This article was developed under the heading: Psychology. Section: Philosophy.
Every person, while studying at school, has heard more than once about human needs (basic needs, primary, secondary). Moreover, everyone knows Maslow’s theory of classification of needs. Therefore, we all know that every person needs food, water, shelter, and socialization to exist. But what is a need? How is the concept of “need” viewed in psychology? Why are such needs unique to humans? What theories of needs groups exist? Let's understand this basic concept of psychology and humanities together.
Human needs are the subject of research in various sciences and fields of activity.
What are needs
The term “need” is studied by many sciences, including psychology, social science, and philosophy. Therefore, interpretations can differ dramatically.
As a general rule, a need is a person’s need for something (things, objects, people, socialization processes), without which a person does not feel comfort, security and stability. In simple words, it is a person’s need for something.
According to another approach, need is an internal psychological and functional feeling of a person, which is expressed in the lack of any objects or objects, status, which change in contrast to the content of each specific person and the corresponding situation.
It is important to note that the term itself is characteristic not only of people, but also of representatives of the animal world. They also have a need for something - food, water, safety. However, humans are distinguished by the presence of spiritual and social aspirations, which, as such, are absent in animals.
Main features
In our lives there are different categories of social and psychological nature. And “need” is one of those terms. But what distinguishes it from other concepts that at first glance seem quite similar to anyone. Let's look at the main signs:
- They are constantly changing. This is due not only to the fact that in the course of life a person has different priorities, but also to the fact that needs depend on the character of a person, his worldview, life principles and values;
- They are dynamic. This means that they can be improved in the process of developing a person’s personality;
- They depend on the kind of life a person leads. What does it mean? Firstly, each personality is formed in the process of socialization. This means that a person and his needs depend on his environment, interests, and activities. Secondly, the acquired profession and skills also modify the aspirations of the individual;
- Possibility of recourse. In this case, a person may return to previous stages if primary needs are not adequately satisfied.
The hierarchy of needs itself (pyramid of needs) characterizes the stages of personality development.
Brief Definition
A need is a need for something that motivates a person to take action to satisfy it.
Subjectively, it is felt as discomfort, tension, “internal itching.” At the moment of satisfaction, these unpleasant sensations are replaced by a feeling of pleasure and relaxation, which serve as a reward to the person for his efforts.
A person constantly experiences several needs. To ensure normal life, we need food, water, fresh air, comfortable living conditions, etc. These needs are basic, primary. Failure to satisfy them leads to serious health problems and even death.
There is another group - secondary. They arise only when a person’s basic needs are “closed.” These include spiritual, social and existential needs. We will talk about them in more detail when we consider A. Maslow’s pyramid.
Needs can be conscious or unconscious. Conscious ones turn into motives and determine human activity. The unconscious is hidden in the subconscious and sometimes breaks out in the form of strong emotions.
Meaning in human life
So, we have figured out what human needs are. But what is their significance in our lives? Let's figure it out.
Firstly, needs personify the personality itself. Therefore, their diversity allows us to say that the personality is versatile.
Secondly, needs influence the effectiveness of human activity. Psychology notes that they must be satisfied in the process of human activity. Therefore, when the concentration of the force of need is in the range of the “golden mean” (average strength), then human activity is most effective. When it is at a weak or strong level of so-called strength, then the work becomes ineffective.
Example. If a person has a need to realize himself as a leader, boss or adept in a specific field. But at the same time, he has been working for many years as a low-level employee, this is fraught with the following consequences. Firstly, he will not be satisfied with his work and life. Secondly, he will be deeply unhappy and aggressive towards others and himself. Thirdly, he develops a dislike for what is happening, cynicism. In general, such a person ceases to be healthy, since he cannot realize himself.
Human needs are satisfied in the process of his activities
Life cycle
Let's look at how a need arises, develops and is realized. At the initial stage, it is felt as a vaguely realized and unformed need for something. It acts as an internal hidden condition for activity, in the form of a certain ideal.
Next, the need is objectified and specified, acquires details and becomes the driving force of human activity. For example, an individual discovers a craving for love and begins to look for a partner for a relationship.
