step of the pyramid is dedicated to physiology. This group of needs includes all things that are determined by biology in a person. This includes the need to eat, be able to drink clean water, and maintain one’s physical existence in comfortable conditions. Physiology also includes sexual relations and impulses, normal sleep, etc. Until a person is satisfied with these things, he constantly thinks about them and needs exactly this.
Only when a person is not bothered by unsatisfied passion, hunger, desire for sleep, physical pain in the body, etc., can he move to a higher level of needs and discover in himself a desire for more.
Safety
Maslow included security issues as a separate category of needs. Security is meant in a broad sense: a full range of phenomena that ensure the stable existence of a person. What is meant by the need for security:
- No visible likelihood of injury or health problems;
- Avoiding dangerous conflicts with other people, which can lead to injury, imprisonment, etc.;
- Separately, the scientist attributed to security the need for a person to belong to a family, group, social stratum of the population, since all this helps to stabilize life.
Eliminating any danger that could cause serious trouble is the need for safety.
Social level - love and belonging to something
Man is a social being and can only exist surrounded by his own kind. A person’s needs for communication, work and leisure with like-minded people, the desire to have his own family, a couple for sexual and social life, an adequate moral and psychological environment around - all this is also important for each of us. It is enough to have serious troubles in at least some of this and the comprehension of other, higher needs may turn out to be closed to the individual.
At this stage we are not talking about socialization of the highest type - the desire to create, change the world, etc. The conditions of basic socialization are considered: the presence of a social circle, like-minded people, close people. If a person, say, is not part of a team or group, and is isolated from society, then he may experience great discomfort about this, suffer and become isolated on these problems. Even people with serious problems, disabilities, and blind people try to form their own groups, support each other, and communicate.
Prestige and reputation – respect and recognition
The next thing that Maslow’s pyramid reveals to us is a person’s needs in terms of developing a reputation and occupying a prestigious place in society. At this level the following stands out:
- The need for self-respect. A person is not hungry, dressed, shod, in a warm home, he has a social circle and work, but then the need for respect and self-esteem appears. We cannot agree to work all our lives in one capacity in one place - we want career growth, we do not want to constantly receive the same amount of salary - we want bonuses and promotions, we will not agree to work in an economically advantageous place, but where they do not respect us, they try to humiliate us – we need the respect of others;
- Recognition, achievements, positive opinions of others about us. Almost every person wants to be respected, to be praised for his work, to be spoken of well as a specialist, etc. if this is not the case, then even financially profitable work or actual achievements in some way are not perceived so joyfully and brightly;
- At the top of the pyramid is the highest level - needs of the spiritual type. Here the author of the theory highlights such important things as spiritual search, knowledge of the world around us, self-expression and self-realization of existing talents, natural abilities, and positive inclinations.
Separately, at the highest level, Maslow's theory mentions the concept of self-actualization. This term refers to the most complete development of one’s talent and abilities, which is only available to a person. The discovery of all talents and abilities in oneself, their development to the maximum point, is available, according to Maslow himself, to only about 2% of all people. Self-actualization in the supplemented pyramid of 7 steps is placed separately from the needs of the spiritual type.
Creation
If a person has successfully satisfied all his previous needs in the specified hierarchy, then he has a need to create - create something new, engage in music, aesthetic development, write, enjoy nature, etc. Creativity stands out separately in the list of the highest human needs, since it reveals a unique personality ability to create something new, to be able to empathize with works of art.
Aesthetic level of needs
Almost all of the higher needs that are addressed at the top of the pyramid relate to creativity and aesthetic feelings. Only after a person covers the lower needs, is no longer distracted even by achieving success, a career, the approval of others, since he deserves them in full, only then the heights of comprehension of the aesthetic level of perception of the world are revealed to him. At this stage, a person sees beauty around him, harmony, learns to enjoy music, images and create independently in any area.
Spiritual level of self-actualization
Self-actualization has already been discussed below - this is a person’s desire to reveal all his strengths in maximum manifestation. Maslow himself and other later researchers believed that only an insignificant 2-5% of people could achieve self-actualization in a more or less complete form. All the efforts of the majority of the planet's population are aimed at survival, material wealth, pleasure, satisfying the need for respect, fame, but very, very few reach self-actualization.
