About five percent of the world's population experiences panic attacks. Usually these are young people between the ages of twenty and thirty. Moreover, women are more susceptible to the disease. Panic is a normal reaction of the body to stress, but what are the reasons for its appearance, since there seem to be none?
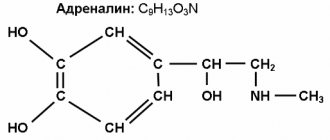
A panic attack causes a powerful release of adrenaline, a hormone that involves preparing the body for an extreme situation and reacting to it, such as flight or fight. Breathing and heart rate increase, hyperventilation of the lungs occurs, which leads to dizziness, numbness and tingling of the legs and arms.
This is how the body usually reacts to sudden danger, this is normal. Thus, a panic attack is a malfunction of the body that causes the “emergency mode” to turn on, although this is not necessary.
More about panic attacks
Panic attacks are a sharp increase in anxiety and fears that are generated by an internal state and are not related to the current situation. A typical form of panic fear is accompanied by various vegetative-vascular and motor manifestations, such as:
- pronounced feeling of anxiety;
- fear for your health and life;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased sweating;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- trembling in the body;
- lump in throat;
- feeling of lack of air;
- abdominal pain and gastric disorders.
Panic attacks very rarely (about 1%) are a sign of serious diseases, such as heart defects, pheochromocytoma, oncology, etc., in the vast majority of cases they are associated with the psycho-emotional sphere and the autonomic nervous system. It is through the autonomic nervous system that all the mechanisms of panic attacks are realized.
Photo on Unsplash
An atypical form of a panic attack, the so-called “panic without panic,” can be manifested by temporary loss of hearing, voice, vision (a veil before the eyes), a person’s sense of taste and smell disappears, and motor skills are turned off. Such symptoms are usually observed in serious procedural mental disorders.
What main areas of differential diagnosis can you name?
Before answering questions about diagnosis and how to treat panic attacks, I want to remind you what they are. A panic attack is an attack of fear that occurs unexpectedly and without good reason, manifested in a sharp change in psycho-emotional state and accompanied by negative reactions at the physiological level. The main ones are tachycardia, breathing problems, pain in the heart, sudden fluctuations in blood pressure, dizziness, trembling throughout the body, numbness of the hands, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Such symptoms of a panic attack (hereinafter referred to as PA) are similar to the symptoms of some organic diseases and mental disorders. It is in these two main areas that differential diagnosis should be carried out.
Let's start with the differential diagnosis of PA from common somatic diseases:
1. Bronchial asthma. During an attack of asthma, wheezing and difficulty breathing are observed. During panic attacks, there are problems with breathing. Even at its maximum height, a person experiences a feeling of lack of air.
2. Hypertension . In this case, the difficulty of diagnosis lies in the fact that during a hypertensive crisis, real attacks of PA can be observed, which further aggravate the patient’s condition. The sensations of the patients themselves, as well as the absence of elevated blood pressure outside of an attack, help to distinguish PA from a crisis. In addition, in PA, hypertension is not long-lasting and does not lead to left ventricular hypertrophy and retinal damage.
3. Angina pectoris . The localization and nature of pain in PA differs from ischemic pain. Usually they are not associated with physical activity, decrease with distraction, and are not relieved by nitroglycerin. In contrast to myocardial infarction, markers of cardiac muscle tissue necrosis in PA are within the reference values.
4. Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) . It is observed in approximately 10-15% of adults. It manifests itself as sudden attacks of tachycardia, arrhythmia in the form of extrasystoles, sometimes shortness of breath, chest pain and general weakness. Usually the attacks are not dangerous to health; in about half of the cases, symptoms of MVP may not appear at all. But their sudden occurrence and the unusualness of the sensations experienced can provoke true PA, especially in impressionable people prone to hypochondria. Objective examination methods - ECG, EchoCG, FCG, characteristic noises during auscultation in people with MVP help to distinguish between PA and MVP.
