Types of communication
Depending on how communication occurs, on the specifics of people’s behavior, the following types :
- Primitive . Its peculiarity is indifference to the interlocutor, reluctance to understand him, as a rule, accompanied by fast, dismissive speech.
- Formal - or the level of masks. It is also characterized by a lack of interest in the interlocutor. Well-worn phrases, ostentatious politeness, false sympathy - this is a set of cliches under which it is easy to hide the true attitude towards another.
- Secular - empty, meaningless, ritual behavior. Filled with dialogues accepted in appropriate situations, when their content is of no interest to either side.
- Role-based - the basis of the attitude towards the interlocutor is not personal interest, but his social role.
- Business communication already presupposes closer relationships. Focus on results forces you to take into account the character traits, even the mood of your interlocutor. At this level, it is necessary to maintain distance, and the businesslike style characterizes the seriousness of the relationship.
- Interpersonal is close contact with the interlocutor, genuine interest in him.
- Manipulative level of communication - aims to achieve personal gain. The interlocutor is seen as a means, a living instrument on the path to personal interest. The “diplomatic” style is often used to resolve everyday issues.
- Playful or informal communication style . Friendly, light with a humorous twist, communication or flirting, a game devoid of obligations.
- Spiritual level . The highest degree of frankness in a relationship, when a person fully opens up in communication.
The psychology of professional communication can be placed in a separate category. Communication of this kind can be very different depending on its objects.
Classification of types of communication
Definition 6
Communication, as a socio-psychological phenomenon , is contact between individuals, carried out through language and speech and having various forms of manifestation.
Definition 7
Language is a system of verbal signs, a means through which communication between people is possible.
Definition 8
Speech is the use of language for the purpose of communication.
Do you need help from a teacher? Describe the task - and our experts will help you!
Communication, based on its characteristics, is divided into the following types:
Figure 2 . Types of communication
If we consider it based on contact with the interlocutor, then communication can be divided into direct and indirect.
Definition 9
Direct communication (otherwise known as direct) is a natural type of communication in which subjects are nearby and use speech, facial expressions or gestures.
This type is considered the most complete, due to the fact that individuals receive the largest amount of information about each other.
Definition 10
Indirect communication (otherwise, indirect) is created when individuals are at a distance from each other or separated by time.
This type includes correspondence, telephone conversation, and the like. Such communication carries incomplete psychological contact, especially when there are difficulties with feedback.
Communication can also be divided into interpersonal and mass.
Definition 11
Mass communication is numerous contacts between people who do not know each other. It is also communication mediated by different types of media.
This type of communication is divided into direct and indirect. Direct mass communication can be observed at rallies, demonstrations, various meetings and in any numerous social groups (for example, a crowd or audience). Indirect mass communication is one-way in nature and is directly related to mass culture and related means of communication.
If we consider communication according to the equality of partners in it (interpersonal communication), then it is divided into dialogic and monological.
Figure 3 . Types of Interpersonal Communication
Definition 12
During dialogical communication, subject-subject interaction occurs, in this case equal, its goal is mutual knowledge and the desire to realize the goals of each interlocutor.
Definition 13
Monologue communication assumes that the positions of the interlocutors are not equal and have the form of subject-object relations.
This type of communication is divided into imperative and manipulative.
Definition 14
Imperative communication is a form of authoritarian (directive) form of interaction with an interlocutor. Its goal is to control the interlocutor’s behavior, attitudes and thoughts, as well as to force him to perform certain actions or make decisions. In this case, the goal is in no way veiled, being open.
Definition 15
Manipulative communication is a form of communication between individuals, during which the influence on the interlocutor is carried out in a hidden way in order to achieve personal intentions.
Based on the type of communication, role-based and personal communication are distinguished.
Definition 16
Role communication develops under the influence of the status occupied by the interlocutors.
For example, this type of communication can include a conversation between a boss and a worker, or between a teacher and a student. The role-based type of communication is regulated by the rules and specifics of communication that are accepted in society.
Definition 17
Personal communication is directly dependent on the individual characteristics of the interlocutors and the relationships between them.
Communication can also be divided into short-term and long-term. This division depends on the goals, type of activity, individual nuances of the participants in communication, their likes and dislikes, and so on.
Information can be exchanged through verbal and non-verbal interaction. Verbal communication is the use of speech; everything else, the volume and timbre of the voice, gestures, postures, facial expressions (that is, paralinguistic means) is nonverbal communication.