Maslow's 8-step pyramid model
There is also Maslow’s 8-step pyramid, the 7 levels remain the same as in the 7-step pyramid, but another higher level is added - transcendental needs. Researchers point out that when a person has already achieved the discovery of all his talents and skills, earned money and fame, he has a new task - to comprehend the highest meanings of life, existence, and God. Unity with nature, mystical practices at a deep level of consciousness, deep religiosity belong to this 8th stage of transcendence. In practice, this level is available to a few, and sometimes to people who were not too worried about the task of covering previous levels of needs.
Resources and factors of production: land, labor, capital and entrepreneurial ability
The real economy faces two major problems: first, people's needs are, in general, unlimited; secondly, the resources that society has to satisfy them are limited.
Resources are a set of natural, material, social and spiritual benefits that can be used in the process of creating goods, services and other values.
The following types of resources are distinguished:
1. Natural resources – natural forces and substances of nature potentially suitable for use in production, among which a distinction is made between inexhaustible (for example, solar energy) and exhaustible (renewable and non-renewable).
2. Material resources - all means of production created by man, which themselves are the result of production.
3. Labor resources – population of working age.
4. Financial resources – funds that society is able to allocate for production.
The resources involved in the production process are called factors of production.
In economic theory, there are various classifications of factors of production. For example, representatives of Marxist political economy identify such basic factors of production as means of production and labor. Labor power acts as a personal (subjective) factor, means of production – a material (objective) factor. In this case, the leading factor of production is labor.
French economist of the 19th century. J.-B. Say put forward the theory of the “three factors of production,” according to which three factors of production participate equally in production: labor, land, and capital. The distribution of production results (income) is carried out equally between the owners of each factor of production. Currently, economic science identifies four factors of production, including, in addition to the three traditional ones, the factor of entrepreneurial ability. In the context of the development of scientific and technological progress, information is also identified as one of the important factors without which a modern economy cannot operate effectively.
The labor factor is understood as any mental and physical effort that is exerted in the course of economic activity.
According to forms, mental labor and physical labor are distinguished; by level of qualification - unskilled (not requiring special knowledge or skills), qualified (requiring additional knowledge), highly qualified labor (requiring high professional training, deep theoretical knowledge). The results of labor are reflected in productivity and labor intensity. The quantitative assessment of labor is wages, which are formed in the labor market as a result of the interaction of sellers and buyers of labor.
Capital usually refers to investment resources used in the production of goods and services. It includes stocks of material goods, means of production and money, as well as abilities, education, etc. Based on the duration of use, capital is divided into fixed and circulating capital. Fixed capital is capital used in several production cycles (means of production, buildings). Working capital is capital used in one production cycle (raw materials, supplies, cash). Capital is subject to physical and moral wear and tear. The depreciation of capital is called depreciation.
Land is a natural factor of production, which includes, in addition to the land itself, natural resources, mineral deposits, forests, etc.
Entrepreneurial ability is an initiative independent activity aimed at making a profit, associated with risk, responsibility for decision making. Entrepreneurship is a factor that unites and organizes all other factors of production.
Theory and practice
In theory, everything looks quite interesting. Maslow's coherent theory of needs is very logical; it really describes reality and nature well for most people around. But over time, there were many critics of this theory, since in practice it began to increasingly diverge from reality.
The theoretical calculations of A. Maslow began to be actively applied in practice. Here are just a few areas of activity where they were adopted:
- Psychology and sociology. Researchers began to look at society and typical human needs with greater understanding and began to see patterns in all this;
- Maslow's theory is applied in human resource management systems to increase employee motivation and increase their ability to work and efficiency;
- There are many tips on how you can use Maslow’s pyramid in marketing, where it allows you to attract attention and encourage people to make purchases and orders.
Also, the theory continues to interest theoretical researchers who are trying to clarify and supplement it to this day.
Controversial sides of the pyramid and criticism
Psychologists of many directions actively criticize Maslow’s system, finding in it many discrepancies with real life and specific people. Here are the main statements of critics on this issue:
- History knows a lot of cases when the dissatisfaction of basic needs did not make a person more down-to-earth, but, on the contrary, stimulated him to act and create, write songs, develop, comprehend nature and God;
- Each person has their own level of satisfaction with things. One has enough of the meager lunch, another suffers from the inability to eat in the most expensive restaurant in the city;
- The inability to recognize Maslow’s theory as 100% working is also associated with the fact that many people show insatiable aspirations and cannot satisfy the most basic needs, wanting more and more.
Often brilliant people were poor, physically weak, unhappy and despised by society, but this did not prevent them from remaining in history.
