Medical information is reliable Checked by Eremin Alexey Valentinovich
Lack of memory for certain events is called amnesia. It does not always indicate a pathological process; for example, many cannot reproduce the first years of childhood. But most often, amnestic syndrome indicates the presence of a number of neurological or mental abnormalities. According to statistics, 25% of people on Earth suffer from memory impairment to one degree or another.
Classification
Depending on the degree of memory loss, amnesia can be complete or partial. In the first case, a person cannot remember anything from a period of his life, and in the second, he observes vague fragments of events. There is also selective or local amnesia, when the patient loses only a specific skill. This condition is characteristic of psychogenic disorders. According to the time of forgetting, this deviation can be:
- retrograde in the absence of memory for everything that happened before the onset of the disease;
- anterograde, when everything that happens after the first signs of the disorder is forgotten;
- combined (combines retrograde and anterograde amnesia);
- fixation – forgetting what is currently happening, usually lasts for 2-5 minutes.
The type of course of amnestic syndrome can be:
- regressing with gradual recovery;
- stationary, in the absence of positive dynamics and without signs of deterioration, forgetting usually applies only to a certain situation;
- progressive – gradual loss of memory up to its complete loss.
There is also retarded memory loss, when a person’s events are erased some time after stress, acute psychosis or traumatic injury. Immediately after regaining consciousness, he talks about what happened, but later forgetting sets in.
Description of aircraft
The word comes from “let”, meaning the river of oblivion. The technique is used to suppress annoying thoughts or get rid of information that has lost its relevance.
There are two ways:
- Suppression. The more a person tries not to remember, the more annoying the phenomena become. Describe them on a piece of paper, based on all the details. Try to throw out the negativity on paper, visualizing what happened. Then burn the note and watch the fire. At the same time, try to realize that the moments of the past turn into ashes and crumble.
- Delete. Unnecessary data can be eradicated by the “flight rag” exercise. If information is represented in your head by images, mentally pick up the cloth and erase them. Think about how they disappear and are no longer there.
Transient and permanent amnesic syndrome
Transient amnesia is observed with a number of deviations associated with various factors, it happens:
- Transitional global. It is observed in middle-aged and elderly people, more often in males, and lasts for several hours (from 4 to 12). In this case, patients do not lose their identity, but they experience confusion. However, there is no evidence of cerebral ischemia. During the study, the patient demonstrates a profound loss of memory for all events occurring at the time of the attack. A return to the original state is observed within 1-2 weeks to 2-3 months.
- Transitional epileptic. Occurs in patients with epilepsy, sometimes amnestic syndrome manifests itself as the first sign of the disease before the onset of seizures.
- Injuries and head injuries. Typically, after a TBI, an episode of temporary retrograde amnesia is observed; the longer it lasts, the more negative the prognosis, and the likelihood of cognitive impairment, mental disorders, and social problems increases. Post-traumatic syndrome also includes anxiety, irritability and complaints of somatic pathology.
- Alcohol blackouts. Memory lapses associated with alcohol abuse mean that a sober person cannot remember events when he was drunk. But after drinking a strong drink, they easily return.
Complete memory loss is observed in progressive diseases that cannot be completely cured. This happens with dementia, mental illness, inoperable brain tumor and other disorders. Therapy in this case is to stop the deterioration of the condition and take measures to adapt the patient to his amnesia.
How to improve memory. Recommendations from the Neuroscience Center
If you observe alarming symptoms in yourself or in people close to you, indicating memory problems similar to those indicated above, then you need to go to an appointment with a neurologist, neuropsychologist or therapist and undergo a series of special diagnostic tests. If you want to immediately start fighting an undesirable phenomenon before receiving the doctors’ verdict, then take action - start training your memory.
Here are some exercises to improve memory:
- If possible, perform your usual tasks with your eyes closed, from memory;
- If you are a left-handed person, do everyday tasks with your right hand, if you are right-handed, then with your left. Try this rule, for example, writing, ironing clothes, drawing, etc. – You will soon feel a positive result;
- learn Braille, which is used by blind people when reading, or learn sign language - this is useful for memory and can be useful in life;
- type texts on the keyboard with both hands, using all fingers;
- do some handicrafts - start embroidering or knitting;
- learn foreign languages and speak them more;
- try to distinguish the denomination of coins blindly, feeling them with your hands.
