Updated July 23, 2022 529 Author: Dmitry Petrov
Hello, dear readers of the KtoNaNovenkogo.ru blog. The term adaptation is used in various fields (biology, psychology, sociology, etc.).
It is very multifaceted and therefore raises a number of questions, including the main one - what is it all about.
Today we will talk about adaptation, its types, areas of application of the term and the meaning of adaptation in the processes of natural selection.
Adaptation is...
If we talk in simple terms about what adaptation is, we can limit ourselves to one word – “ adaptation ”. This is exactly how this term is translated from Latin.
We are talking about the adaptation of man, as a living being, to environmental conditions. The adaptation process begins from the first minute of an individual’s life, when he takes his first breath, and ends at the moment of death.
Synonyms for “adaptation” are the following words: development, opportunism, simplification, co-adaptation, change, acclimatization, accommodation, habituation.
The phenomenon of adaptation is aimed at fulfilling its main task - maintaining homeostasis . The latter, in turn, is a permanent (non-stopping) process of regulating the balance in the body for the purpose of survival. In this case, by organism we mean the unity of body and psyche.
For example, a person gets used to existing in certain conditions - people, climate, work, etc. When these conditions change, he will have to get used to the new: rebuild his old habits, acquire new qualities, ways of behavior, change his lifestyle in general. And all this in order to feel good in all aspects.
Another example of adaptation: if you want to suddenly get up from a lying position, then most likely your head will spin. This happens because blood rushes to the lower extremities: the blood flow going to the heart decreases in volume, the pressure drops.
To relieve dizziness, the body “catches up” the pressure by constricting blood vessels, the heart begins to beat more often in order to adapt the body to the new position of the body. After a few seconds, all unpleasant sensations go away.
Settlement.
Most species have developed mechanisms to remove offspring from the places where they were born. This process, called dispersal, increases the likelihood that offspring will grow up in unoccupied territory.
Most animals simply avoid places where there is too much competition. However, evidence is accumulating that dispersal is driven by genetic mechanisms.
Many plants have adapted to dispersing seeds with the help of animals. Thus, the fruits of the cocklebur have hooks on the surface, with which they cling to the fur of passing animals. Other plants produce tasty, fleshy fruits, such as berries, that are eaten by animals; the seeds pass through the digestive tract and are “sown” intact elsewhere. Plants also use wind to spread. For example, the wind carries the “propellers” of maple seeds, as well as cottonweed seeds, which have tufts of fine hairs. Steppe plants such as tumbleweeds, which acquire a spherical shape by the time the seeds ripen, are driven by the wind over long distances, dispersing seeds along the way.
Above were just some of the most striking examples of adaptations. However, almost every trait of any species is the result of adaptation. All these signs form a harmonious combination, which allows the body to successfully lead its own special way of life. Man in all his features, from the structure of the brain to the shape of the big toe, is the result of adaptation. Adaptive traits contributed to the survival and reproduction of his ancestors, who had the same traits. In general, the concept of adaptation is of great importance for all areas of biology. see also
HEREDITY.
Adaptation in biology and psychology
Initially, the phenomenon of homeostasis was studied only from a biological point of view: scientists studied how the body maintains the constancy of internal vital activity.
Adaptation in biology is a process aimed at ensuring the above-mentioned constancy under changing external conditions.
For example, if you are used to living in an area with low temperatures, then if you move to a country with a hot climate, you may feel some malaise (disturbance of homeostasis). All physiological resources will be used to restore balance.
Within a few days, the body will adapt its activities to the existing conditions - it will get used to the climate (acclimatization will occur), and your well-being will improve (homeostasis will be restored).
Later, Jean Piaget transferred the theory of adaptation from biology to psychology. From his point of view, adaptation in psychology is a process that includes two ways of regulating mental homeostasis:
- assimilation - the introduction of external factors into the internal environment.
For example, when you study something carefully and put it into practice, knowledge assimilates - it is included in your cognitive sphere. Or an example with assimilation in the context of upbringing - what parents teach their children is put aside “in the subcortex” and in the future becomes their attitudes; - accommodation is a change by an individual in his own cognitions for successful existence in the environment.