Motives are born from needs, which are subsequently transformed into goals. The totality of all motives forms the orientation of the individual.
The longer the need remains unfulfilled, the stronger the internal tension and discomfort. It forces attention to flow towards the object and encourages a person to take active actions.
If you are very hungry, then your attention will snatch images associated with food from the surrounding reality.
At the moment of realization, a person experiences emotional release and a feeling of satisfaction from the achieved goal. There is a release of joy hormones - serotonin and endorphin. This is a kind of reward for the work done and encouragement for new achievements.
Naturally, not every need is realized. Failure to implement this can lead to the following consequences:
- Death of a person. When it comes to basic biological needs.
- Frustration. This is a strong experience due to the unsatisfaction of the most important need for a person, bordering on a nervous breakdown.
- Sublimation. This is the transformation of feelings of dissatisfaction into creative energy.
All of the above means that a person should be attentive to his inner impulses: be aware of, accept and not try to suppress them. This is a necessary condition for the psychological health of the individual.
Psychological structure of needs
But what does the psychological structure of human need (both primary and secondary) look like? Human needs are divided into two structural elements. Let's look at them.
Item
In this case, the needs of the individual are considered as specific categories, things, objects of the material world. That is, in fact, a person always has an awareness of what will help him satisfy this or that need. Therefore, needs are satisfied by obtaining some objectively expressed results of human activity.
Reaction (discomfort)
When an individual's needs are not met, a person experiences discomfort. It's kind of stressful. Which is expressed in the fact that in the absence of the opportunity to satisfy the needs of the individual, a stressful situation arises, aggression, irritability and other characteristics.
Thus, the structure of needs is as follows. Firstly, this is something that can satisfy one or another desire. Secondly, this is what a person will experience if the need is not satisfied. That is, it is a kind of motivation, albeit based on negative feelings.
Definition of the term
This mental state speaks of a desire that has not been satisfied, so discomfort and tension are formed.
This need is determined by the lack of conditions and means to achieve set goals - from basic (eat, get warmth, procreate) to high, for example, self-realization. This sensation regulates the entire human body. It is very important to understand your goals, understand their nature, and also find ways to satisfy them. Otherwise, they begin to act on us subconsciously. So, all the needs can be divided into:
- Conscious - they are understood, accepted, corrected and consciously turned into goals and interests.
- Unconscious ones are not perceived directly, therefore they are actualized emotionally.
Regardless of what needs a person has, whether they are conscious of them or not, they are resolved or replaced - this is how a mental reaction works when it is not possible to achieve what you want.
Let me present the characteristic features of this condition:
- lack of staticity;
- instability, tendency to change;
- the possibility of new ones appearing in place of lost or sold ones;
- dependence of desires on activities.
This condition is inherent in every man and woman from the moment of birth. If for an infant only the receipt of warmth, close proximity to the mother and food are essential, then for a developed, adult member of society there are higher levels of necessity, including self-realization.
Need Development
As already mentioned, the needs of the individual develop and are formed throughout life. Therefore, they go through certain stages of development. There are two of them:
- The first stage is directly related to the fact that in order to carry out any activity, a person develops an ideal or image. Further, this image becomes the hidden motive of human activity;
- The second stage is characterized by the fact that human need is strengthened, specified and fully formed. For example, initially a person may develop a desire to care. He will be aware of this need. Further, after it has been specified, the person will look for the subject of the need for care. For example, a person who can be taken care of, or a person who can take care of himself.
In fact, at the second stage, the so-called phases of needs are replaced. If in the first stage the object of need first arises. Then on the second everything happens exactly the opposite.
Criticism
The criticism of Maslow's pyramid comes down to the fact that it is extremely difficult to apply this model in practice. For example, if a person is not able to meet the basic needs of food and a comfortable place to live, this does not mean that he does not strive to realize his talents. Also, not every person seeks recognition in society - for some, a stable job and starting a family are enough.