Communication functions
- The pragmatic function of communication (or communicative) is the interaction of people at the level of interpersonal or intragroup communication. Communication is an important need for humans.
- The function of formation and development is that communication has a certain impact on the participants in communication, contributes to their development and improvement in all respects. Through communication with other people, a person learns social norms and values that have developed in society, gains knowledge and develops as a person.
- The confirmation function allows communication participants to recognize and confirm themselves.
- The function of uniting and separating people. Communication, on the one hand, facilitates the establishment of contacts between participants in communication, through which the necessary information is transferred. In addition, communication sets up communication participants to achieve common goals and objectives and thereby connects them into a single whole. On the other hand, communication can contribute to the isolation of the individual, as well as differentiation in the communication process.
- The function of organizing and maintaining interpersonal relationships. Communication helps to establish and maintain contacts and relationships between participants in communication, facilitating their joint activities.
- The intrapersonal function of communication is the communication of a person with himself. This can occur in the form of internal or external speech, which is completed as a dialogue. Such communication can be regarded as a universal way of thinking.
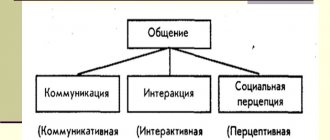
In accordance with the functions performed, three sides of communication :
- communicative , which consists in the exchange of information between participants in communication;
- the interactive side of communication lies in the interaction of people in the communication process;
- the perceptual side of communication, which lies in the fact that in the process of communication people perceive each other in a certain way.
Communication as communication
Communication can take the form of communication, which has a number of specific features:
- First, and above all, is the presence of two individuals, whose mutual information implies joint activity. Information must be accepted and understandable, therefore every communicative process is a unity of activity, communication and cognition;
- Secondly, the exchange of information involves influencing the behavior of the partner, i.e. there must be the possibility of mutual influence of partners on each other through a system of signs;
- Thirdly, in communication, influence is exercised when the communicator and the recipient have a single or similar system of codification and decodification;
- Fourthly, the possibility of communication barriers arising, then the connection that exists between communication and attitude clearly appears. Information disseminated in society passes through a kind of “trust-distrust filter.” This filter operates in such a way that true information may not be accepted, while false information will be accepted.
Figure 1. Communication as communication. Author24 - online exchange of student work
There are tools that weaken the effect of filters and promote the acceptance of information. Collectively, these means are called fascination, an example of which may be the musical or color accompaniment of speech.
Note 2
The communication process includes five elements: communicator - message - channel - audience - feedback.
In the process of communication, three positions of the communicator are distinguished - an open position, when he is a supporter of the point of view expressed, a detached position - the communicator is emphatically neutral, while orientation towards one of the points of view is not excluded, and a closed position, in which the point of view of the communicator is kept silent.
Among the communication skills, emphasis is placed on non-reflective and reflective listening. Non-reflective listening is an attentive silence that is used when the speaker is formulating a problem and the goal on his part is to release himself emotionally. When the speaker needs help solving a problem, not just emotional support, reflective listening is used.
Information exchange in communication has the main goal of developing a common meaning, a common point of view regarding various situations, which is characterized by a feedback mechanism.
There is indirect inverse, i.e. a veiled form of transmission of psychological information and direct communication.
During indirect feedback, rhetorical questions, ironic remarks, unexpected emotional reactions, and ridicule are used. In such cases, the communicator himself must guess what the communication partner wanted to tell him.
Communication styles
In communication psychology, there are several styles:
- Ritual communication is communication in which the main task is to maintain relationships with other people. In real communication, there are many so-called “rituals” - situations when a person behaves in a strictly defined way. All that is required from him is knowledge of how to behave in each specific case. For example, greeting acquaintances or strangers, talking about the weather and everyday problems - all these are elements of ritual communication.
- Manipulative communication is communication that comes down to the fact that one of the participants in the communication manipulates the other, i.e. One of the participants is a means to achieve a certain goal. But you should not assume that such communication is only negative. Professional communication and communication for the purpose of learning are manipulative in nature. In order to successfully cope with this type of communication, it is necessary to know the goals of the interlocutor, as well as the laws and techniques of manipulative communication.
- Humanistic communication is more of a personal communication that involves understanding and empathy. It is impossible to determine any single goal of humanistic communication. An example of such communication is a conversation between a doctor and a patient, pedagogical communication, etc.
- Authoritarian communication implies authoritative communication by one of the participants in communication. He does not encourage the initiative of his interlocutors; he considers his point of view to be the only correct one.