In this case, a person does not get used to what is, but changes himself, rebuilds what already exists - develops new ways of behavior and reactions. For example, when a woman becomes a mother, she changes many of her habits.
Thus, psychological adaptation represents an equal ratio of two vectors of human intellectual activity.
Reproduction.
A critical step in ensuring the continuity of life is reproduction, the process by which genetic material is passed on to the next generation. Reproduction has two important aspects: the meeting of opposite-sex individuals to exchange genetic material and the raising of offspring.
Among the adaptations that ensure the meeting of individuals of different sexes is sound communication. In some species, the sense of smell plays an important role in this sense. For example, cats are strongly attracted to the smell of a cat in heat. Many insects secrete the so-called. Attractants are chemical substances that attract individuals of the opposite sex. Flower scents are an effective plant adaptation to attract pollinating insects. Some flowers smell sweet and attract nectar-feeding bees; others smell disgusting, attracting flies that feed on carrion.
Vision is also very important for meeting individuals of different sexes. In birds, the male's mating behavior, his lush feathers and bright colors attract the female and prepare her for copulation. Flower color in plants often indicates which animal is needed to pollinate that plant. For example, flowers pollinated by hummingbirds are colored red, which attracts these birds.
Many animals have developed ways to protect their offspring in the early stages of life. Most adaptations of this kind are behavioral and involve actions by one or both parents that increase the chances of survival of the young. Most birds build nests that are specific to each species. However, some species, such as the cowbird, lay eggs in the nests of other bird species and entrust the young to the parental care of the host species. In many birds and mammals, as well as some fish, there is a period when one of the parents takes great risks, taking on the function of protecting the offspring. Although this behavior sometimes threatens the death of the parent, it ensures the safety of the offspring and the preservation of genetic material.
A number of animal and plant species use a different reproductive strategy: they produce a huge number of offspring and leave them unprotected. In this case, the low chances of survival of an individual growing individual are balanced by the large number of offspring. see also
REPRODUCTION.
Types of adaptation
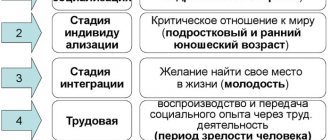
As mentioned above, adaptation is the adaptation of a person to the environment.
Modern science identifies 5 types of the phenomenon under consideration:
- Biological – adaptation to external conditions in the process of evolution (what is this?) by changing metabolism and organ functions. For example, the earliest people living in the wild had a brain with a volume of about 550 sq.cm.
For comparison, a modern individual’s brain volume reaches 1800 sq.cm. We can say that man has become smarter over many millions of years, thanks to progress: the brain has grown along with the development of civilization.
- Physiological adaptation is the restructuring of organic functions in accordance with environmental changes.
An example is visual adaptation: if you turn off the lights at night, you will not see anything for the first few minutes. Then your eyes will get used to the darkness, and you will begin to distinguish the furniture and objects around you. This can also include acclimatization, which was discussed above. - Socio-psychological – inclusion of the individual in society (family, class, team, community, etc.). In the process of adaptive behavior, an individual adapts to social norms and rules, adopts values and moral principles, and harmoniously merges into a new space.
An example here would be a situation where a child is enrolled in a kindergarten. First, the mother comes with the baby to the group for a couple of hours, then leaves him alone with the children for the same time, then the time spent in the kindergarten increases.So, gradually the child learns to be in a group without his mother and gets used to the established rules.
- Professional adaptation is the connection of the individual to the profession (work activity), the establishment of harmonious relationships with work and colleagues.
However, in the process of adaptation, an adaptation crisis may occur, which is associated with a discrepancy between expectations and reality. In this case, a person may need the help of a psychologist or mentor to enter the professional environment more comfortably. - Personnel adaptation – introducing new employees to the conditions, norms, rules and tasks of work, joining the established team.
This is an important stage that all employers need to consider: a new employee may show poor performance not because of a lack of knowledge, but because of the stress experienced in connection with a new situation for him.