In addition, expand your range of interests, read more, visit places and institutions you have not been to before, go to plays and performances, walk in parks, meet and communicate with people, make new friends.
Perform the recommended exercises, follow the listed rules, take care of your health, and your memory will not fail you until old age!
Manifestations of amnestic syndrome
A classic sign of amnesia is the inability of a person to recall a certain period of time in his life. Most often, recent events are forgotten first, and then more distant ones. In a regressing process, recovery is observed in the reverse order. Some types of disorder involve false, fictitious memories, or confabulations. With their help, the body tries to fill the gaps. At the same time, the person sincerely believes in the truth of his “memories.”
Amnestic syndrome after a stroke is characterized by hypo- and paramnesia (general memory loss and confusion of present and past events). At the same time, speech impairment and movement deficits are noted. Memory loss occurs in psychoorganic syndrome, and cognitive dysfunction is also observed. A person loses the ability to assimilate new information, his attention decreases, and his thought processes slow down. With dissociative amnesia, the patient becomes absent-minded, begins to wander, and often experiences affective disorders. Transient global loss of memories is characterized by complete disorientation. With Korsakoff's syndrome, several types of amnesia are often combined.
With a stationary disorder, a person often suffers and worries about his condition, is tormented by a feeling of guilt, and becomes depressed. Progressive amnestic syndrome leads to complete helplessness; a person can leave home and get lost in a familiar area. There is a gradual loss of skills and knowledge. At the end there is complete disorientation and constant care is required.
Exercises
I offer a number of trainings to help cope with the problem.
"Visualization"
Imagine negative moments in the form of dust sticking to your body. And then mentally pour water on yourself to wash away this dirt and, thereby, cleanse your consciousness.
Another option is to write down the event in detail on paper and burn it. Try to go into detail to “pull out” the negative feeling from yourself. If there is an object that reminds of a traumatic event, the memory can be buried.
"Perception"
The technique is to understand the situation like an episode from a movie:
- Play it through your head, putting yourself in the shoes of each participant.
- Do the same, but imagining that you are looking at the screen, change the playback speed from low to high.
- Color the picture in different colors: blue, greenish, red.
- Change the size of those participating in the dialogue.
Experience shows that this reduces the significance of the moment and the people in it.
Organic amnestic syndrome
The causes of organic amnestic syndrome can be various lesions of brain tissue: cerebral arteries, white matter, nerves or cerebral cortex. It also leads to the appearance of hematomas and hemorrhages in the central nervous system. The cause of the deviation is sometimes carbon monoxide poisoning with massive brain damage.
When the functions of the temporal regions are disturbed, as happens with epilepsy, they also lead to the fact that a person develops amnestic syndrome. Its causes are:
- malignant tumors, especially when the ventricular walls are damaged;
- Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia (Lewy, Creutzfelt-Jakob, atherosclerosis and other pathologies);
- Wernicke's disease;
- herpetic encephalitis;
- tuberculous meningitis in severe form;
- transient ischemic attacks (lead to temporary amnesia).
Another common cause of amnestic syndrome is alcohol addiction. Many have noticed that short-term memory loss occurs when intoxicated. Experts associate it with a lack of B vitamins, since ethanol is their antagonist.
Treatment of alcoholic amnesia in our clinic always includes a full course of therapy for this disease with the addition of drugs to improve cognitive and mnestic functions.
Cognitive amnesic syndrome
The word “amnesia” itself, translated from Greek, means memory loss, which greatly affects a person’s cognitive abilities. Memorizing events and information is the basis of learning and the emotional coloring of what happened. That is why amnestic syndrome is very traumatic; it not only reduces the patient’s quality of life, but also affects his loved ones.
This condition is considered as a complex of symptoms under various diagnoses. But clinical medicine allows it to be indicated as an independent disease if the cause of the disorder cannot be identified. Typically, amnestic syndrome has two characteristic features:
- loss of memory for past events (retrograde amnesia);
- inability to remember current information (anterograde amnesia).
Other functions of cognition in this case are rarely affected, but may be impaired because they depend on the patient’s memory:
- ability to concentrate;
- organization in space;
- abstraction (visual or auditory).