Need for achievement in McClelland's theory
The theory of acquired needs from the American psychologist David McClelland almost does not consider the primitive needs of a person. The scientist devoted his work to the study of motivational levers that force objects to engage in a given activity, and to the study of the desire of some people to prevail over others.
In the course of his work, the scientist concluded that only an individual who makes efforts to satisfy his higher-order needs and moves steadily in this direction is able to develop with increasing efficiency. Each successive achievement of an object is based on the experience gained during the period of overcoming the previous stage.
Gradually, a person who has chosen the right tactics for his dynamic growth develops the so-called step length. This means that all the goals that he sets for himself do not exceed his real capabilities and do not require him to strain his strength, and after achieving them, a person can calmly and without pause move on. People of this order are capable of responsible decisions, and the individual tasks that they undertake are always carried out with high precision.
Further research by the psychologist showed that the described need for achievement is characteristic not only of individuals, but also of certain societies. Groups united by high aspirations and having a clear goal developed successfully in the economic and educational spheres, while societies with a low need for results had a very weak internal structure.
Primary and secondary needs
Many researchers agree with Maslow that all human needs can be divided into primary and secondary:
- Primary: food, sleep, physical health, freedom of movement, etc. Primary needs according to Maslow are necessary for everyone as a basic condition for further development;
- Secondary needs open up in some people who have solved problems of the primary level. This is creativity, doing the arts, enjoying nature, music, etc. The highest level of secondary needs is self-actualization.
Also, for a small number of people with realized self-actualization, the need for transcendental development opens up - unity with nature, the Creator, a higher understanding of the meaning of life and other things that are far from mere mortals.
Complicity and dominion according to McClelland
The next point in the theory of acquired needs McKelland calls complicity as the need to establish friendly contacts with those who appeal to the object. The higher a person’s need for the approval of others, as well as for the good attitude of everyone around him, the more developed his communication abilities are and the easier it is for him to make new acquaintances. Intolerance of loneliness can be an acquired or original quality of a person, but the ability to form a friendly environment around oneself comes to a person with experience.
The need to rule is expressed among people in both positive and negative meanings. In the first case, the individual seeks to manipulate other people, suppress their resistance and control all processes and reactions that arise in the environment. In the second case, the subject feels the need to renounce any responsibility and tries, if possible, to avoid situations in which he will have to answer for his actions or the actions of other people.
Based on McClelland's theory of human needs, we can conclude that all three acquired components of a developed personality not only do not need to be arranged in a hierarchy, but each is capable of taking a predominant role. Thus, with an increased need for power and well-developed leadership or dictatorial abilities, the need for complicity may manifest itself minimally.
Violated needs
If some needs are not satisfied to a sufficient extent for a given person, they are considered violated and can cause big problems. The examples are as follows: the lack of normal sleep prevents a person from working, learning to think, he only wants to sleep, hunger provokes him to look for food and not think about anything else, physical injuries force him to suffer and seek salvation from his problem, everything else does not bother a person. Sometimes, even if a person does not have banal respect in the team, but has money, a position, and lower needs are satisfied, he can suffer even because of this one violated need.
Interests
Another concept that is worth considering within this topic is interests.
Each person has his own interests, and they can often be confused with needs, but it should be remembered that there are certain differences between these terms. Interest in a certain object is the position of an individual in terms of his abilities and requests. And here there is a connection between needs and interests. Yes, these concepts are not interchangeable. But complementary, for sure. It should be noted that interests do not exist without needs, and those, in turn, cannot exist without interests. The direction and nature of interests depend on the social group and status of the individual.
Interests can be divided according to their focus:
- Social;
- Spiritual;
- Political.
If we divide all interests according to another classification, namely according to the social affiliation of the individual, we can obtain the following list:
- Individual;
- Group;
- Public.
The interests of an individual may be of a purely strategic nature. In this case, a person may sacrifice the interests of other people in order to achieve them. That is why each individual must take care of creating certain personal interests that will not allow him to interfere with another person in pursuing his interests. Achieving your goals should not involve interfering with another person's goals. Do not neglect moral standards and existing life values. But this is a question of the psychology of each individual.
When does Maslow's pyramid not work?