Genetic basis.
Also on topic:
BIOLOGY
In each species, the program for the development of traits is embedded in the genetic material. The material and the program encoded in it are passed on from one generation to the next, remaining relatively unchanged, so that representatives of a given species look and behave almost the same. However, in a population of organisms of any species there are always small changes in the genetic material and, therefore, variations in the characteristics of individual individuals. It is from these diverse genetic variations that the process of adaptation selects those traits or favors the development of those traits that most increase the chances of survival and thereby the preservation of genetic material. Adaptation can thus be thought of as the process by which genetic material increases its chances of persistence in subsequent generations. From this point of view, each species represents a successful way of preserving certain genetic material.
To pass on genetic material, an individual of any species must be able to feed, survive until the breeding season, leave offspring, and then spread them over as wide an area as possible.
Types of disorders and methods of eliminating them
Violations are easier to notice by the inability of an individual to adapt to a group. Psychology and psychiatry, as related fields, use the same diagnostic criteria presented in the International Classification of Diseases:
- decreased attention and concentration;
- loss of the ability to do usual activities;
- obsessive thoughts, excessive preoccupation with the situation;
- loss of interest in work and hobbies;
- refusal of social contacts.
Tests, interviews, and psychometric studies are used as diagnostic tools. Based on the results, the patient is prescribed treatment. Psychotherapeutic methods and medications are most often used:
- Anxiolytics - Phenazepam and its analogues. They reduce anxiety, normalize sleep and digestion. They can be addictive, so they are used carefully, in small doses. If side effects occur, the drug is discontinued.
- Antidepressants - Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline. Normalize the production of hormones, regulate the functioning of the nervous system. The drug is selected individually. When taking the medicine, the patient should keep an observation diary and note changes in his emotional state.
Professional psychotherapeutic methods of treatment - hypnotherapy, autogenic training, cognitive exercises.
To independently increase your ability to adapt, you need to choose techniques that increase stress resistance and activate the body’s compensatory capabilities. Automotive training, meditation, and yoga are most suitable for this. Exercises that relieve muscle tension affect vital activity, emotional state, and reduce the risk of developing maladjustment.
Arturli zhagdaylardagi beyimdelis
Organismal kondeliktti tyrshilik zhagdayina, enbek zhuktemelerinde, azalary men tissuederinde unhemi korektik zattar men su tapshilygy, otegі zhetіspeushіgі, temperature uytkular, gazdardyn ulestik kysymynyn ozgeristeri baikalady. Wasps ozgerister zhane olardy retteushi zhuyeler kalypty physiologicalyk mekhander archyly organismnіn beіmdelіs negіzіn zhasaida.
Kanday da bіr climatik faktorlarg beyimdelіs kezinde adam aғasy kalypty omir suru alanynd ardaiym faktorlardyn kurdelі kompleksterim kezdesіp otyrady.
The temperature is always important. And the temperature of the body will be undesirable. Adam suyk zherlerde nemese tonazytkyshtarda zhumys іstegende, algashky kezde onyng zhylu ondirui tiimsiz, orasan kop, al zhylu shygaruy alі de zhetkіlіkіz bolada. Keyin zhylóndiru men zhylúgaru protsesterí ténestírílíp bejímdelístín tiyanakty kezí kalyptasada. The connection was made to change the temperature of the water supply mode. Munda beyarnamalik beyimdelіs kubyly oldmen qatar, suykty kabyldaudy bejeimdeytin zhan dané temperatureson belgіlі yrgyry zhasaityn arnayi mekhander katysady.
Balalardyn temperaturelyk ozgeristerge aserlenisi zhas kezenderine saikes zhetiledi. Algashky balalyk shakta olar zhogary temperaturedan gөrі salkyndykty zhaksy koredі.