A person ceases to show initiative and independence, and is almost always in a complacent state. Immediate memory with repetition of just spoken phrases or series of numbers is retained. Some patients in the acute phase of the disease develop a tendency to invent answers or events. With dementia, the patient sometimes replaces lost information about himself with information that he once saw or read. At the same time, adventures are presented to them as their own, but this is done unconsciously.
What is “Memory”?
Memory is a complex structured mechanism that allows people to perceive the information around us, process the received data and store it.
Each of us has this function from birth and has the opportunity to train and develop it.
Unfortunately, the opposite effect is also possible under the influence of various factors that can negatively affect attention and memory.
Attention is a directed emphasis on an action or event. This process is a similar cognitive phenomenon as memory.
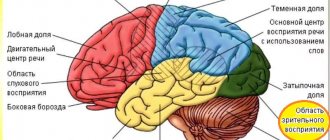
What happens inside the brain
According to biologists, memory is the result of the functioning of a web of neural connections in which central nervous system reactions occur. A person perceives and perceives the objects around him through receptors: hearing, vision, smell, touch, taste. All information is transformed into electronic impulses that are sent to our brain. This is the final point where all collected information is stored.
We are able to remember even the smallest nuances or insignificant events if they are supported by one of the receptors. Memory is also unique in that a person is able to add various details to memories: “experienced” emotions, conclusions, and so on. In essence, we do not remember the actual event, but a slightly modified personal impression.
Where is the information stored?
Currently, scientists do not have answers to the specific question “Where and how is information stored in the human brain?” Many theories and assumptions have been put forward, but none of them have been confirmed.
In scientific circles, there is an opinion that the information received is stored in neural circuits.
Psychogenic amnesia
Conditions that lead to the loss of memory of a certain part of data about one’s personality are called psychogenic. These types of amnesia include:
- Katathimnaya. The patient forgets only those data that are in some way related to psycho-emotional experiences.
- Hysterical. Often observed in hysterical psychopathic syndrome. In this case, the person cannot remember only the traumatic moment.
- Post-hypnotic. The patient is unable to reproduce what happened to him in a trance state. This is usually part of the suggestion.
- Dissociative. Refers to the body's protective reactions that do not allow the destruction of mental functions. Memory for events that cause severe stress is erased. It differs from other types of psychogenic amnesia in that the loss itself is a treatment and relief from further problems.
- Dissociative fugue. Also refers to defense mechanisms, but at the same time a person escapes from a difficult situation by moving to another city and forgetting about his past life and his personality. At the same time, he retains his basic skills completely. After some time, events are restored, usually this happens suddenly and immediately.
How a neurologist treats memory
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to understand what disease caused the problem. Medicines should be used only those prescribed by your attending physician; self-medication is unacceptable. It is optimal to undergo a complete diagnosis of brain activity, vascular health, and electroneuromyography.
It should be remembered that rapid memory deterioration in itself is not a disease; this symptom only warns of the emergence of a more serious disease that needs to be diagnosed and therapeutic or radical treatment begun. This will help restore the previous quality of life, prevent the patient from separating from society and deteriorating adaptive functions. When memory impairment is detected, nootropic drugs are usually prescribed.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of amnestic syndrome requires the participation of several specialists, depending on the basic picture of the disease. A neurologist, narcologist, neurosurgeon, and infectious disease specialist are involved in the work, and if necessary, a psychiatrist is consulted. To determine pathology, the following is used:
- Study of the medical history based on data from a survey of the patient and his close relatives, as well as provided medical documentation.
- Assessment of the state of the nervous system. It helps to determine the presence or exclude organic brain damage and the consequences of traumatic brain injury.
- Mental state assessment. It is performed in people with suspected psychogenic amnesia and symptoms of a mental disorder.
- Studies of the characteristics of the blood circulation of the central nervous system in case of probable vascular disorder. For this purpose, REG, ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head, and MRI are performed.
- In case of traumatic brain injury, a CT or MRI of the brain is prescribed. These methods help to accurately determine the presence, size and location of a tumor, hematoma, tissue degeneration, and lesions after a stroke.
- EEG is used to determine abnormal electrical activity in the brain during epileptic seizures.
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine. Allows you to conduct a drug test, determine the level of vitamin B1, and the presence of toxic substances in the body.
- Study of cerebrospinal fluid. Sampling of cerebrospinal fluid and its analysis is used in cases of infectious origin of amnestic syndrome or intracranial hemorrhage.