- Democratic communication - this style is characterized by encouraging the initiative of participants in the conversation, paying attention to the interests and goals of all participants in communication.
- Liberal communication. People who adhere to this style of communication are rather uninitiative, “go with the flow”, and make concessions to other participants in communication.
You need to especially carefully select your communication style when working on the psychology of communication with a client - this can be done in our online courses.
Share this article:
I liked the article
Lecture on the psychology of communication “The concept of communication”
Exercise 1.
The hardest thing to learn is a common language.
Alexander Kumor
Communication
is a multifaceted process of developing contacts between people, generated by the needs of joint activities and including the perception and understanding of another person, the exchange of information, and the development of a unified interaction strategy.
Types of communication:
- “Mask contact” is formal communication in which there is no desire to understand and take into account the personality characteristics of the interlocutor. The usual masks of politeness, severity, indifference, etc. are used. – a set of facial expressions, gestures, standard phrases that allow one to hide true emotions and attitude towards the interlocutor;
- Formally - role-based - the content and means of communication are regulated by the roles of communication partners: doctor and patient, traffic inspector and traffic violator, conductor and passenger, etc.
- Business communication – the purpose of which is to organize and optimize one or another type of activity: production, scientific, educational, etc. With such communication, the personality characteristics and character of the interlocutor are taken into account, but the interests of the matter, and not the personality of the interlocutor, are in the foreground;
- Secular is determined by formal politeness; the essence of communication is its non-objectivity, i.e. people say not what they think, but what is supposed to be said in such cases;
- Spiritual, interpersonal - the deep structures of the personality are revealed. Characterized by complete mutual understanding;
- Primitive - when they evaluate another person as a necessary or interfering object: if necessary, they actively come into contact, if it interferes, they push away, aggressive rude remarks may follow. If they get what they want from their interlocutor, they lose further interest in him and do not hide it;
- Manipulative – aimed at extracting benefits from the interlocutor using various techniques (flattery, intimidation, “showing off”, deception, demonstration of kindness) depending on the personality characteristics of the interlocutor.
Forms of communication:
— Direct communication
– carried out with the help of organs given to humans by nature (head, hands, vocal cords, etc.);
— Indirect communication
– associated with the use of special means and tools (stick, footprint on the ground, writing, television, radio, telephone, etc.);
— Direct communication
– this is a natural “face-to-face” contact, in which information is transmitted personally by one interlocutor to another;
— Indirect communication
involves the participation of an “intermediary” through whom information is transmitted;
— Interpersonal communication
is associated with direct contacts of people in groups or pairs and implies knowledge of the individual characteristics of the partner, joint experience in activities, and understanding. For example, communication in the family, at work, at college, etc.;
— Mass communication
– these are multiple connections and contacts of strangers in society, as well as communication through the media.
There are various forms of interpersonal communication
:
formal
(role-playing, business, functional) and
informal (
contact and indirect).
Differences
between
formal
and
informal
communication are expressed:
— the degree of inclusion of interpersonal relationships;
— the degree of consideration of the partner’s personal characteristics;
— a measure of the use of an arsenal of methods of psychological (rather than official, normative, institutional) influence.
Functional
(role-based, business, formal) communication proceeds according to norms and rules. For example, in business communication in a teaching environment, there are norms of official etiquette that do not allow a teacher to address his colleague on a first-name basis in the presence of students.
Informal
Interpersonal communication is divided into:
- contact and indirect
Contact
communication has its own specific features.
In contrast to mediated
communication, contact (direct) communication is characterized by active feedback, enriched by the context, the communication situation, and is served by a wide range of verbal and non-verbal means, is playful in nature and uses mechanisms of reflection to a greater extent. Contact communication involves direct communication between individuals and is considered as a certain level of achieved understanding, agreement, and degree of psychological intimacy.
In general, the mutual transition and mutual enrichment of formal and informal interpersonal communication, the richness of their forms determine the success of professional activity, provide a good climate in the team, promote good health and the preservation of neuropsychic health.
Communication functions:
— the pragmatic function of communication is realized through the interaction of people in the process of joint activity;
- the formative function manifests itself in the process of human development and his formation as a personality;
— the confirmation function is manifested in the fact that only in the process of communication an individual can understand, cognize and approve in his own eyes. Signs of confirmation include: introductions, greetings, and attention.
- function of organizing and maintaining interpersonal relationships;
— the intrapersonal function of communication is dialogue with oneself. Thanks to this function, a person makes decisions and performs actions.