5. Endocrine pathology of the thyroid gland (hyper- or hypothyroidism) and adrenal glands (pheochromocytoma). For differential diagnosis, ultrasound and CT scan of these organs, tests for thyroid hormones (T4, T3, TSH) and catecholamines are performed. 6. Disorders of hypothalamic-pituitary regulation . These disorders can be differentiated from PA by the presence of a history of disorders such as: • menstrual irregularities; • galactorrhea; • polycystic ovary syndrome; • primary infertility; • weight fluctuations; • bulimia attacks; • increased levels of prolactin in the blood; • more pronounced neurological symptoms; • EEG data.
7. Epilepsy . Epilepsy attacks are characterized by short duration (1-2 minutes) and specific psychomotor and sensory epileptic phenomena. Objectively, changes are observed in the EEG both during an epileptic seizure and between attacks. 8. Hypoglycemia , i.e. decrease in blood glucose levels. It may be a consequence of an overdose of insulin in diabetes mellitus, some liver diseases, surgical interventions on the stomach, prolonged hyperthermia, hyperhidrosis, anorexia, fasting, and large gaps between meals. Often occurs during pregnancy. It is accompanied by symptoms similar to PA - tachycardia, dizziness, tremor, increased sweating, weakness and increased anxiety. The main distinguishing criterion of hypoglycemia is a reduced concentration of glucose in the blood. But it is not always possible to detect this decrease at the time of an attack, and in the interictal period the indicator may be within normal limits. Therefore, another way to distinguish an attack of PA from a state of hypoglycemia is to try to stop the attack by eating something sweet containing sugar. With PA, this will not lead to anything, but during an attack of hypoglycemia, after about 20 minutes the condition will significantly improve due to the restoration of normal glucose levels. The mental disorders with which PA should be differentiated include the following: • Psychosomatic , or somatoform. They are also characterized by cardiovascular disorders, but unlike PA they are accompanied by other symptoms - disturbances in speech, vision, hearing, gait, voice changes, seizures, etc. • OCD (obsessive-compulsive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder). The obsessive thoughts and actions characteristic of it can also be expressed in PA, but to a much lesser extent. With OCD, there may be panic attacks, but they are not typical for it and occur mainly when trying to suppress obsessive thoughts and actions, i.e. with psychological violence of the patient against himself. • Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Panic in this case can occur under circumstances reminiscent of the mental trauma received. In their absence, PA does not develop. In addition, a person prone to panic attacks tries to avoid situations that can provoke them, and with PTSD, the patient avoids those places or situations in which the event that caused the trauma may occur. For example, with PA a person is afraid to ride the subway because he once developed a panic attack there, and with PTSD because he previously became a victim of aggressive actions or accidents there and is afraid to again become a hostage to circumstances or terrorists. • Hysterical attack. Characterized by demonstrative behavior, “inflating” unimportant and insignificant symptoms. Most often observed in egocentric people, people prone to dramatizing situations and with inflated demands on the surrounding community. With real PA, a person never plays to the public, he is completely focused only on himself, his feelings and his excessive panic fear. It is almost impossible for even the closest people to “break through” to his consciousness.
Only by excluding the presence of organic structural changes in organs and making sure that he is dealing with true PA, developing independently or against the background of other mental disorders, can a psychotherapist prescribe adequate and effective therapy for panic attacks.
Signs of a panic attack
It's surprising that not everyone who suffers from panic attacks knows what it is. It often happens that a panic attack is mistaken for some kind of heart disease, because they have a number of similar symptoms.
A vegetative crisis (an alternative name for a panic attack) can begin with increased heart rate, chest pain, and a feeling of shortness of breath. Patients attempt to relieve symptoms with the help of heart medications, but in this case they will not have the expected effect.
Photo on Unsplash
Other signs of a crisis include trembling hands, dizziness, excessive sweating, chills, a feeling of unreality of what is happening, impending loss of consciousness, inexplicable uncontrollable fear. At the same time, the presence of fear is not at all necessary: at the moment of an attack there may not be a panic attack, but instead, sadness, tearfulness or aggression are felt.
The duration of a panic attack can vary. The average duration is from 15 minutes to half an hour. Frequency of attacks: from several episodes a day to a couple of times a month. In principle, this is not a dangerous phenomenon, but there is a risk that panic attacks can have a bad effect on the psychological state, which will only increase their number.