In general, these 5 Maslow levels may not always work. The theory is valid if you look at humanity in a generalized, theoretical way, without taking into account the many special cases when it does not work. The pyramid usually does not work in the following cases:
- We are dealing with an extraordinary person. If we meet an unusual person who has some kind of spiritual filling above the usual, then such a person may neglect many things for the sake of the higher, say, earn less in order to have more time to engage in art;
- The opposite case is that some people cannot rise above the basic levels, although they are fully satisfied. Instead of simple food, they look for gourmet food, instead of a resort in their own country, they work and collect money for a trip to Thailand, instead of self-realization in the family, they endlessly change lovers for the sake of imaginary respect and envy of others, etc.
We can say that deviations in Maslow’s theory work most clearly on people outside the average type: geniuses and various deviants.
The essence of the concept
Every person needs something. Everything depends on the living conditions, the individual’s activities, material objects, etc. This is the individual’s need. That is, this is the internal state of a person, because of which something is felt to be insufficient. The need manifests itself differently for everyone, depending on certain situations. Experts have noticed that the need never ends. If a person has satisfied one need, another immediately appears. This cycle happens throughout life. Each need is manifested by certain emotions. A person becomes angry and irritable when he cannot satisfy a need, that is, negatively disposed. Positive emotions only appear when everything has worked out.
If needs are not met, discomfort appears, which gradually develops into a negative state. That is why people try to create all the conditions for a comfortable and prosperous life. Every living organism needs something. This is not necessarily a person, but also plants, animals, insects and other living creatures. The concept and classification of needs are considered in diverse aspects. However, psychologists associate them with human needs in different areas and directions. This is the essence of every need.
What is the meaning of Maslow's pyramid
If Maslow’s pyramid is considered, the human needs in it are stated rather conditionally, vaguely, the theory is sometimes far from practice. But it has a meaning and it is quite simple - looking at the picture of the pyramid, we must understand that a person is a complex being and there are things that concern him first, and there are things that can be put off until later.
By understanding what motivates people, you can effectively build communication and work process with them, find the right incentives for collaboration and increase the efficiency of employees.
A satisfied need ceases to motivate
Another interesting phenomenon is that if a need has already been satisfied, it often ceases to motivate a person. Almost all of us know this, but for some reason Maslow did not take this phenomenon into account in his theory. After all, the system of needs is also conditional in the sense that if a person has achieved what he wants, he does not rejoice at it for long, again falls into boredom, despondency, and looks for new supports for further growth.
We know from our own lives that it is enough to buy, study, build something - interest in it immediately disappears, the faster the more lively, active and ambitious the person is. But this is not reflected in Maslow’s pyramid.
features
Basic Needs
Basic needs, in both Maslow's hierarchy and Murray's theory, are those that people must frequently meet in order to survive and be physically healthy. These are aspects of our lives based purely on biology; and many of our impulses are designed to satisfy them.
Primary needs are part of a category known as “scarcity needs.” This means that we feel them when we lack a fundamental element for our survival. They are also the only ones whose absence can cause health problems or even death.
The primary or basic needs in both theories are the same: sleep, food, water and shelter. However, Maslow also added to this category the need for sex, which is a little different from the others in the sense that the lack of it may not kill us, but it does have a significant impact on our physical health.
Primary needs are regulated by the oldest parts of our brain. When some of them are not covered, we feel more motivated to try to solve the problem. This causes us to forget all the other elements of our lives in order to try to satisfy them.
Both Maslow and Murray believed that before working on the needs of the following categories, it was necessary to satisfy the primary colors at least in large part. Otherwise, it is almost impossible for us to concentrate on anything else, and our health quickly deteriorates.
Secondary needs
Contrary to what happens with primary needs, the absence of secondary needs does not directly threaten our life or physical health.
However, the absence of any of these elements has a very negative impact on our mental well-being. Embracing them is therefore also fundamental to a satisfying existence.
This section separates Maslow's and Murray's classifications. Although both talk about similar elements for the secondary needs category, the specific elements included are slightly different.
However, both psychologists agree that most secondary needs are also deficient; that is, they are motivated by an attempt to avoid the absence of some important element for our well-being (in this psychological case). Thus, Maslow talked about five types of secondary needs, which were classified in the form of a pyramid
This requires the researcher to meet those lower in the hierarchy before moving on to the next. Five categories: safety, belonging, recognition, self-actualization and cognition
Thus, Maslow talked about five types of secondary needs, which were classified in the form of a pyramid. This requires the researcher to meet those lower in the hierarchy before moving on to the next. The five categories are: safety, belonging, recognition, self-actualization and cognition.
Murray, on the other hand, spoke of secondary needs as "psychogenic." For this author, they have the same meaning, so we usually try to cover them at the same time. The categories included in this group are ambition, materialism, power, affection and information needs.