Karpenko
According to the criterion
“goal of communication”,
he identifies
eight functions
that are implemented in any interaction process and ensure the achievement of certain goals in it:
— contact — establishing contact as a state of mutual readiness to receive and transmit messages and maintaining communication during interaction in the form of constant mutual orientation;
— informational — exchange of messages (information, opinions, decisions, plans, states), i.e. reception - what data is transmitted in response to a request received from a partner;
- incentive - stimulating the activity of the communication partner, which directs him to perform certain actions;
— coordination — mutual orientation and coordination of actions to organize joint activities;
- understanding - not only adequate perception and understanding of the essence of the message, but also the partners’ understanding of each other;
- amotive - inducing the necessary emotional experiences and states from a communication partner, changing one’s own experiences and states with his help;
- establishing relationships - awareness and fixation of one’s place in the system of role, status, business, interpersonal and other connections in which the individual will act;
- implementation of influence - change in the state, behavior, personal and meaningful formations of the partner (aspirations, opinions, decisions, actions, activity needs, norms and standards of behavior, etc.).
Answers on questions:
In my opinion , communication psychology studies
the interaction of people, through the development of contacts between them in joint activities, is the understanding and perception of the people around them, as well as the exchange of information.
In communication they highlight
informational, persuasive, expressive, suggestive and ritual models of communication. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Information model of communication.
It is usually used to transmit and receive information, analyze it, interpret it and comment on it. The transmitted information expands the information fund of communication participants, provides innovative information, explains the circumstances of the current situation, provides specific facts and figures that allow one to gain new knowledge or make an effective decision.
Persuasive communication model.
This model allows you to make communication participants like-minded people and get out of a particular situation with the greatest productivity. However, persuasion is a complex communication process, and not everyone is able to use this communication model to its maximum effectiveness.
Expressive model of communication.
The purpose of this model of communication is to form a psycho-emotional mood among the participants in the interaction, to convey feelings and experiences, to induce the necessary social action, and to involve them in specific actions. To use this type of communication, it is necessary, for example, in your public speech (lecture, speech) to use a variety of not only verbal and non-verbal communication techniques, but also audio, video and other illustrative means.
Suggestive model of communication.
Suggestive, i.e. suggestive, a model of communication, the art of suggesting rather than telling, is widely used in interaction practice, for example, at business meetings or in educational conversations with people in need of motivational correction.
For negotiations, presentations, public lectures, press conferences, trades, and business meetings, all 4 communication models are undoubtedly important. Each performs its necessary role.
The information
model
will sufficiently fully convey the information and facts necessary for people to perceive. However, in order for communication in the information model of communication to be effective, the following conditions are necessary: taking into account the cognitive capabilities of specific interlocutors, their individual attitudes towards obtaining new information and the intellectual capabilities for its processing, understanding and perception.
Persuasive Model
just as important. It will help convince people of the correctness of their facts, attitudes and decisions. But again there is a “BUT”. The most difficult task of this model is to turn an opposing opinion into a coinciding (necessary) one.
Next is the expressive function
, it provides a favorable climate for the same presentation, negotiations, and so on, which is the key to success. But due to differences of opinion, this climate may go in a negative direction.
And the advantages of the latest model, suggestive
, the suggestion itself. Some people are easily influenced psychologically.
To factors
The following human characteristics contribute to
suggestibility
- diffidence;
- anxiety, restlessness;
- timidity, low self-esteem;
- feelings of inferiority;
- increased emotionality, impressionability;
- poor command of logical analysis;
- faith in authorities.
But again, I believe that the difference of opinion (more than half the number of people present) will contribute to the ineffectiveness of this communication model.
Ritual model of communication.
The goal is to consolidate and maintain the norms of relationships, to ensure psychoregulation of the social psyche in large and small groups.
Conditions
- an artistically designed environment, canonization of actions and concentration of attention on the algorithm of their execution, the ceremonial nature of interaction and its orientation towards a binary impact (on those who perceive and perform the ritual at the same time).
Forms of communicative processes of influence:
• ritual acts;
• ceremonies;
• rituals;
• ritual complexes.
Technological features of organizing communicative action:
• reliance on national and territorial-professional traditions and communication norms;
• preliminary conclusion of a convention on the order of the ritual;
• concentration on the intrinsic value of ritual actions;
• theatricalization of communicative behavior.
The considered communication models do not cover all the possibilities of business communication, but they allow us to determine the specifics of interaction, the characteristics of the interlocutor and competently use the genre, communication means and technologies, and obtain the planned (predicted) result.