There are many examples in history when people achieved success in life precisely because their basic needs remained unsatisfied. Thus, living in poverty can force a person to seek acceptance in society, bypassing the needs of security and belonging. And unrequited love can become an incentive to create magnificent works of art. For example, Van Gogh's passion for painting is attributed to failures in love.
The theory is criticized because of its hierarchy and the impossibility of fully satisfying needs. For example, physiological processes will always be relevant - a person constantly needs to drink, eat, and sleep. For some people, only part of the needs may be important.
The fact that over time Maslow completely revised his own theory is often cited in favor of criticism. In later work, he changed the motivational concept and abandoned the multi-level system.
In the new version, Maslow divided human needs into two types:
- “Scarce” (inferior). These are needs caused by a shortage of something and, accordingly, saturated.
- "Existential" (highest). This type of need is dictated by growth and development and is therefore insatiable.
Like the previous theory about the hierarchy of needs, the new vision was presented by the psychologist in the format of an assumption. The author hoped to find confirmation in the future, but did not have time.
The pyramid of needs should not be taken as an unshakable truth. This is not a strict classification of human needs, but an attempt to determine the more and less significant of them. Basic needs will dominate for most people. But different people may have different motivation systems, and for some, higher-level needs will be more important. By the way, according to Maslow, only 2% of people reach the level of self-actualization.
It turns out that Maslow’s pyramid still makes sense, but it does not need to be interpreted literally. For example, in marketing, the pyramid of needs is actively used when developing a sales strategy. The general principle of the theory is interpreted as follows: it is important to monitor trends in needs and direct efforts to satisfy more pressing ones.
Types of needs
In psychology, needs are often divided into groups. They are characterized and combined according to certain characteristics and factors. Let's look at each such group in more detail.
Basic human needs are divided into specific groups and types of needs
Biological needs
Such needs are often called “basic needs” or “human physical needs.” This means that such a set of desires and ideas is characteristic of absolutely every individual. In this case, it does not matter what character a person has or what values he has. Biological needs include:
- Food. Like any other living being, humans need food to continue to live and function;
- Water. Another necessity without which a person physically cannot function;
- Sleep - good rest for the body is the most important factor for life.
Such needs are also called natural needs. Moreover, there is a classification of lower and higher needs. Biological needs act as the lowest human needs.
Material needs
Many researchers also include biological needs as part of their material needs. Although this is not entirely the right approach. Of course, with the help of objects of the material world, natural needs can be satisfied. However, their satisfaction is not a material matter.
What is included in material needs? We can distinguish the following types:
- Purchasing things, equipment, furniture;
- Purchasing a house, real estate;
- The need for material wealth.
We can say that material needs are what are used to satisfy basic and higher levels of human needs.
Social needs
Communication and socialization are the engine of our progress and development. Therefore, almost from birth. the child has a strong need for interaction. For example, a small child under 3-4 years old is attached to his mother. That is, his development depends on his attachment to his mother and the satisfaction of his social needs.
The group of social needs includes the following elements:
Love
In communication
Friendship
Understanding
Support
In interaction
Thus, a group of social needs remains with a person throughout his life. For example, it is unlikely that at least one individual will be able to live in complete isolation and lack of communication.
Spiritual Needs
Human needs are also spiritual. What does it mean? Firstly, they are fundamental in nature. That is, they shape our personality and our worldview. Secondly, spiritual needs are related to how we perceive ourselves and the world around us. Simply put, the spiritual desires of our personality are associated with a sense of aesthetics and delight.
The structure of this group includes the following types of needs:
- Art;
- Faith;
- Career and Education;
- Self-realization.
Thus, we can say that they personify a person’s spiritual harmony with himself. That is, these are the desires that make a person happier.
The possibility of creative (spiritual) self-realization is necessary for the human personality
Afterword
Satisfying needs is important for adequate personality development. If biological needs are ignored, a person can get sick and die, and if higher needs are unsatisfied, neuroses develop, intrapersonal conflicts and other psychological problems arise.