Dr. Isaev’s clinic has all the conditions for a full examination of a patient who has lost his memory. The hospital is equipped with modern equipment and a laboratory. If necessary, it is possible to conduct consultations with experienced specialists in any field of medicine.
Is it possible to erase a person's memory?
The brain part of the body is responsible for this function. Thanks to it, information is remembered, stored and reproduced. However, with all the latest technologies and brilliant successes in the scientific world, this topic has been studied rather poorly.
Conducted research and experiments have not given scientists a clear answer to how this property works and what its principles are. Methods for partial or complete removal of memories cannot be predicted. Therefore, it is highly not recommended to use memory erasing in solving problems.
However, such a phenomenon does exist. In science it is known as amnesia. This is not an isolated disease, but only a consequence of certain disorders in the body. Which ones I have already described above.
I will only add that external catalysts, such as serious injuries, are also unpredictable and can cause damage to physical and mental health, as well as lead to tragic consequences. Internal reasons related to human psychology, in turn, provide hope for recovery, and with effort, the process can be made controllable.
Treatment of amnestic syndrome in Moscow
The goal of helping a patient with memory loss is to restore it or stabilize the condition and achieve long-term remission. Amnestic syndrome does not have a specific treatment regimen. Each patient receives an individual care plan. It depends on the cause of the development of the disorder and the characteristics of its manifestation. For the organic form, medications or surgery are used primarily, and for the psychogenic form, psychotherapy is used. The most commonly used drugs are:
- vascular agents to reduce blood viscosity and expand the microvasculature and improve cerebral blood flow;
- neuroprotectors, nootropics and antioxidants to improve metabolism in brain cells, reduce their sensitivity to ischemia, and normalize cognitive functions;
- anticholinesterase drugs and ginko biloba preparations for dementia in order to reduce the progression of dementia in the elderly and increase daily activity;
- In Alzheimer's disease, memantines are used to improve mnestic functions.
For patients with mental disorders, antidepressants, antipsychotics, tranquilizers, and mood stabilizers are used. They help normalize behavior, restore control over the biological rhythm, improve mood during depression, and eliminate anxiety, phobia, and anxiety.
Dr. Isaev’s clinic uses only proven, certified drugs with minimal side effects. They must be taken strictly according to the course prescribed by the doctor.
If a tumor, hematoma or cyst is detected in the brain, it is surgically removed. Methods of psychotherapy allow, in combination with medication, to accelerate the recovery of the patient’s memory. In the absence of organic disorders, hypnotherapy helps to restore memories. These patients use a cognitive-behavioral technique that allows them to identify negative mental dogmas and replace them with positive ones. With its help, a person relates to his problem more easily and this helps him speed up his recovery.
With the psychogenic form of amnesia, the goal of treatment is not so much to restore memory, but to help the patient accept its loss. The method of psychoanalysis eliminates psychotraumas coming from early childhood, and family therapy improves relationships between loved ones and helps optimize the prognosis for amnestic syndrome. For people with a lack of inclination to demonstrate their feelings and experiences, creative types of treatment in the form of art therapy and fairy tale therapy help. Help for alcoholics with amnesia is provided in the form of the use of vitamins and means for detoxifying the body.
Types of memory disorders in older people
Medical statistics show that cases of sudden memory loss in older people have recently become more frequent. This happens completely unexpectedly; a person of advanced age simply forgets his name and address and does not recognize close relatives. Such memory disorders are being studied at the Moscow Serbsky Institute, but a technique has not yet been developed that completely restores mental activity.
It is known that memory loss in the elderly is associated with deterioration in the functioning of parts of the brain - the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. Doctors say that the precursor to Alzheimer's disease is the neurological disease multiple sclerosis.
Energy in the pineal gland of the brain fades with age, so in the worst case, the memory is completely erased. Of course, there is also a positive scenario for the development of the disease, when it develops very slowly, barely noticeable, if the person does not aggravate his condition with bruises, head injuries and other factors.