Basic information and theories of origin
A panic attack can last from a few minutes to an hour. But most often it lasts no more than half an hour and goes away as abruptly as it appeared. And although it does not pose a serious threat to physical health, such attacks of severe fear are very exhausting and damage a person’s mental state. In addition, having once suffered such an attack, people are unconsciously afraid of its repetition and are constantly in a state of stress, which further aggravates the situation. In the future, panic attacks can lead to:
- avoiding crowded places and limiting movement;
- fear of being alone;
- fear of being far from home or in a place where it is impossible to quickly receive qualified medical care;
- severe depressive states;
- disturbances in concentration;
- loss of performance.
Today, panic attacks are not uncommon among either women or men. Although women are 5 times more likely to suffer from them than men. According to statistics, about 10-20% of people around the world experience a panic attack at least once in their lives. In other words, almost every fifth person experienced an attack of severe fear at least once. Therefore, many experts already consider panic attacks not even as a disorder, but as a feature of human behavior.
At the same time, about 0.5-1% of people regularly experience panic attacks. But this is an average. It varies greatly depending on a person's region of residence, country, social conditions and other factors. In such situations, they already speak of the presence of pathology, and in 2/3 of all cases, neurological or mental disorders are detected. And 20% of people from this number have alcohol or drug addiction.
Most often, panic attacks are observed in women and men aged 25-45 years. Although they can also occur in older people and adolescents. It has been noted that they are more typical for people with an above average level of intelligence.
Panic attacks can occur on their own or develop against the background of other diseases, not only mental, but also pathologies of the cardiovascular, endocrine system and others. Sigmund Freud once attempted to describe panic attacks by calling them anxiety attacks. Subsequently, they were considered as a manifestation of vegetative-vascular dystonia and were called an emotional-vegetative crisis.
A large amount of work has been done on the study of anxiety states, and only in 1980 the term “panic attack” was introduced, including in ICD-10, to describe the main manifestation of such disorders. But research in this area and anxiety disorders developing against the background of panic attacks is still ongoing. The result of this was the creation of a number of theories of the occurrence of panic attacks, although today many experts are inclined to believe that a panic attack is a consequence of a combination of various factors described in individual theories.
It has been precisely established that the primary source of their development is the physiological processes occurring in the body as a result of stress, namely changes in the functioning of the temporal lobes of the brain and some parts of the limbic system (a set of brain structures located on the sides of the thalamus). As a result of anxious thoughts, adrenaline is released, which aggravates anxiety. This in turn can trigger a panic attack, which increases anxiety. This creates a vicious circle that can be difficult to break.
Catecholamine theory
This hypothesis is based on the possibility of a panic attack occurring against the background of an increase in the level of catecholamines, which include adrenaline. They are produced by the adrenal cortex in response to stress factors. These compounds have stimulant properties, meaning they cause blood vessels to constrict, which leads to increased blood pressure levels, and also stimulate the nervous system and lead to an increase in heart rate.
Genetic theory
This theory is based on the fact that 15-20% of people suffering from panic attacks have relatives with the same anxiety disorders.
Psychoanalytic theory
This hypothesis was developed by S. Freud and has since been refined by other researchers. According to it, panic attacks occur against the background of a lack of emotional, including sexual, release, and the presence of a person’s conflict with himself and his needs. This leads to physical tension. Over time, a conflict or other stressful situation provokes the development of anxiety.
Behavioral theory
This theory is based on the connection between a panic attack and external causes, which can be situations that threaten a person in one way or another. The resulting increase in heart rate is recorded by the body as a trigger. And subsequently, when the pulse rate increases, which may be a symptom of one or another heart pathology, a panic attack develops even in the absence of a threat.
This theory also describes cases of the development of anxiety states in people prone to pessimism. For example, one day, while in transport, a person is struck by the thought that an accident might happen. If it causes fear, a panic attack may develop even against the background of complete well-being and no danger to life. In such cases, a panic attack is not a consequence of a direct threat, but of a far-fetched potential situation.
Cognitive theory
This theory is based on a person’s ability to misinterpret their feelings. Thus, shortness of breath after exercise or increased heart rate may be mistakenly perceived as life-threatening. The result is fear and a panic attack.