It is worth noting that there are exceptions to the rule “first satisfying some needs - then developing others.” We are talking about creators and warriors who can set higher goals, despite unmet physical needs, such as hunger and lack of sleep. But for the average person the following data is typical:
- physiological needs are satisfied by 85%;
- in safety and security – by 70%;
- in love and belonging – by 50%;
- in self-esteem – by 40%;
- in self-actualization – by 10%.
Needs are closely related to the social situation of human development and the level of socialization. Interestingly, this connection is interdependent.
Additional types of needs
However, at the moment, other types of elements necessary for humans are also being identified. They are also called “secondary needs”. Because they are different for each person. Moreover, they may, in principle, not arise in an individual. Let's look at the main ones.
Need for movement
At its core, the need for movement is a type of biological need. In reality, without movement, the human body atrophies. It becomes unviable. Therefore, being without movement, a person is in danger of not being able to satisfy any of his desires.
Power as a need
Such a vital necessity is individual and specific. Therefore, it may not be present in all people. That is, the desire for power is a consequence of the established foundations of the individual.
Surely, you have thought more than once that someone you know definitely needs to be a leader. Or, on the contrary, they believed that the person was too cruel. Because he wants to dominate others. This is the very need for power. What it may include:
- Firstly, the desire to take a leading position in any relationship;
- Secondly, the desire to be a boss at work;
- Thirdly, a person’s high level of ambition;
- Fourthly, the use of methods of suppression in relation to others and an inflated sense of self-importance, as well as egocentrism;
- Fifthly, the possibility of reaching the stage of a tyrant in any social relationships.
Safety
This desire is also considered as the primary needs of a person. This need is inherent not only in humans, but also in animals. For example, for a normal life, every person must feel safe. That is, he must have a house, a roof over his head, as well as a certain income that will allow him to ensure his life.
There is a point of view in which the need for security is considered one of the fundamental ones. And this is indeed the correct position. That is, such a need is justified by physiological and instinctive reasons.
Achieving results
This life guide also depends on the individual. There are so-called people - conquerors, careerists. To feel complete and harmonious, they need to constantly achieve something. For example, set a goal to get a promotion at work and work hard towards it.
Career ambitions are also a type of human need
Need depending on another
It's more of an emotional whim than a physiological one. Despite the fact that it is based precisely on instincts.
So, a person is a living being who tends to think about the continuation of his kind. Therefore, due to the social characteristics of each individual, there is a need for close social and emotional connections.
Quite often in practice there are cases when a person feels inferior for several reasons. Firstly, he does not have a partner or a so-called love relationship. Secondly, he cannot realize his feelings (tenderness, kindness, care, love, etc.).
Liberty
What is included in this human need:
Freedom in relationships (the ability to freely choose your environment)
Spiritual freedom (freedom to choose profession, education, religion)
Freedom of movement (the ability to travel, change home)
A significant example of the need for freedom is the lockdown that occurred in March 2022. After being confined within four walls and unable to move freely, especially in Moscow, many experienced the first stages of depression. Moreover, specialist appointments have seen an influx of people suffering from disorders that have been made worse by isolation from the outside world.
How did the image of the pyramid of needs come about?
The theory of needs was developed by Abraham Maslow, but he was not involved in the creation of the pyramid. There was not a single graph in the psychologist’s work.
It is believed that the first graphic representation of the hierarchy of needs was published in 1975 - in the textbook by W. Stopp. Since then, the scheme has been used inextricably with Maslow’s theory. That’s what they call it: Maslow’s pyramid or pyramid of needs.
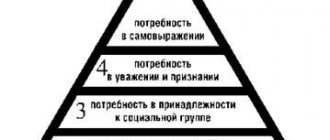
The pyramid is often depicted in the shape of a triangle. The lowest wide part covers basic needs, then the following levels are displayed towards the top:
- Physiology (hunger, thirst and other natural needs).
- Security (feeling of security, lack of fear).
- Belonging and love.
- Respect and recognition (fame, success, prestigious status).
- Cognition (gaining knowledge, skills and abilities).
- Aesthetics (striving for beauty, searching for ideals).
- Self-actualization (realization of abilities and desires).