The sphere of scientific communication
is distinguished
by the fact that it pursues the goals of the most accurate, logical, and unambiguous expression of thought.
The leading position
in the scientific style is occupied by monologue speech.
Speech genres
, embodying this style of language are:
- scientific monographs;
- science articles;
- dissertations;
- various educational genres;
- scientific, technical, popular science literature;
- scientific reports;
- lectures.
In most cases, the scientific style is implemented
in written speech. However, with the development of mass communication, with the growing importance of science in modern society, and the increase in the number of various kinds of scientific contacts, such as conferences, symposiums, seminars, the role of oral scientific speech is increasing.
The main features of the scientific style
are accuracy,
abstractness
, logic and objectivity of presentation. It is they who form this functional style and determine the choice of vocabulary used in works of a scientific style.
Requirement
The accuracy of scientific speech
is predetermined by
such a feature of the vocabulary of scientific style as terminology.
In scientific speech, special and terminological vocabulary is actively used
. Recently, the role of international terminology has increased.
Feature
The use of vocabulary in a scientific style is that polysemantic stylistically neutral words are used in a scientific style not in all of their meanings, but, as a rule, only in one.
Business communication is a form of communication based on the principles of business etiquette, aimed at interacting with individuals or a group of individuals (organization) to achieve mutually beneficial results.
Successful business communication skills and understanding of the personality characteristics of the interlocutor and his interests should be considered a determining factor in the process of conducting business meetings.
Features of business communication are that:
- the interlocutor in the dialogue process acts as a significant person;
- the interest of people in the process of business interaction characterizes good mutual understanding in the assigned tasks;
- The primary goal of business communication is productive and effective cooperation.
Business communication is divided into two types:
:
1. Direct (immediate direct contact. Face to face or telephone conversation.)
2. Indirect (when there is some time delay in the interaction process, that is, emails, business notes, commercial proposals, etc.).
Journalistic style
- functional style of speech, which is used in
the following genres
:
- article
- feature article
- reportage
- feuilleton
- interview
- oratory speech
The journalistic style serves to influence people and inform them through the media (newspapers, magazines, television, posters, booklets).
It is characterized by the presence of socio-political vocabulary, logic, emotionality, evaluativeness, and appeal. It widely uses, in addition to neutral, high, solemn vocabulary and phraseology, emotionally charged words, the use of short sentences, chopped prose, verbless phrases, rhetorical questions, exclamations, repetitions, etc.
The linguistic features of this style are affected by
the breadth of the topic
: there is a need to include special vocabulary that requires explanation.
On the other hand, a number of topics are in the center of public attention, and vocabulary related to these topics takes on a journalistic connotation. Among such topics, we should highlight politics, economics, education, healthcare, criminology, and military topics. The journalistic style is characterized
by the use of evaluative vocabulary that has a strong emotional connotation (an energetic start, a firm position, a severe crisis).
Communicative style of personality
- a set of familiar ways and means of establishing and maintaining contacts with others in various forms of interaction - in conversations, negotiations, discussions, disputes, as well as in various interaction situations - developing ideas, making and formulating decisions, overcoming conflicts.
The communicative style of a person causes either a comfortable, uncertain (neutral), or uncomfortable effect on partners. It depends on how the individual perceives their condition, what energetic influence it has on them and to what extent it contributes to the emergence of an atmosphere of fruitful cooperation. There are three communication styles
: synergistic, non-synergistic and anti-synergistic.
Synergistic style
(from
the Greek
cooperation, commonwealth) differs in that the individual, through his manner of interaction with partners (partner), contributes to the unification of energy potentials and increasing the efficiency of joint activities. This becomes possible, firstly, thanks to the unhindered energy-information exchange between participants in business relations and, secondly, as a result of the addition and synchronization of their energies. The more partners who have synergy, the more clearly a special socio-psychological effect is manifested in their communication - together they achieve higher results than they could achieve if they acted separately.
The nonsynergic style
(Latin
non - no, no) is characterized by the fact that the individual cannot or does not want to contribute to the success of joint work. She takes the position of a detached observer, refrains from taking initiative, does not demonstrate complicity and empathy in the work process. All this indicates the passive manifestation of the individual’s energy potential, her weak participation in energy and information exchange, as well as the lack of synchronicity in interaction with the energies of partners.