Causes of panic attacks and risk factors
Panic attacks can be caused by any illness or experience. Most often they occur in people whose lives include at least one of the following factors:
- lack of physical activity;
- caffeine abuse;
- bad habits;
- suppression of emotions within oneself;
- lack of proper sleep and rest.
The tendency to panic attacks develops under conditions of an accelerated pace of life and chronic stress. Sometimes the condition develops against the background of mental disorders, but can also accompany coronary heart disease, mitral valve prolapse, thyrotoxicosis, depression, post-traumatic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder and other diseases.
Stages of panic attacks
There are three stages of a panic attack:
- initial – warning signs of a panic attack appear. This may be some anxiety, uncertainty, heaviness in the head, inexplicable discomfort;
- expanded - a feeling of anxiety and fear appears, which steadily increases. It is at this stage that the main symptoms affecting the cardiovascular and respiratory systems occur. When anxiety and fear turn into panic, a person can no longer control himself;
- final - a feeling of lethargy, fatigue and weakness appears.
Foreplay can last up to half an hour, this time is quite enough to provide assistance and get rid of a panic attack. Panic, when a person is in a state of derealization, lasts on average about 30-40 minutes, maximum an hour. After a panic attack ends, it sometimes takes a day or more to fully recover and get rid of the consequences.
Photo by Max Nelson on Unsplash
Most often, panic attacks occur in the evening and at night, which can cause chronic insomnia, which in turn is a risk factor for the development of a panic state.
Symptoms of panic attacks
Symptoms characteristic of panic attacks are conventionally divided into two groups: physical and mental. The first group includes bodily sensations, and the second – mental ones.
Mental symptoms of panic attacks:
- Fear of death;
- lump in the throat;
- a feeling of unreality of what is happening;
- pre-fainting state.
Physical symptoms of panic attacks:
- Frequent heartbeat;
- hot flashes;
- chills;
- increased sweating;
- dry mouth;
- diarrhea;
- chest pain;
- numbness of the limbs;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness;
- dizziness.
Sometimes a panic attack follows an atypical scenario in the absence of fear and other manifestations. Instead, one of the body’s functions is temporarily disrupted - vision is lost, the gift of speech is lost. Another name for such attacks is hysterical neurosis.
Drug therapy
Certain medications can help reduce some of the symptoms of a panic attack. If the patient’s brain has a disturbance in the exchange of neurotransmitters, the balance of the processes of excitation and inhibition, then they are prescribed much more than in milder cases.
At the first stage, medications relieve the attack, and then restore the functioning of various brain systems. They are able to eliminate the panic state altogether, or weaken it.
- Tranquilizers are prescribed at the very beginning of treatment and not for long, as they cause addiction. These drugs extinguish the severity of the attack, stabilize the autonomic system, and normalize sleep.
- Antidepressants require caution - you need to be careful about their contraindications, so the selection is strictly individual. It is interesting that similar products from different manufacturers can have different effects on the patient.
- Antipsychotics are used extremely rarely - only if panic disorder cannot be cured with other medications, as well as in the presence of a personality disorder or metabolic disorders in the brain. In addition, they are very difficult to find.
- Neurometabolic drugs are very active, so they are used strictly in courses and administered in the presence of a doctor. They allow you to reduce the doses of other psychotropic drugs.
It is necessary to emphasize once again that all of the above medications are prescribed personally. The doctor should pay special attention to their effect on the patient, especially in the first days, monitor the intake, cancel and re-prescribe in case of adverse events.
Diagnosis of panic attacks
Even a doctor cannot always separate the symptoms characteristic of a panic attack from the manifestations of another disease. To clarify the diagnosis, the skin is examined, reflexes are checked, and the abdomen is examined.
Photo by Ani Kolleshi on Unsplash
The main methods of examination are electrocardiography, listening to the lungs and heart, measuring pulse and oxygen saturation. A panic attack is diagnosed based on a set of data obtained.
What to do during a panic attack
- Autotraining . The patient must tirelessly convince himself during a panic attack that this is a temporary phenomenon, its symptoms are not dangerous and will soon pass.
- Technique of switching attention . A panic attack can be easily dealt with if you stop thinking about it. This can be easily done by simply switching your attention to something. Slowly count to 50, do simple addition or multiplication in your head, talk to someone about an abstract topic.