Schematic representation of Maslow's pyramid
In 2010, a group of scientists from the USA and Canada updated the pyramid taking into account modern realities. In their opinion, basic needs remained the same. In the same way, people need food, security, belonging and love. As for the upper levels, reproductive goals come to the fore: maintaining relationships, finding a suitable partner and raising children. Self-actualization is combined with recognition. At the same time, scientists note that needs sometimes shift and are interchanged.
Updated pyramid of needs
However, Maslow himself did not rule out deviations from the hierarchy. Some people may stop at the lowest level, others are more in need of self-actualization than security or recognition. Maslow considered such exceptions to be features of a person’s personality or a consequence of unfavorable external circumstances.
The hierarchy of needs remains popular in psychology, within the framework of sociology research, and in management training. However, Maslow's pyramid is often criticized and called outdated.
Why is it important to share your needs and wants?
In order to answer this question, it is necessary to understand how needs differ from wants.
| Needs | Desires |
| 1. Needs are always constructive. Your needs always speak of importance, necessity for your normal functioning and life; 2. Needs are deep and fundamental; 3. They also allow you to find harmony with yourself. | 1. They are destructive. That is, desires can harm the development of personality and life. for example, drug addiction is a “want”, not a need; 2. Desires can be imposed by other people; 3. Desires can also be superficial. That is, they will not satisfy your true needs. |
Comparison of human needs and desires
Let's look at a specific example. So, you have an apartment in which you live. At the same time, you want to buy a dacha. But there is no money for it. This makes you irritated and angry with yourself. In this case, buying a summer house is a desire. On the contrary, if you have nowhere to live, then purchasing housing is a necessity.
So why is it important to differentiate between them? Firstly, this way you can properly distribute your energy and activities. Secondly, it will help you know yourself and other people better. Thirdly, it will allow you to set priorities correctly.
Maslow's pyramid in work and business
People go to work to satisfy physical needs and provide security, in other words, in search of stability. When you can already meet your daily needs, it is time to strive for career growth, success and recognition.
And entrepreneurs, in turn, can analyze the desires of employees and help satisfy them: promote them, increase wages, hold corporate events in the Maldives, open a soup kitchen, provide training. This also includes improving the workflow: connecting automated systems that take over the routine.
Automation of email newsletters
Send chains of trigger messages: welcome, abandoned cart, reactivation, combining email, SMS and web push within one chain.
Set up trigger mailings
How to understand what you need and what you just want
In fact, we have already indicated in what ways this can be distinguished. But to make it easier for you, you can ask yourself the following questions:
- Can I live without this? For example, buying an expensive dress is not necessary. So, you can leave this desire and buy it when there are more material resources;
- What will this give me? Such a question helps explain to yourself the true nature of your obsession;
- Will I limit myself to this acquisition? It is important to understand here that your desires should not compete with your needs. Therefore, determine what is more priority for you.
Many people are not aware of their needs, so they often feel unhappy
Features of formation
Different types of needs are not formed in the same way. Physiological needs are innate, they are transmitted to a person from his mother and father. Without their satisfaction, the body may die; people have to live with them until death. These needs cannot be imposed by force or prohibited.
Primary spiritual needs are also born with people. In the life of every person there is love, harmony, relationships with others. For the normal development of mental health, a person must self-actualize. Without satisfying these needs, the body will not die, but will be stuck in frustration for a long time.
All basic needs are fully formed by the end of adolescence. They can develop further, but only through changing their content or methods of achievement.
A person cannot exist without contacts with the outside world. But first of all, he cares about satisfying his basic and secondary needs. Without this, he will not be able to develop normally physically and psychologically.
Theories about needs
In the theory of psychology, many classifications of needs have been developed and considered. They are called differently - theories about needs. At the moment, their meaning comes down to the division of needs on various grounds. Any of the theories may seem quite absurd to you, but all collected here are basic in the theory of psychology. Let's put aside prejudices and look at each objectively. Surely you have met at least one of them.