Bul, arine, olardyn zhylu rettelisinin tolyk zhetilmegendigin korsetedi. Oytkeni balalardyn wasps zhas kezenderinde zhylu rettelui, terisinin kurylysy, now tamyrlanuy zhete kalyptaspida. Sondyktan terі bezderіnіn sana zhetkіliktі bologanymen, terleu aserlenіsі ғzanaţ zhylu šaruyųn tolík kamtamasyz etpeydі. Zhas ұlғaygan sayyn terleu kusheye tүsedі. Balalar omіrіnіn algashky aylarynda terі әrі suyktyk, әrі zhylylyk titirkenshdirgіshterge berdey shigada. Bіr zhaska deyіngі balalarda, ulkenderge karaganda, іshіnar reflexіk terleu Ote zhoghari baikalada temperature.
Sonymen bіrge balalardyn dene aumagy men salmagynyn araqatynasy ulken bolgandyktan, azanyn zhylu shygaruy karkyndy otedi. Balalyk shakta bastalgan klimatka beіmdelіs ote tiіmdі zhane otornykty bolada. If you are tired of the body, now the devices will be safe. In fact, we are talking about the psychiatry, the immune system, and the anatomy and physiology. rekshelikterine saikes zhagdaylar zhasaluy tisis.
This will prevent the reaction from causing disadaptation of the kalpa.
Beyimdelu reactiony kalpas – korshagan orta factorlaryn aserinen tuyndagan adam aғzasynyn zhauap take zhuyesіnіn ozgeru stepi. In addition, there is a problem with the pathology of the body - disadaptation of the tight back. Mysaly, sportshylarda cardiosclerosis boluy, zhugіru kezinde zhurek zhumysynyn buzyluyna akelip soguy mukkin.
Adam and zhogary temperature beyimdelіs reactions.
Burners temperature and then suykka beyimdelu tektes bolada. Alaida munda organismdegі ozgerіster suyktykka karaganda karama-karsy. Bul rette beyimdelistin bastapki kesi tynys, zhurek sogysyny n zhilіlenuinen bastalady. Aғzada kan moulsheri qaita bolіnіp, іshkі ағзалAIDа ol азаяди yes, срткћдень мілшері қайта мълінінін, ішкі ағзалAIDа oli азaяді Yes, срткћдћнћ dene betinің tamyrlarynda kan ағымы zhedeldeydі.
And the burn temperature su-tuz almasuyn reteytin endocrindik zhuyeler arkyly ikemdeledi. Antidiuretic hormonal salts belsendiriledi. Sebebi kop terlegendikten, and su mulsheri azayady, al osmoreceptorlar archyla hypothalamus mol akparat zhetkіzedі. Soytіp ADH byrekke aser etyp, sudyn kayta sіnіrіlіluіn kusheytіp, diuresis dézhidі.
Diagnostics
An individual can be diagnosed with adjustment disorder based on the presence of symptoms:
- Asthenic - fatigue, increased irritability, sleep disturbance.
- Anxious - increased excitability, causeless anxiety, drowsiness, nausea, dizziness, loss of a sense of security.
- Depressive - predominance of decadent mood, decreased concentration, apathy.
- Behavioral reactions - indifference to the team, withdrawal into negative habits, a sharp change in the usual way of life.
- Inappropriate emotional reactions - increased level of aggression, sudden outbursts of anger, followed by apathy.
- Cognitive reactions - decreased speed of information processing, intellectual productivity.
- Vegetative syndrome - muscle spasms, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, sweating, rapid heartbeat.
In cases of severe adjustment disorder, a person experiences suicidal mood. This does not necessarily lead to a suicide attempt, but is often accompanied by self-harm: the person cuts himself.
Factors
The causes of adaptation disorder are emotional and stress factors. They provoke the development of a negative emotional state in which a person is unable to adequately respond to changes in the environment. Such reasons include:
- emotional and psychological abuse;
- difficult life situation caused by sudden changes in external conditions;
- chronic central nervous system disorders;
- somatic diseases;
- prolonged increased mental stress;
- being in a situation of limited resources (lack of sleep, malnutrition).
At risk are people whose living conditions contribute to adaptation disorder: military personnel, medical workers, migrants, elderly people, students.