- Normalization of the respiratory process . A person often experiences shortness of breath during a panic attack. This happens due to an imbalance in the gas balance in the blood. It needs to be normalized as soon as possible. To do this, you need to press a paper bag very tightly to your nose and mouth, and slowly inhale and exhale into it for about thirty seconds. In the absence of a package, you can use folded palms.
Is it possible to overcome forever
To overcome panic disorder forever, long-term work with a psychotherapist, taking a course of medications, and the patient’s efforts are required. It is important to find the root cause of anxiety - it is often hidden deep in the subconscious. Next, you need to learn how to independently smooth out the symptoms during an attack.
The nuances of therapy depend on the severity of the disorder, its duration, severity and personal characteristics of the body. It is believed that the most severe PAs occur in those patients who perceived the first attack as a fatal catastrophe. The sooner treatment begins, the faster and easier it will be. Full recovery occurs in the presence of two factors - a competent treatment regimen and a lot of effort from the patient.
Medications to treat panic attacks
Drug treatment of panic attacks includes the use of the following types of medications:
- tranquilizers;
- neuroleptics;
- antidepressants;
The main disadvantage of these methods is the instability of the effect after taking a course of medications. For some, after a year, for others even earlier, relapses of panic attacks may occur. Doctors attribute this to the fact that the patient has not developed the skills to manage emotions in stressful situations.
Treatment
Increased self-esteem
One of the areas of treatment for panic attacks is to work on increasing self-esteem and self-confidence. And also on the ability to be critical of the personality of your parents. The ability to criticize the upbringing that was given to him by his parents will allow a person to move forward, working on his personal characteristics and developing his own individuality, rather than freezing in place, afraid to change what the adults who are significant to him have created.
In the process of psychotherapy, a person goes through the following stages:
- Understanding that parents are not perfect, since they are ordinary people;
- Protest against the methods of education that parents used and against the parents themselves;
- Separation - mental separation from parents;
- The beginning of the formation of one's own personality;
- Acceptance and gratitude to parents for doing everything they could and as best they could to raise their child.
- Accepting yourself as you are and starting to build your life in accordance with your own preferences.
Disclaimer
It is worth noting that all the procedures described in this section are best carried out under the supervision of a psychotherapist or psychologist. Or at least visit him periodically and tell him about the work done in order to receive the necessary recommendations and make adjustments to your wellness actions.
Self-treatment
Simultaneously with working on self-esteem, it is necessary to carry out procedures that help reduce anxiety.
Helps reduce anxiety:
- Breathing exercises;
- Sports activities;
- Autogenic training;
- Relaxation exercises.
Medicines
Also, if a psychiatrist or neurologist prescribes medications, then you should not neglect them, just as you should not get carried away.
Medicines should be treated as an auxiliary tool that facilitates psychotherapy and the dosage of which should be constantly reduced as psychotherapeutic treatment progresses.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapeutic treatment can be carried out in various directions:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy. It will help you develop the habit of not being afraid of panic attacks.
- Body-oriented therapy. Will teach you to understand the body signals that precede panic attacks, as well as manage bodily reactions to reduce symptoms.
- Hypnotherapy. It will help create new internal attitudes that promote mental immunity, helping to predict and prevent panic attacks.
In addition to all of the above, a psychotherapist will help you understand the causes of PA. During psychotherapeutic sessions, it will become clear what underlies this disorder and what events or series of events led to it.
Complex treatment
In order for the treatment of panic attacks to be successful, a certain number of vectors must converge:
- A doctor prescribing medications must respect psychotherapeutic methods of treatment and understand that medications do not fully treat a mental disorder, but only relieve certain bodily symptoms and adjust the chemical and hormonal background of the body. As soon as a person stops taking them, his body stops producing the chemical elements necessary to maintain health. Therefore, in the long term, medications lead to addiction.
- The psychotherapist should also not sabotage drug treatment, but should enter into collaboration with the doctor to discuss the results of drug-psychotherapeutic treatment, as well as determine and adjust the dosage of medications.
- The third condition is the cooperation of the patient himself with the specialists treating him. He should try to be honest with them and follow all their instructions. In other words, the patient must feel responsible for what happens to him and not shift it to the people treating him.