Anti-synergistic style (Greek.
anti - opposite) is expressed in active destructive forms of behavior of the individual when interacting with partners. It harms the process and results of joint activities by the fact that it usually demonstratively opposes itself to the majority, either conflicts itself, or provokes conflicts between partners, and with its moods determines the chaotic nature of the emotional connections of the interacting parties. Anti-synergism sharply interferes with the energy-information exchange between partners and has a destabilizing effect on their joint biopsychic field. As a result, cooperation breaks down, and its results are lower than the effectiveness of individual group members.
Task No. 2.
Task No. 3.
Verbal communication (VC) –
This is an information and semantic exchange, interaction between people, occurring through speech and natural language.
Nonverbal communication
is the exchange of information without the use of speech. This is communication using facial expressions and various sign systems.
Language
- a complex sign system, naturally or artificially created and correlating conceptual content and typical sound (spelling).
Speech
- a historically established form of communication between people through linguistic structures created on the basis of certain rules.
Hearing
- the ability to listen carefully to another person's messages.
Kinesics
- a set of body movements (gestures, facial expressions) used in the process of human interaction (with the exception of movements of the speech apparatus).
Facial expressions
- “expressive movements of the facial muscles, which are one of the forms of manifestation of certain human feelings” [3] or “muscle movements in coordinated complexes, reflecting various mental states of a person” (L. M. Sukharebsky, 1966).
Gesture
- some action or movement of the human body or part of it, which has a certain meaning or meaning, that is, being a sign or symbol.
Takeshika
- nonverbal communication of people through touch (patting, shaking hands, kissing, hitting, etc.), as well as the field of psychology that studies it.
Proxemics
- a field of social
psychology
and semiotics that studies the spatial and temporal sign system of communication.
Monologue – 3
Dialogue – 1
Polylogue – 2
Task No. 4.
Reveal the main stages of a business conversation.
A business conversation is the most effective form of persuasion and motivation of interlocutors to accept your ideas, views, positions, and to “tune” people to certain actions.
The conversation can be formal
or
informal
,
individual
and
group
,
short-term
or
long-term
.
The basis for the success of
a business conversation is the clear logic of its preparation and conduct.
Stages of a business conversation
:
- Starting a conversation.
A psychologically correct start to a conversation is important for its successful conduct and achievement of planned results.
Task
- attract attention, interest, create an atmosphere of goodwill and trust.
Techniques for establishing contact:
organization of space, visual contact-eye contact, convenient mutual position, greeting, joining the interlocutor: according to state, in relation to something, according to interest, using the technique - small conversation - conversation on abstract topics, but interesting for the partner, asking questions questions are of particular importance to the partner.
- The ability to win over your interlocutor, to arouse in him a feeling of sympathy and goodwill towards you.
This can be achieved by addressing your partner by name, first name and patronymic. Addressing a person by name:
this is a manifestation of attention to a given individual, affirmation of a person as an individual, satisfaction of the need to establish himself as an individual, the formation of positive emotions, and a disposition to the source of these emotions.
- Transmission of information, presentation of one’s position and argumentation.
At the beginning of this stage, information about the partner’s position, problems and wishes is clarified. The transmission of information must be accurate and understandable - there should be no ambiguity or understatement. The information should be sufficient for your partner and at the same time concise. Do not use ambiguous words or, if it is necessary to use a particular word, explain in what sense you are using it; do not use professional terms or foreign words that are unfamiliar to your partner. During the conversation, periodically ask your interlocutor questions; but ask the first questions so that they are short, interesting and non-debatable.
- Dialogue of participants.
This stage includes a direct business conversation on the essence of the problem, argumentation and counter-argumentation. During the dialogue, firmly adhere to the main direction of the conversation, consistently pursue your thoughts, and persistently defend your position.
- Argumentation
- this is the rationale for the proposed provisions. With the help of arguments, you can completely or partially change the position and opinion of your interlocutor, soften contradictions, and critically examine the provisions and facts presented by both sides.
Tactics for using arguments
: at the beginning of the conversation, strong arguments are put forward, since during this period attention is concentrated on the perception of information; in the middle of the conversation, less strong arguments are used, taking into account the weakening of attention and perception; at the end of the conversation, stronger, weightier or, as they are also called, “killer” arguments are put forward , against which it is difficult to object. Adapt your arguments to the personality of your interlocutor, use terminology that is understandable to the interlocutor, otherwise he will not understand your argument.
- Summing up the discussion.
Clarifying the points of view of the interlocutors, identifying options for building a mutually acceptable position.
What requirements should be observed when discussing business information to maintain contact with the interlocutor?