Memory loss in older people is divided into types, which depend on the characteristics of the lost information:
- By prevalence. Loss of memories can be complete or partial;
- By time period - long-term or short-term;
- For forgotten events. There are anterograde and retrograde memory loss. In the first case, an elderly person completely forgets events from his past, but remembers what happens every day perfectly. Unfortunately, anterograde memory loss progresses over time towards complete loss of information about the past. In the case of retrograde brain disorder, the patient does not assimilate everyday events, but remembers what happened decades ago;
- By speed - the loss of memories occurs gradually or suddenly, which is associated with the natural wear and tear of the body;
- Global amnesia - an elderly person remembers absolutely nothing from his past and present. New events are also not stored in memory;
- Selective - individual events from past years appear in the memory of an older person;
- Visual - associated with visual perception, when an elderly relative ceases to recognize his loved ones. Sometimes enlightenment occurs when a person seems to remember someone, but definitely does not remember either the name or the significance of the person in his life;
- Reversible and irreversible;
There are several additional types of memory loss in which the body is affected by external factors, rather than changes in general condition:
1. Korsakov's loss occurs in people who abuse alcohol. During periods of severe hangover or intoxication, they tend to forget certain events.
2. Senile loss - develops gradually as a person ages. Usually the old people themselves may not notice this, but the interlocutor realizes that the main topic of conversation is increasingly becoming the events of bygone years.
3. Post-stroke memory loss, when the attack leaves an imprint on a person’s ability to see, hear, feel, think and remember information.
Amnesia is commonly referred to as complete or partial memory loss in older adults. It can be caused by completely different reasons. In combination with attention and thinking disorders in older age, it develops into senile dementia or dementia.
Disruption of thought processes significantly affects a person’s life. Over time, more and more information is forgotten. At the beginning, events are erased from memory in separate fragments.
Old people cannot remember whether they closed the door behind them, turned off electrical appliances, or took their medicine on time. Over time, the events of young and mature years do not emerge in memory, and after a certain period of time, the people surrounding the elderly person become strangers to him.
1. Short-term amnesia.
The pathology is mild in nature, manifested by some forgetfulness and is not recognized by the elderly as a dysfunction. Recent events, for example, from the past month, are erased from memory. But then the information pops up in my head again. If memory loss lasts daily in older people, you should definitely consult a doctor for recommendations. Otherwise, this uncomfortable state will cause stress and further weakening of the ability to remember. Therapy will help stabilize memory, and the patient will have no reason to get upset ahead of time. Early treatment will prevent symptoms from progressing, and healthy cognitive function will remain for many years.
2. Sudden memory loss.
This type of amnesia occurs suddenly, and the patient finds it difficult to carry out even basic household chores. A sharp loss of memory in older people manifests itself, for example, when a person left the entrance to go grocery shopping, and he suddenly forgot his goal and rushed to the nearest park. The reason for this may be pathologies in the brain or emotional experiences.
If close relatives do not take care of timely treatment and assistance for the elderly person, the disease can progress and become unsafe. Interruptions in mental activity worsen the quality of life, cause fear for the future and are met with misunderstanding from those around us.
3.Sudden amnesia.
The most complex case of the disorder, which is not diagnosed at the progression stage and is difficult to predict. An elderly person completely forgets everything that is important for his normal life - first name, last name, address, family members.
Such severe memory loss in older people makes it difficult to identify them, especially if they do not have a passport with them. Sudden amnesia explains the disappearance of pensioners when they cannot remember the location of their home and search the surrounding area without success. When asking them a question about their place of residence, random passers-by receive incomprehensible phrases in response, since the thoughts in their heads are also confused. If you are lucky, individual fragments of memories will appear, but there is usually no logic, and there is no single picture. If you find elderly people with memory loss, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Competent therapy will help stabilize the condition, and the case of severe amnesia will be erased from consciousness.
We recommend
“Products for people with dementia that will make life more comfortable and safer” Read more
Questions and answers
At what age does amnesia most often occur?
Typically, amnestic syndrome appears in people after 65 years of age due to senile changes in the brain. In other age groups, amnesia can occur after trauma, severe intoxication, or as a result of severe psycho-emotional shocks.
Is it possible to restore memory without taking medications?
Even with a regressing form of the disease of organic origin, certain groups of drugs may be required to restore memory in full. They will help normalize metabolic processes and restore bioelectric impulses. If amnesia appears after stress, then in mild cases, competent psychotherapy will be sufficient.
Our doctors
Pankov Alexander Rostislavovich
Neurologist
41 years of experience
Make an appointment
Novikova Larisa Vaganovna
Neuropathologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Belikov Alexander Valerievich
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
22 years of experience
Make an appointment