Treatment results
If client-doctor-psychotherapist cooperation is established, then a decrease in the number of panic attacks will gradually be observed, as a result of which they will stop completely.
As treatment progresses, the dosage of medications should be reduced until they are completely discontinued. All this should happen against the background of psychotherapeutic treatment.
As general anxiety decreases, both phobias and panic attacks will go away, that is, complete physical and mental recovery will occur.
Author: Dmitry Malin - clinical psychologist
Consequences of a panic attack
Constantly recurring panic attacks can lead to neurotic personality changes, when a person develops internal blocks on a subconscious level that do not allow him to receive full and effective help. When a person gets used to his neurosis, any attempts to bring him out of this state encounter active resistance. This can lead to loss of ability to work, social maladjustment and disability.
If the attacks are pronounced and occur very often, the person becomes antisocial. In this case, to get rid of them, you need the help of a psychiatrist or psychotherapist and treatment in a hospital setting.
Is it possible to go crazy from panic attacks?
Manifestations of a panic attack are often a feeling of unreality of everything that is happening around, disorientation in space and time, loss of control over one’s actions, deeds and the world around us. All these symptoms are often accompanied by a fear of going crazy.
Many people who have survived an attack do not know how to get rid of panic attacks forever, and are afraid of developing psychosis, schizophrenia and other serious mental disorders. To dispel these fears, you need to know the nature of panic attacks.
Photo by Ian Espinosa on Unsplash
During a panic attack, the rhythm of breathing involuntarily changes, it becomes more frequent, which is a natural protective reaction of the body - preparation for fight or flight in any dangerous situation. As a result, excessive amounts of oxygen enter the blood. This leads to acidification and dilation of brain vessels, which, in turn, causes a feeling of derealization.
This condition increases the fear of the possibility of dying or going crazy. Every patient must understand that this is a natural reaction of the body, in which no changes occur in the central nervous system, and all fears are only subjective sensations that have no neurophysiological basis. A qualified psychologist at our center can explain all this to him.
Psychotherapy
Good results in the treatment of PA are achieved only with a combination of medication, pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy. The central task of the latter method is to gradually bring the patient to an awareness of the essence of the problem. Other goals of psychotherapy:
- identification and elimination of psychological intrapersonal conflicts;
- modification of previous inappropriate reactions to stress;
- developing healthy patterns and attitudes, attitudes and attitudes for learning mature adaptation mechanisms;
- working with self-control and adequate ways of responding;
- identifying the root causes of pathology.
In the cognitive behavioral approach, a psychotherapist or clinical psychologist teaches the patient techniques to control his own thought process. The client learns to understand his own condition and is able to identify factors that provoke anxiety. The nuances of the lifestyle and rhythm of life are examined.
Psychoanalysis helps to discover the subconscious, underlying causes of PA. Other approaches to the psychotherapy of panic disorder are classical or Ericksonian hypnosis, family consultations, and Gestalt direction. Psychotherapeutic relief of symptoms is the most effective method. Treatment takes from six months to 2-3 years. It takes effort from both the therapist and the patient.
How to get rid of panic attacks and fear
To get rid of panic attacks, it is necessary to observe a strict sleep and wakefulness regime, stop using various stimulants, normalize the psycho-emotional state, and also receive rational and competent psychotherapeutic help. It includes:
- Cognitive training will allow the patient to understand what a panic attack is and why he should not be afraid of it - although the sensations are very unpleasant and sometimes quite scary, he will not die from them or become disabled. Understanding and awareness of this is the key to successful treatment and getting rid of attacks.
- In case of severe panic attacks, when correction of the condition is required, it is worth using anti-anxiety drugs - antidepressants.
- Emotional and mental conflicts are usually programmed in childhood. To get rid of panic attacks, you need to find out their root causes. By learning to manage your thoughts, you can learn to manage your fears. We will help you with this.
How to behave during the interictal period
Therapy for panic attacks during periods of calm includes several key points. The main thing is to get rid of stress, traumatic situations and internal tension.
It is very important to increase the body's ability to withstand stress. A set of measures will help with this .
- Learn to control your emotions and actions, take responsibility for them. To do this, analyze situations, your decisions, why you acted this way and not otherwise, what would have been better for you to do in this case. Write down your thoughts. If you have made wrong actions, review them and build a model of correct behavior. Now you know how to behave in a similar situation.