Advantages and disadvantages
Maslow's pyramid is valuable for studying large masses of people when there is no need to look closely at individuality. If we talk about its pros and cons, we can highlight the following:
- Pros. The ability to understand large masses of people, the applicability of theory to work in large teams, the ability to explain the behavior of individual people quite accurately, and have leverage over them. Also, thanks to theory, you can better understand yourself;
- Of the minuses: A. Maslow could not thoroughly describe each individual with his theory, take into account the variability of character, inconstancy, the presence of geniuses, dependencies on certain things. Many people behave differently and do not have the priorities that they should have, if assessed from the point of view of Maslow's theory.
Many psychologists believe that the pyramid is already outdated and today, when most people do not worry about low needs, it does not reflect reality.
Practical significance of Talley's theory
As already mentioned, the TNI (Tally Needs Inventory) questionnaire, announced by Tally, was never created, which, however, does not reduce the prospects for its use. A psychodiagnostic method for identifying personality characteristics and its development based on the non-satisfaction or satisfaction of his deficit and meta-needs can be a very valuable tool for the therapist as an opportunity to give a quick and objective assessment of his current state of self-actualization and self-development. 25The method can be very useful when working in existential groups, in cognitive and behavioral therapy, and in logotherapy. The TNI method can be of exceptional value in the selection of personnel by recruiting agencies, and the factor structure of needs - in more accurately identifying target groups when positioning the object of advertising and Public Relations.26
Application of Maslow's pyramid
Maslow's pyramid can be most successfully applied in certain areas, such as:
- marketing
- life
- work and business
- when building a career
- running a company
Let's expand on each topic a little for a broader understanding.
Application in marketing
Maslow shows human needs in the form of a hierarchy, so marketing companies and marketers can rely on this theory in order to understand exactly how to attract this or that category of people. If it is necessary to motivate, say, employees, then lower incentives such as increasing salaries or reducing working hours work here; management employees are already concerned about other issues: comfort, conditions for career growth, respect from management.
Application in life
The application of this theoretical concept in life is quite limited, but it can be useful for every person. We must not only look at what is at the top of Maslow's pyramid, but also cover basic needs if there are problems there. This will help relieve stress and tension, cope with professional burnout, and open up mental strength for new and greater achievements.
Maslow's pyramid in work and business
In these areas, the use of the theory under consideration comes down to competently stimulating your employees, understanding how to properly influence their performance, attitude towards work and work responsibilities. By managing to some extent the basic needs of people and clients, we can make ourselves more attractive in their eyes and offer solutions to specific pressing problems. After all, a business is more successful the more effectively it solves a client’s problem.
In building a career
In career matters, we should always remember what is at the top of Maslow's pyramid, but not try to jump straight there, since such a “maneuver” is available to very few geniuses. In a career, the pyramid will always help you remember that there are basic things that we cannot turn a blind eye to, so that they do not drag us down and close off the possibility of further growth. For example, if we work in conditions of low wages and cannot provide for our family, we work without respect from colleagues and superiors - this will greatly hinder or even slow down our growth.
In the practice of enterprise management
You can use Maslow's theory in business management. Here, too, everything is simple: each subordinate at his level and the ability to satisfy his needs must be selected with optimal incentives, satisfy these basic needs, or be given a real hope of satisfying them. If you add some qualities to your work that cover higher levels, you can also reduce stress from problems at lower levels. For example, a job where the boss respects and treats his subordinates well will be more interesting to many people than a high salary, but a bad attitude, which can lead to causes of professional burnout.
Spiritual aspirations
Spiritual interests develop in a person in connection with the desire to enrich life experience, broaden his horizons, and develop creative abilities.
View gallery
The growth of personal potential forces an individual not only to be interested in the culture of humanity, but also to care about representing the values of his own civilization. Spiritual aspirations presuppose an increase in psychological tension during emotional experiences, awareness of the value of the chosen ideological goal.
A person with spiritual interests improves his skills and strives for high results in the field of activity and creativity. An individual treats work not only as a means of enrichment, but learns his own personality through work. Spiritual, biological and social needs are closely intertwined. Unlike the animal world, in human society the primary need is for biological existence, but it gradually turns into a social one.
The nature of the human personality is multifaceted, hence the variety of types of needs. The manifestation of aspirations in various social and natural conditions makes their classification and division into groups difficult. Many researchers offer various distinctions, putting motivation at the forefront.