The most famous theory is Maslow's Pyramid
This theory is fundamental for many branches of knowledge. It is considered within the framework of medicine, psychology, and jurisprudence. This theory has become completely conformist and generally accepted in society. But what is it? Let's figure it out:
- Firstly, Maslow's pyramid is named after the researcher of the same name - Maslow;
- Secondly, the essence of this theory comes down to the fact that needs are divided into primary needs and secondary;
- Thirdly, it assumes that a person develops a special hierarchy of needs. Which act as a certain priority for a person.
Pyramid of needs according to the theory of A. Maslow
Primary Needs
According to Abraham Maslow's theory, primary needs are those that are associated with human physiology. These include the following needs:
- Food;
- Water;
- Reproduction of the genus (reproduction);
- Housing;
- Dream.
Secondary needs
Secondary needs include social, spiritual and other types. They mean that their satisfaction is possible only after the basic (primary) ones have been satisfied. What can they include:
- Communication;
- Power;
- Self-realization;
- Creation;
- Safety;
- Confession.
According to Maslow's theory, primary and secondary needs are distinguished
Alderfer's theory
The theory of this scientist comes from similar positions. However, it is more specific. She identifies three groups of possible human needs. Let's look at each of them.
Existence needs
It is logical that this type includes those desires that form the basis of human existence and life. So, these will include: sleep, food, water, safety. Simply put, these are the same biological needs, or primary ones according to Maslow’s theory
Need for communication
In simple words, this is the need for social connections (socialization) and communication. In addition, Alderfer also includes “high” (spiritual) needs in this group - self-realization, power, creativity and others.
Need for growth
Such a group is more associated with the optional, or additional aspirations of a person, which we examined earlier. For example, this group may include a person’s aspirations for self-development, self-training and education.
Fromm's theory
Erich Fromm is a famous psychologist. He devoted his life to the study of human personality. Therefore, in his works one can also find theories about human aspirations. They are divided into five main categories.
| Group | Content |
| Making connections | In this group of needs, Fromm implies that each person sees his goal as building social connections and contacts with other people. For example, friendship or building a family. |
| Overcoming | According to Fromm's theory, every person is initially an animal, and only then a person. Therefore, the basic need of people is to overcome their animal instincts. |
| Roots | Man is a social being. Consequently, everyone wants to feel part of the world, society, a small group. Everyone strives to leave behind a certain kind of “legacy”. |
| Identity | In other words, self-identification. That is, each person strives not to be like the others. In the process of growth and life, everyone tries to identify themselves among billions of other people. |
| Belief system | A person’s whole life is a need to build one’s own ideals, foundations and values. |
Erich Fromm's theory of human needs
As we see, Fromm proceeds more from a psychological point of view and the internal content of the individual. With other owls, Fromm identified the special psychological needs of humans.
McKelland's theory of acquired needs
David McCalland in the 20th century identified a special group of aspirations - acquired in the process of life. At the same time, he did not deny the validity of other existing theories. Thus, according to McKelland, the following types of acquired needs are distinguished:
- Need for power;
- In involvement;
- In success.
There are many psychological theories about needs
Advantages and disadvantages
Now let's understand the advantages and disadvantages of Abraham Maslow's theory.
Advantages
- It allowed us to organize needs and explain in simple language what a person needs.
- Was the basis for the creation of theories of motivation.
- It has influenced all areas of human life - it is used both in business and in everyday life.
- Helped me understand people's values.
- Convenient for self-analysis to understand thoughts and desires, as well as structure your goals.
Flaws
- There are no ways to empirically measure the degree of satisfaction, which means the theory cannot be considered evidence-based.
- The pyramid is a simplified system; it is not suitable for everyone; it is necessary to further segment people’s desires.
- The model does not take into account cultural differences and characteristics. Also, due to objective reasons, namely changes in a person’s lifestyle, it is already outdated and requires improvement and updating.
- The theory does not explain how a satisfied need can re-motivate a person.
- The study also does not help in the study of extraordinary actions, namely, it cannot explain their motives.
- According to the theory, a person satisfies desires from the bottom up, but he constantly needs food, which means that there is an inverse relationship.