- Let more positive emotions into your life. Watch pleasant, funny films, do what you love more often, communicate with positive people. Try to be alone less.
- Stop making derogatory remarks about yourself. Praise yourself for your achievements, accept your shortcomings and work on them. Don't make comparisons between you and other people. Pay attention to yourself, look after yourself.
- Try not to mentally return to traumatic situations that happened to you in the past. To avoid reliving negative emotions. Try to remove all things that may remind you of this event.
- Find something you like. Direct your energy to creativity, not to dark thoughts.
Meditation will help you relax. It will relieve not only emotional tension, but also muscle tension. There are professional practices that require special training and knowledge of techniques.
At the everyday level, you can meditate by turning on relaxing music and taking a comfortable position. The best way to do this is to lie down. Close your eyes or focus on one object. Breathe deeply, evenly and mentally repeat the pre-prepared phrases: I am calm, my fear is receding, I have everything under control, and any other phrases adapted to your condition.
Treatment and prevention of panic attacks
Treatment of panic attacks should be aimed at eliminating the source of the attacks and smoothing out the unpleasant symptoms. The optimal way to combat panic attacks is a competent combination of medications and non-drug therapy. The main methods of treating attacks:
- taking antidepressants as prescribed by a doctor;
- psychotherapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures (MDM of the cerebral cortex, electrosleep, chromotherapy, aromatherapy, reflexology);
- relaxation massage;
- physiotherapy.
Additional treatment of panic attacks is practiced with herbal decoctions with a calming effect - infusions based on mint, lemon balm, chamomile, motherwort, etc. It is necessary to reduce the amount of stress to a minimum. Spicy foods, strong tea and coffee, and alcohol should be excluded from the diet.
Who to turn to for help and how to diagnose
Poor awareness among people about panic disorder leads to the fact that some consider it completely frivolous, while others consider it a dangerous incurable mental illness. Therefore, they believe, you should not go to doctors: in the first case there is no need, and in the second the main role is played by the fear of being branded as mentally ill. Both opinions are completely unfair: it is both very serious and completely controllable and treatable. A competent approach will allow you to successfully and fairly quickly get rid of the problem.
First of all, you need to understand that you need to contact only experienced, highly qualified specialists - a psychiatrist, who will develop treatment tactics based on the causes of a panic attack, because they are the ones that need to be eliminated. The doctor will determine why the patient’s nervous system could not withstand the load and malfunctioned in the form of panic manifestations.
The doctor must carefully examine the patient to establish an accurate diagnosis and study the symptoms. The selection of therapy is made based on the characteristics of the patient’s body on an individual basis. The work of a professional consists not only of recommendations and prescribing certain medications, but also of carefully monitoring the progress of treatment and, if necessary, its correction.
As for the psychologist, such a specialist is useless in this case - he is not able to identify the causes of the pathological disorder and prescribe medication and psychotherapeutic treatment, which, in case of getting rid of this problem, are necessary. The picture is the same with sorcerers, psychics and “wise” advisers from the Internet - they will only bring harm to the patient, which is then quite difficult to correct, aggravating his not the best condition.
The psychiatrist, first of all, will seek advice from a cardiologist, therapist, endocrinologist, neurologist, or psychotherapist. This is necessary to exclude the presence of somatic and serious mental illnesses.
It should immediately be noted that a therapist in ordinary clinics does not have the opportunity to carefully and competently examine the patient. In addition, long queues and the nervous atmosphere in them often serve as an impetus for another panic attack, and the person generally loses all desire to be treated.
In specialized paid clinics, such a picture is not observed: any person who comes here receives great attention. In addition, it is usually comfortable; highly qualified doctors work here, “armed” with advanced techniques and equipment for accurate diagnosis and successful treatment. The latter implies the use of pharmacology, psychotherapy, physiotherapy in combination, as well as changing the usual lifestyle.
The attitude of the patient himself to the treatment of panic attacks is also important - he must understand his problem, that this, in essence, is not a disease at all, but a sign of a disorder of higher nervous activity. For a successful result, you need the desire and good will of the patient, compliance with all the doctor’s recommendations.