Some interesting facts about Maslow's theory
Here are examples of interesting facts about the issue under consideration that will be of interest to readers:
- Maslow himself was only interested in very strong personalities like Abraham Lincoln and believed that, despite all the efforts of an individual, only 2% of people can achieve maximum personality development, or self-actualization;
- In Abraham Maslow's basic article on the hierarchy of human needs there is no image of a pyramid - it was completed later by other researchers of the issue;
- The unspoken truth of the scientist’s theory is that a person can develop and move higher and higher in life only under one condition - he is driven by higher values and there is a need to achieve a dream, a higher goal of existence.
In general, Maslow’s theory of needs is very interesting, well-known, and will probably cause controversy for decades to come, both among psychologists, marketers and scientists, and among ordinary people interested in this issue.
See also:
Who is a marketer and what does he do?
complete guide Freelancing - what kind of profession is it and who are freelancers?
How to write articles correctly: stages, methods with examples and important details
Setting up Yandex.Direct yourself 2019
Setting up Yandex.Direct in a day, step by step instructions
Guerrilla marketing - how does the technique work?
Scope of practical application of William Talley's meta-model of needs
In 1986, Talley theoretically substantiated the possibility of using the needs model for therapeutic purposes and, especially, in psychodiagnostics. He announced the possibility of creating a questionnaire exploring the respondent’s need situation. It was assumed that the questionnaire would consist of approximately 60-80 questions, based on the results of which the diagnostician would receive a reliable and sufficient picture of his personality. 20TNI was patented a year later as a trademark, but has never been created to this day.
Talley's personality cartogram. Announcing the very possibility of creating a questionnaire, Talley assumed that it would reveal the current situation of the respondent in each specific social position. 21For each factor, approximately 15-20 questions were expected that would reveal the current value of the factor, which would determine the area of further therapeutic or social work with the respondent. The test is expected to be promising in individual client counseling, in logotherapy, as well as a tool that helps more effectively recruit and test candidates. In the latter case, Talley suggested that the very concept of personnel order should be modified taking into account the characteristics of the results obtained. On the other hand, a similar one, when used in pairs of already tested methods, can not only answer the question of what, for example, the intellectual potential of the respondent is, but also what its dynamics and future prospects are. For example, when using a standard IQ, a stable IQ in the range of 105-130 with FC1 is unsuitable for work that requires increased attention and perseverance; with FC2, on the contrary, there is a good propensity for methodology and routine intellectual work; with FC3, it implies high learning ability and a tendency to use in those types of activities that require constant learning of new material and new skills, and with FC4 - the respondent is of little use for a team style of work and can be maximally adequate in individual work.
Figure 2 shows a conditional example of the result of a respondent’s questionnaire according to Talley. The test results are clearly displayed on the profile (TNI map). To analyze the result, as Talley suggested, it is enough to know only the results of the values for each factor.22 In this case:
Rice. 2. Conditional example of the result of a respondent’s questionnaire according to Talley
Talley abandoned the concept of metapathology in the sense proposed by Maslow, “who pointed out that metaneeds are on a continuum with fundamental needs, so that the frustration of these needs gives rise to metapathologies,” manifested in a lack of values, meaninglessness, or purposelessness in life. According to Talley, any manifestations of metapathology are nothing more than crises of transition from lower needs to higher ones in cases where these transitions remain incomplete. An individual who was unable to overcome difficulties and obstacles on the path to satisfying his needs “gets stuck” at the “index” stage like “Buridan’s donkey”, unable to both come to terms with dissatisfaction and retreat to contentment with what has already been acquired, and to achieve the conquest of a new milestone . At the index stage, which becomes protracted and chronic, a person can behave one way or another, but one of the most common forms of behavior is “devaluing a need”23, the desire to explode its meaning, to call it into question. Talley cites in this regard not only the well-known “grapes are green” principles, but also those when a chronically dissatisfied person begins to oppose and resist the desired social status, quality or property. 24 Thus, according to Talley, factor 2-FP+3, if it becomes chronic, can indicate such qualities of an individual as rudeness, cynicism, invectivization of vocabulary, tendency to alcoholism and drug addiction, irritability, indiscriminate change of sexual partners, dislike for children, an artificially bachelor lifestyle, intolerance towards people, hatred of animals and even sadistic personality traits. This, as Talley points out, is a very general picture. TNI can provide more accurate results, especially in combination with other psychodiagnostic tools.